Enzyme-assisted de-emulsification of aqueous lipid extracts
A technology of enzymatic activity and protease activity, applied in the field of compositions containing enzymes, can solve the problems of reduced oil yield, low efficiency and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
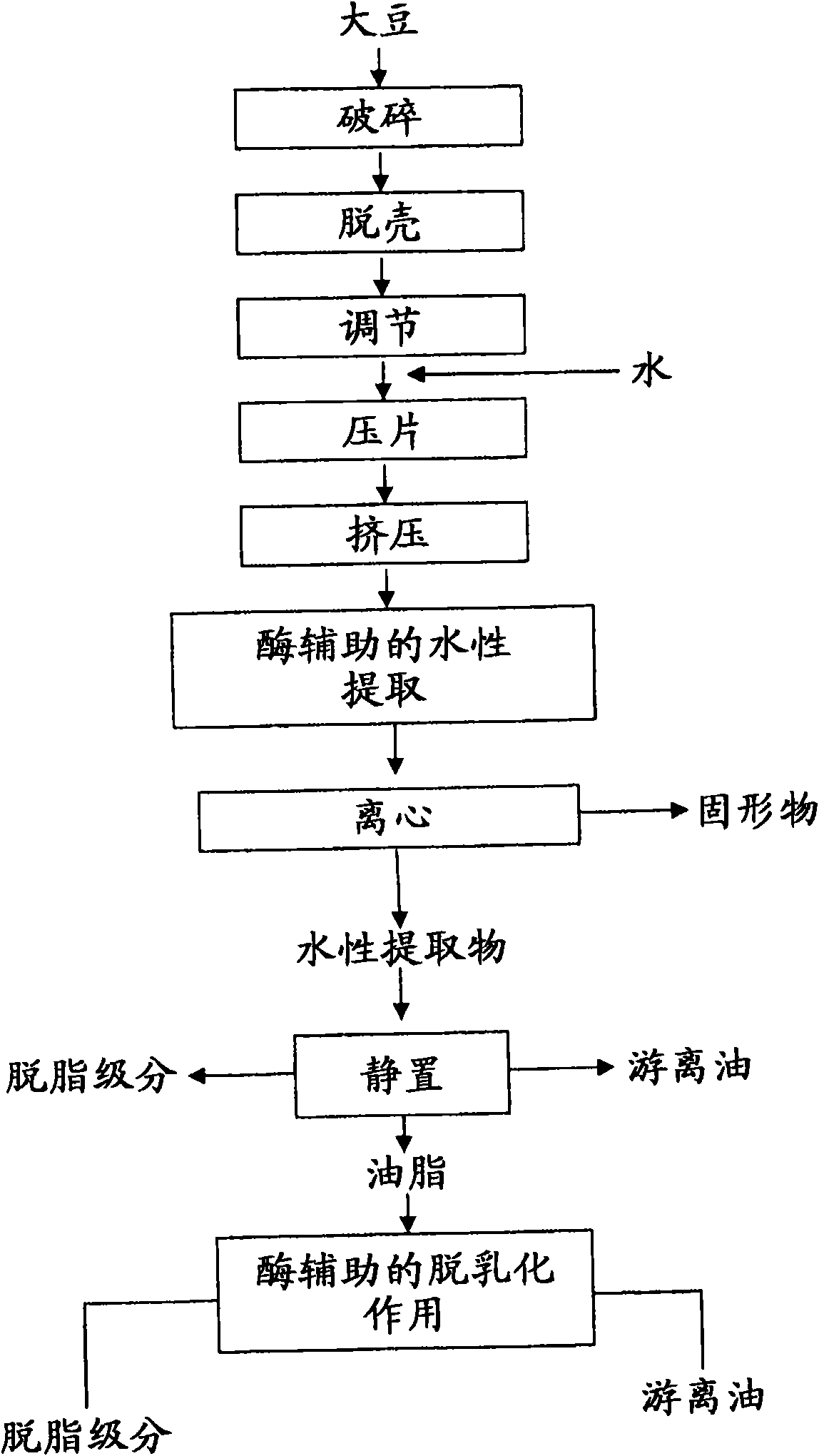
[0104] Demulsification of oil-in-water emulsions obtained from extruded and enzymatically treated whole-fat soybean flakes
[0105] Enzyme Screening: Proteases and Phospholipases
[0106] Table 1-1 summarizes the enzymes tested on oil-in-water emulsion (2% w / w oil-in-water emulsion) at a concentration of 500 mg. About 1.2 kg of extruded full fat soy flakes were used as starting material. Using a temperature-controlled water bath equipped with a Lab-Stirrer LR 400C (Fisher Scientific), at a speed of 150 rpm, after adjusting the temperature to 50°C, the pH was adjusted to 7.0 with 2N NaOH, and 0.5% (w / w) (based on soybean flakes) was added weight) Multifect Neutral (Genencor-A Danisco Division). The temperature and pH of the reaction were maintained at the above values for 1 hr. After 1 hour of incubation, the pH was raised to 8.0 for 15 minutes. Insoluble residues were removed by centrifugation at 3,000 g for 15 minutes in a SLA-3000 fixed angle rotor (Sorvall RC5BPlus,...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Example 2: Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Free Oil Yield
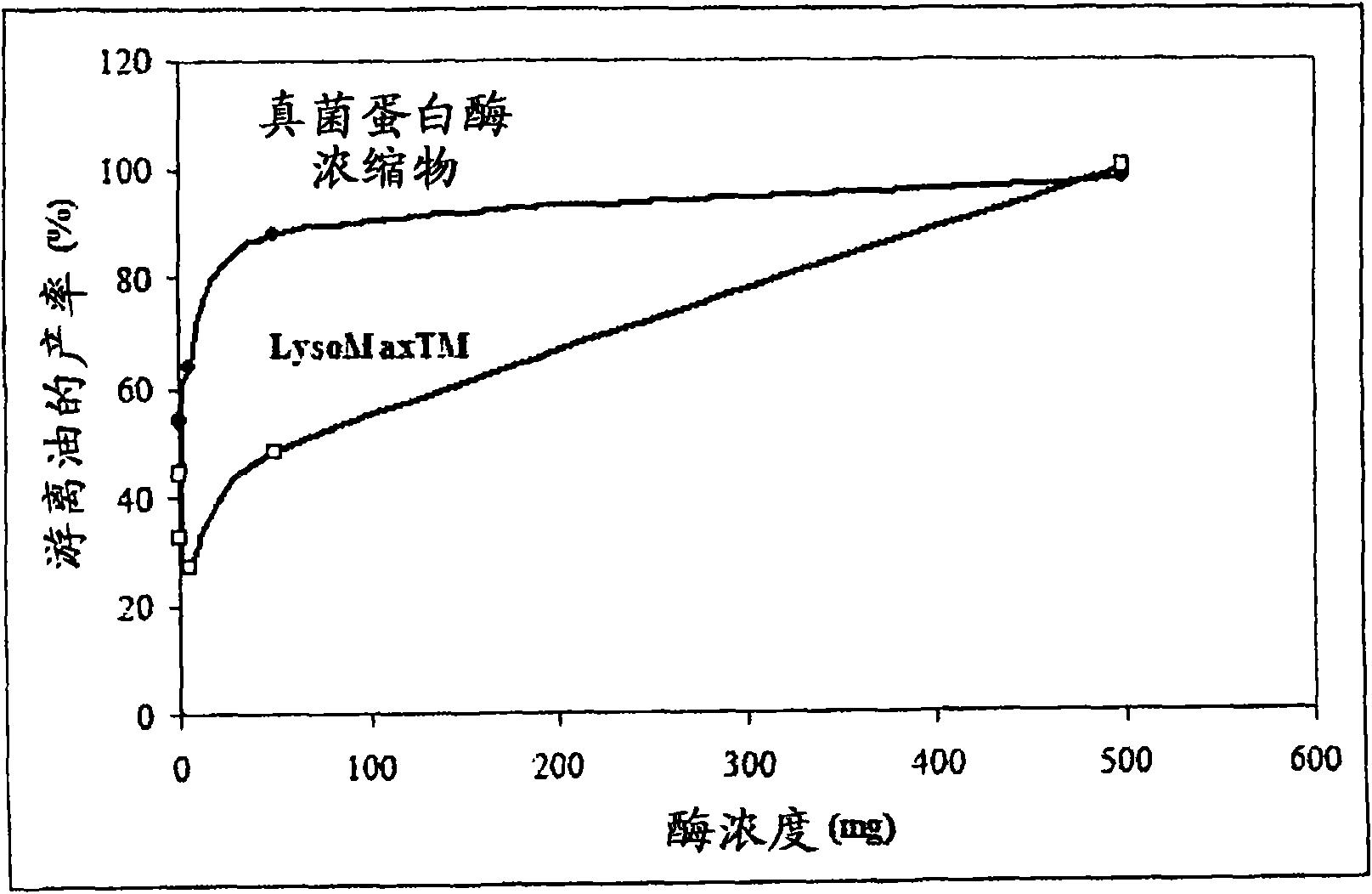
[0118] Enzymes (0.5, 5, 50 or 500 mg each) were added to 20 g samples of the oil-in-water emulsion. The enzyme amounts correspond to percentages of 0.002, 0.02, 0.2 and 2 (w / w) %, respectively. figure 1 The results are shown graphically. figure 1 Shown, the yield curves are for each enzyme, fungal protease concentrate and LysoMax function of concentration. Each data point presented is the average of two independent experiments.
[0119] A recovery oil yield of 44% was obtained for the control (ie, oil-in-water emulsion without added enzyme activity). When 0.2% FPC was added, 88% of the oil was recovered. Instead, use the same concentration of LysoMax Enzymes, only 48% of the oil was recovered. Thus, while individual protease or phospholipase activities were able to improve yields with increasing enzyme concentrations, fungal protease concentrates were more effective than LysoMax at low concentrations...
Embodiment 3
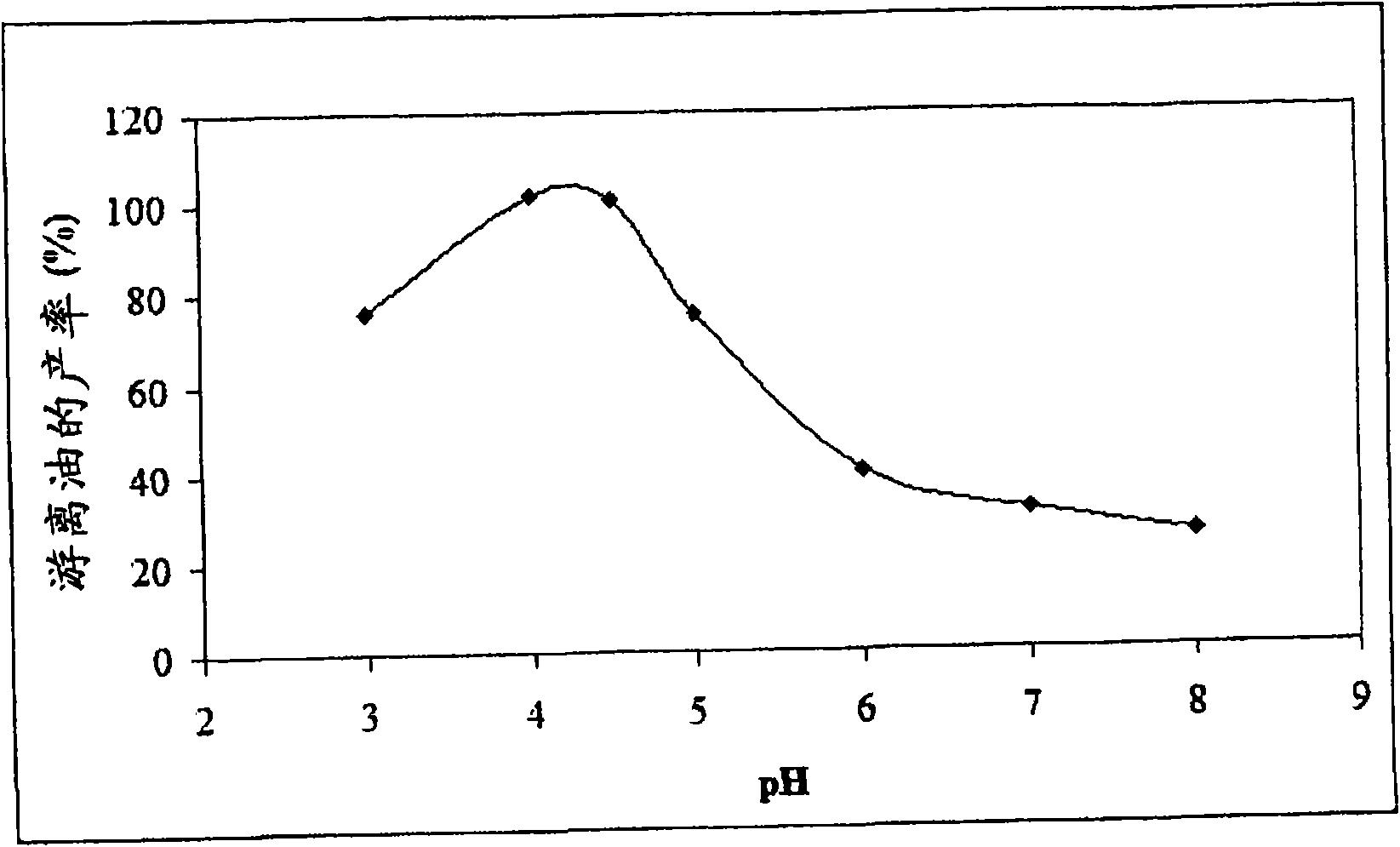
[0120] Example 3: Effect of pH on Demulsification of Soybean-derived Oil-in-Water Emulsions
[0121] The pH of the emulsion was adjusted to the desired point with hydrochloric acid. The emulsion was stirred at 50°C for 10 minutes before centrifugation to separate and recover the oil. From figure 2 The graphs provided show that there is a direct relationship between pH and recovered oil yield. The highest yields were obtained at a pH between about 4 and about 4.5, which corresponds to the pi of soybean protein. A pH of about 4.2-4.3 appears to be the optimal condition for oil recovery from the emulsion. The oil recovered at a pH above about 6 (about 40% or less) was substantially lower than the results obtained at a pH of less than about 5.5 (about 50% or more). It was observed that the response curves were reminiscent of the solubility of those soy proteins obtained as a function of pH.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com