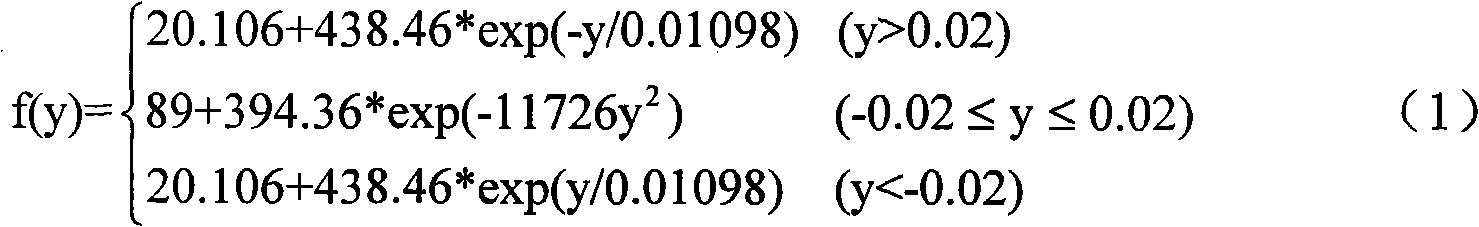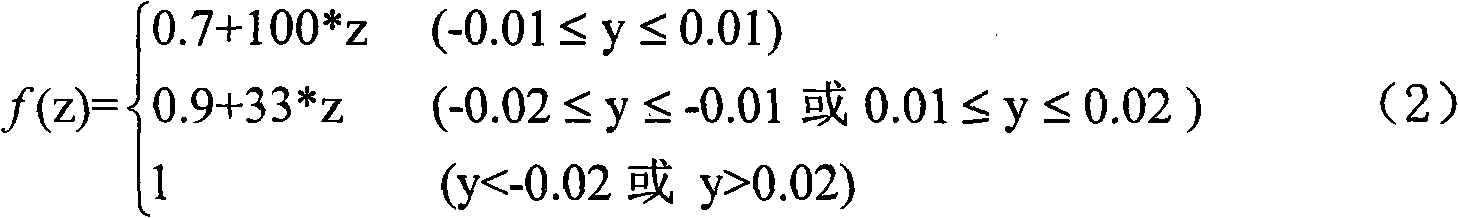Method for analog calculation of welding value by taking temperature as control variable
A technology of numerical simulation and variable control, which is applied in the program control of sequence/logic controller, welding equipment, electrical program control, etc., and can solve the problem of low efficiency of numerical simulation, low accuracy of calculation results, and poor control of welding temperature field and other issues to achieve the effect of improving efficiency, ensuring accuracy, and simplifying the calculation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0009] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
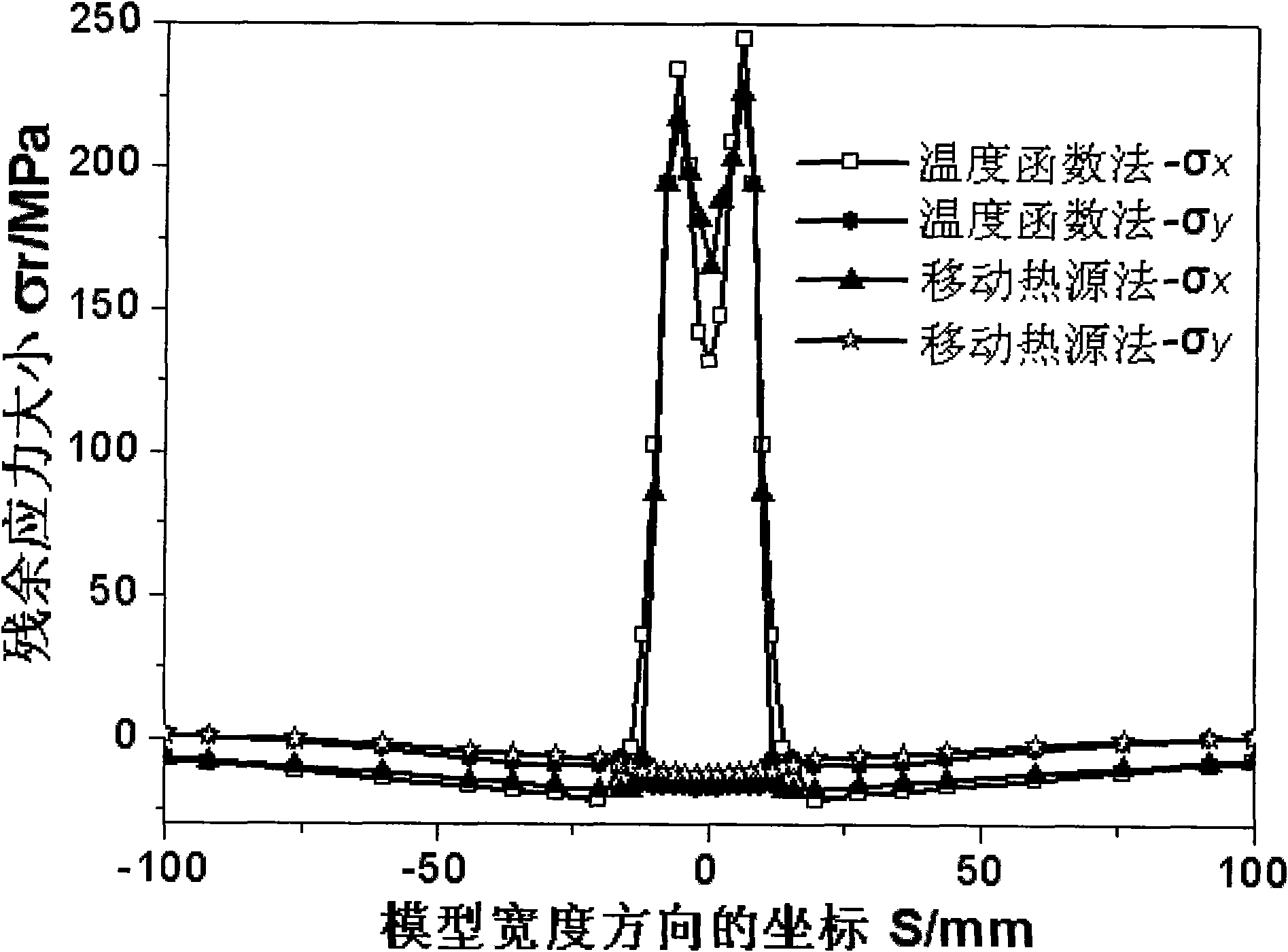
[0010] In the welding numerical simulation, the present invention adopts the moving heat source method to obtain the quasi-steady-state temperature field, arranges the distribution of the temperature field into a four-dimensional function of time and space, and then adds the temperature distribution function as a thermal boundary condition to the mechanics of the welded structure. Stress and deformation analysis are carried out in the analysis model, and the welding residual stress and residual deformation of the model are calculated. In order to improve the efficiency of analysis and calculation, the temperature distribution function adopts a segmented pattern along the direction of the weld, and the specific steps of the inventive method are as follows:
[0011] 1) Organize the welding temperature field distribution into a function of time and space...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com