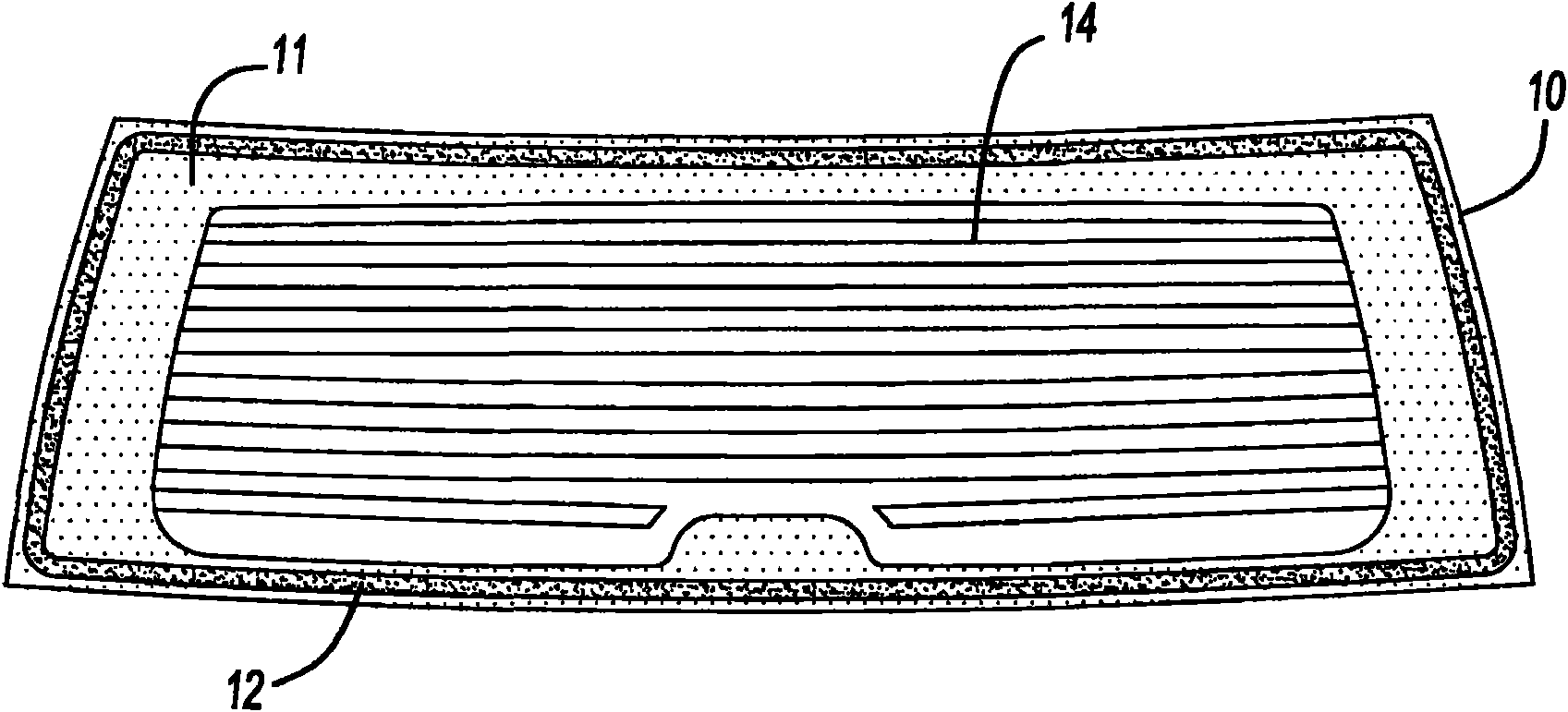
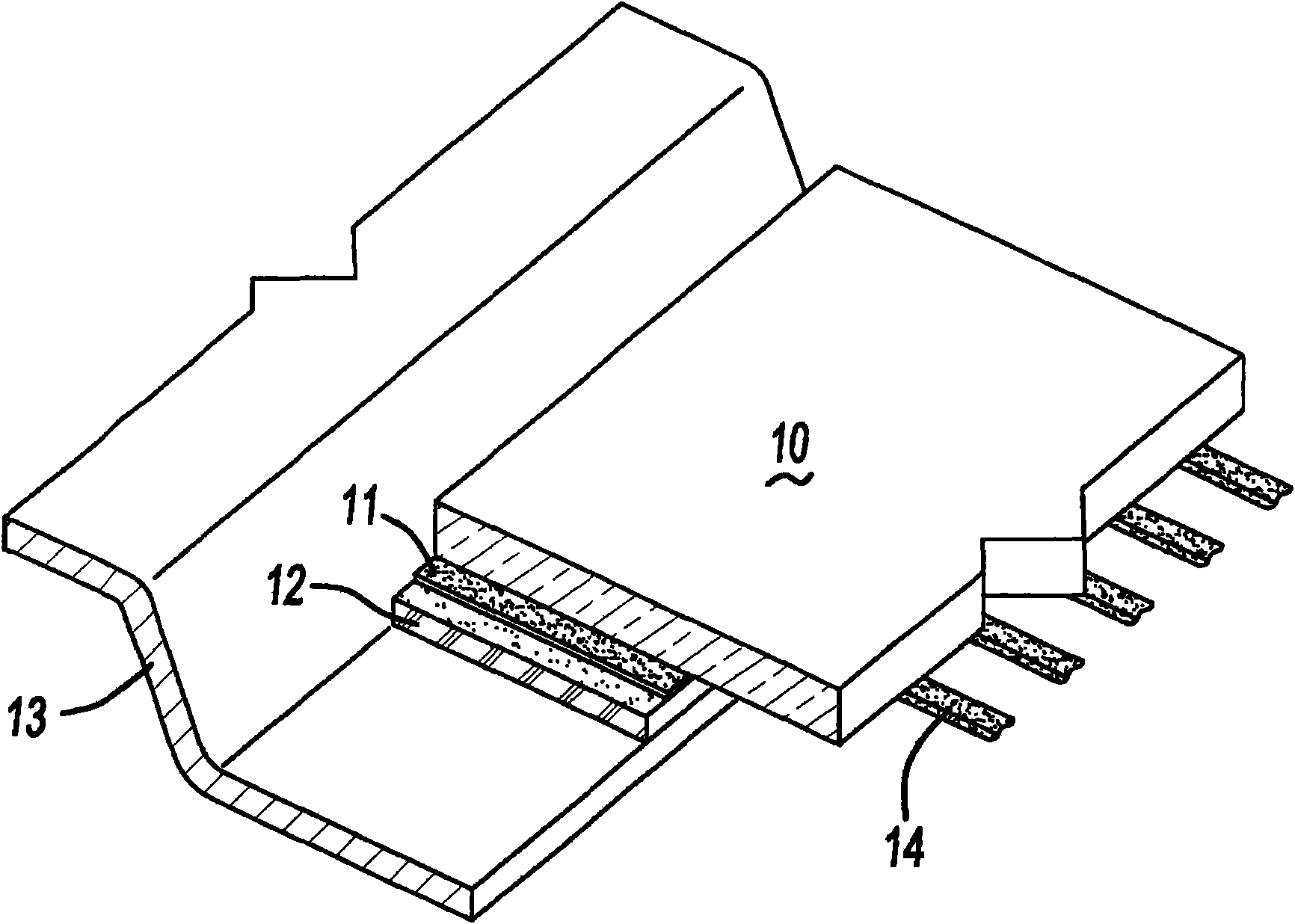
Improved composites and methods for conductive transparent substrates
A technology of conductive composite materials and composite materials, which is applied in the field of transparent substrates and can solve problems such as restricting the use of materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0108] Tables 1 and 2 below illustrate the preparation of the conductive composite material according to the present invention. The ingredients of Table 1 were mixed as described to form a matrix, and then combined with the ingredients of Table 2 so that the composition of Table 1 accounted for about 20% by weight of the obtained composite material. The resulting composite material is cured by ultraviolet radiation.
[0109] Table 1
[0110] Add the following to Max 60 Cup
[0111] Table 2
[0112] Add the following to MAX 20 CUP
[0113] The material is applied to a thickness of approximately 20 microns in an area of 1 mm wide and 75 mm long. The resistance measurement is performed and converted into resistivity (1 / conductivity) by the following equation: resistivity=(resistance×width×thickness) / length. After UV curing, the obtained material immediately showed 1395×10 at 23℃ -8 Resistivity (Ohm-m), 737×10 after four days of curing -8 After that, the resisti...
Embodiment 2
[0115] The following table exemplifies the preparation of the conductive composite material according to the present invention. This embodiment exemplifies a composition generally formed by the following steps: mixing monomers (optionally in the presence of a wetting agent), adding a conductive material to it, and then adding a photoinitiator and optional organofunctional silane. At concentrations within ±10% of the stated value, similar results are expected.
[0116] table 3
[0117] Add the following to Max 60 Cup
Component
wt%
Isobornyl acrylate (SR 506, Satomer)
5.99
5.99
Tripropylene glycol diacrylate (SR306, Sartomer)
2.83
2.83
Acrylic
2.51
2.51
Aliphatic polyurethane diacrylate (CN985B88 and CN964A85,
Sartomer)
9.96
9.96
Polyether modified polydimethylsiloxane (BYK UV 3510, BYK-Chemie)
0.15
0.15
Quickly mix for...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| visible light transmittance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com