Development of prodrugs possessing a nitric oxide donor diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate moiety using in vitro/in silico predictions
A nitric oxide, prodrug technology, applied in the field of predicting and developing prodrugs with a nitric oxide donor diazene-1-onium-1,2-diol moiety using in vitro/in silico
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
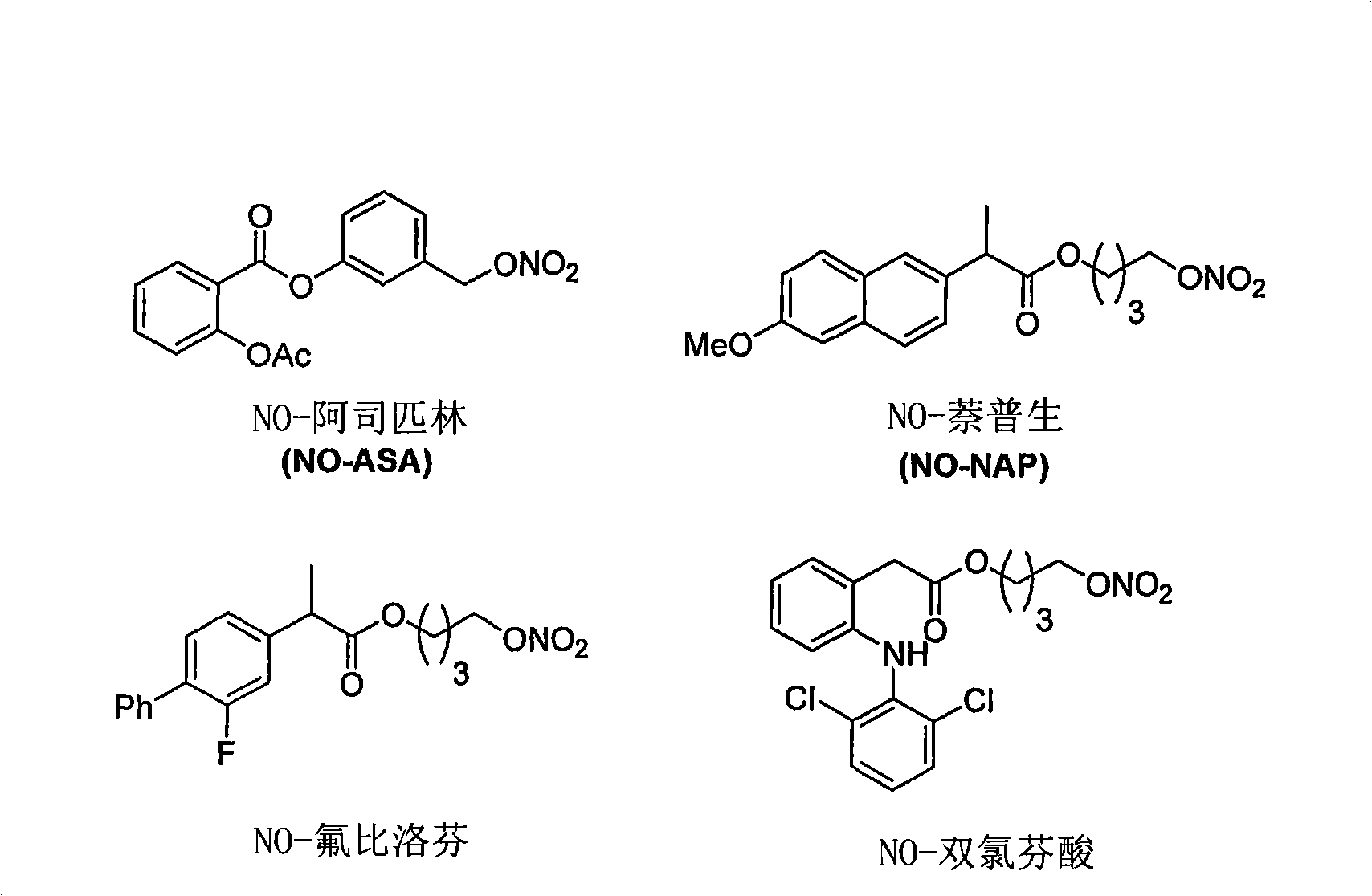
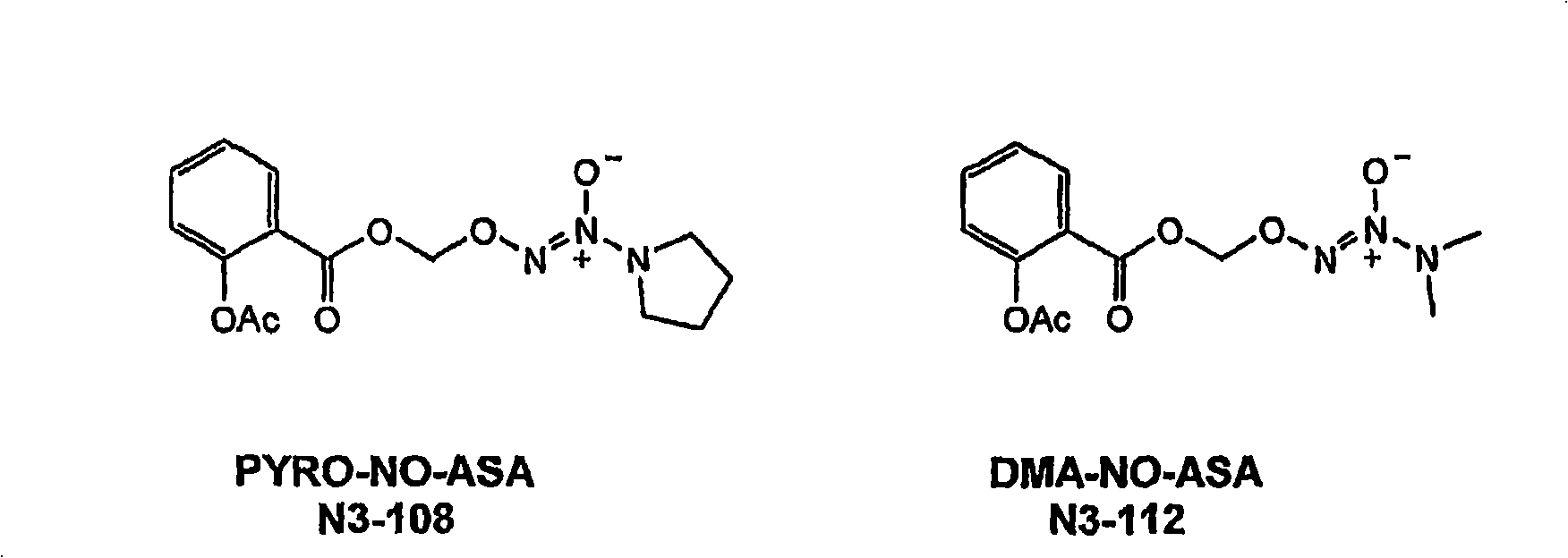
[0179] Selection of appropriate NO-NSAID candidates
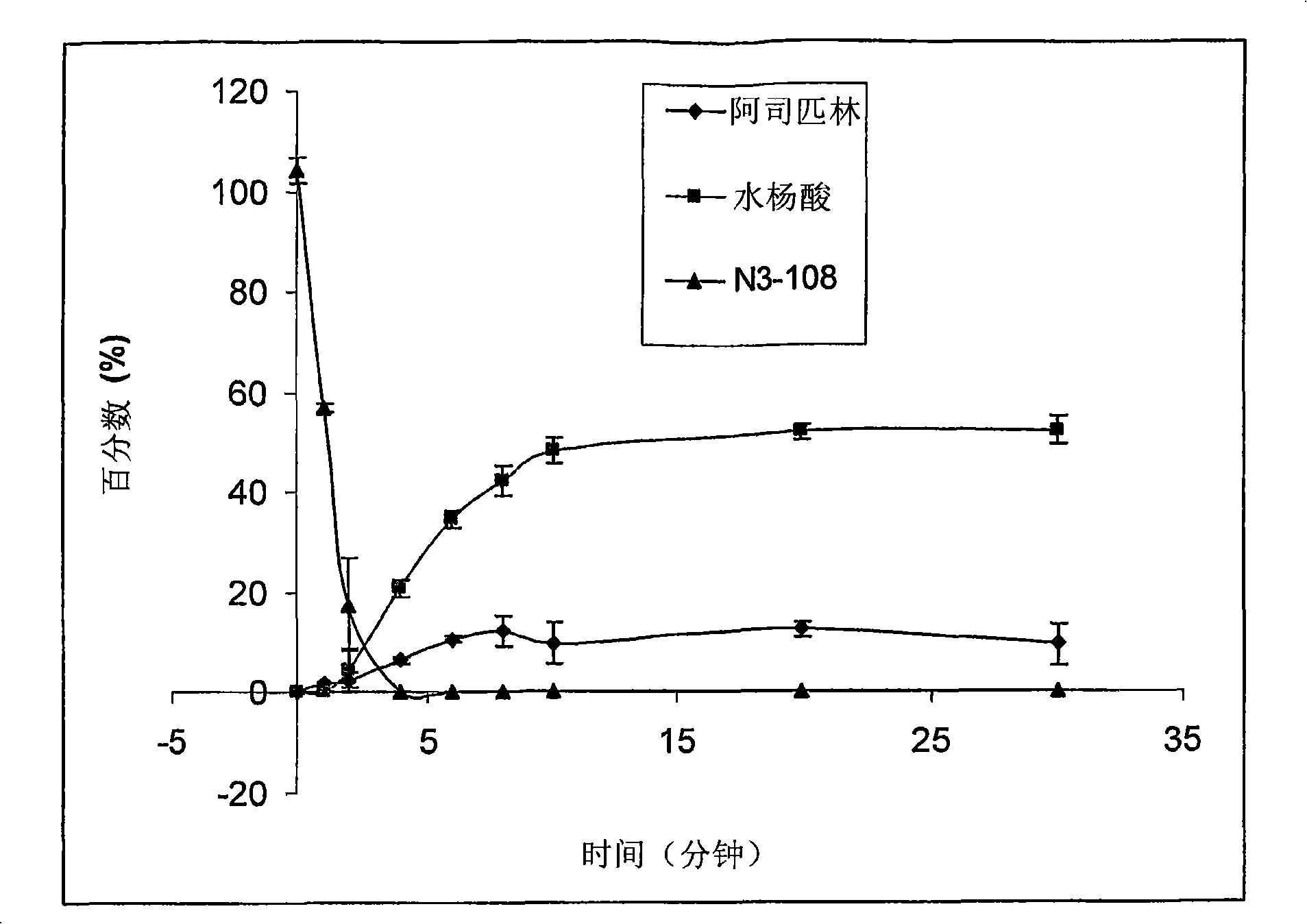
[0180] The main objectives of this example are (1) to provide in vivo data (i.e., NSAID and NO kinetic data) to train the in silico representation of the pharmacokinetic / pharmacodynamic model; (2) to validate model predictions; and (3) to select Appropriate NO-NSAID candidates for future development. NO-NSAID candidates are considered leads when they show the potential to retain their initial NSAID anti-inflammatory activity, supported by NO production and PK data, without undue gastrointestinal, cardiovascular and renal events.
[0181] The anti-inflammatory activity of non-selective and selective NSAIDs was determined indirectly using biomarkers indicative of the ability to inhibit COX-1 and COX-2 activity. Measured NO activity correlates with its potential ability to counteract NSAID side effects such as cardiovascular and renal events.
[0182] Myocardial infarction and ischemic events in high-risk patients led to the...
example 2
[0231] Physiologically based pharmacokinetic / pharmacodynamic models
[0232] The goal of this example is to demonstrate an embodiment of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic computer model in silico that incorporates all major processes and parameters and is capable of producing the output data described.
[0233] The model consists of a number of chambers, each representing a specific anatomical region. For each compound of interest in the model, each chamber has a specific volume (volume of distribution) and has a uniform internal concentration of the compound (the "well-stirred" case) ( Figure 13 ). Compounds are transported between compartments at a rate proportional to the amount of substance in the starting compartment (first order kinetics). These transports reflect diffusion and bulk flow between physiologically adjacent compartments. Many of these transports represent plasma circulation, and the sum of these flows into any compartment is equal to the sum of all...
example 3
[0238] Effects of NSAID and NO Donor on Platelet Aggregation
[0239] The objectives of this example are: (1) to study the effect of NSAID and NO donor on platelet aggregation, vasodilation and thrombosis; (2) to study the potential relationship between NSAID and NO donor in platelet aggregation, vasodilation and thrombosis. Interaction; and (3) Effect of NSAID and NO on COX function.
[0240] Methods published by Al et al. (2006), Hanson et al. (2005), Turkan et al. (2004) and Tubara et al. (2001) will be used to accomplish these goals.
[0241] The in vitro results obtained from these studies will be used to model the time course of platelet aggregation, vasodilation and thrombosis following administration of the NO-NSAID candidate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com