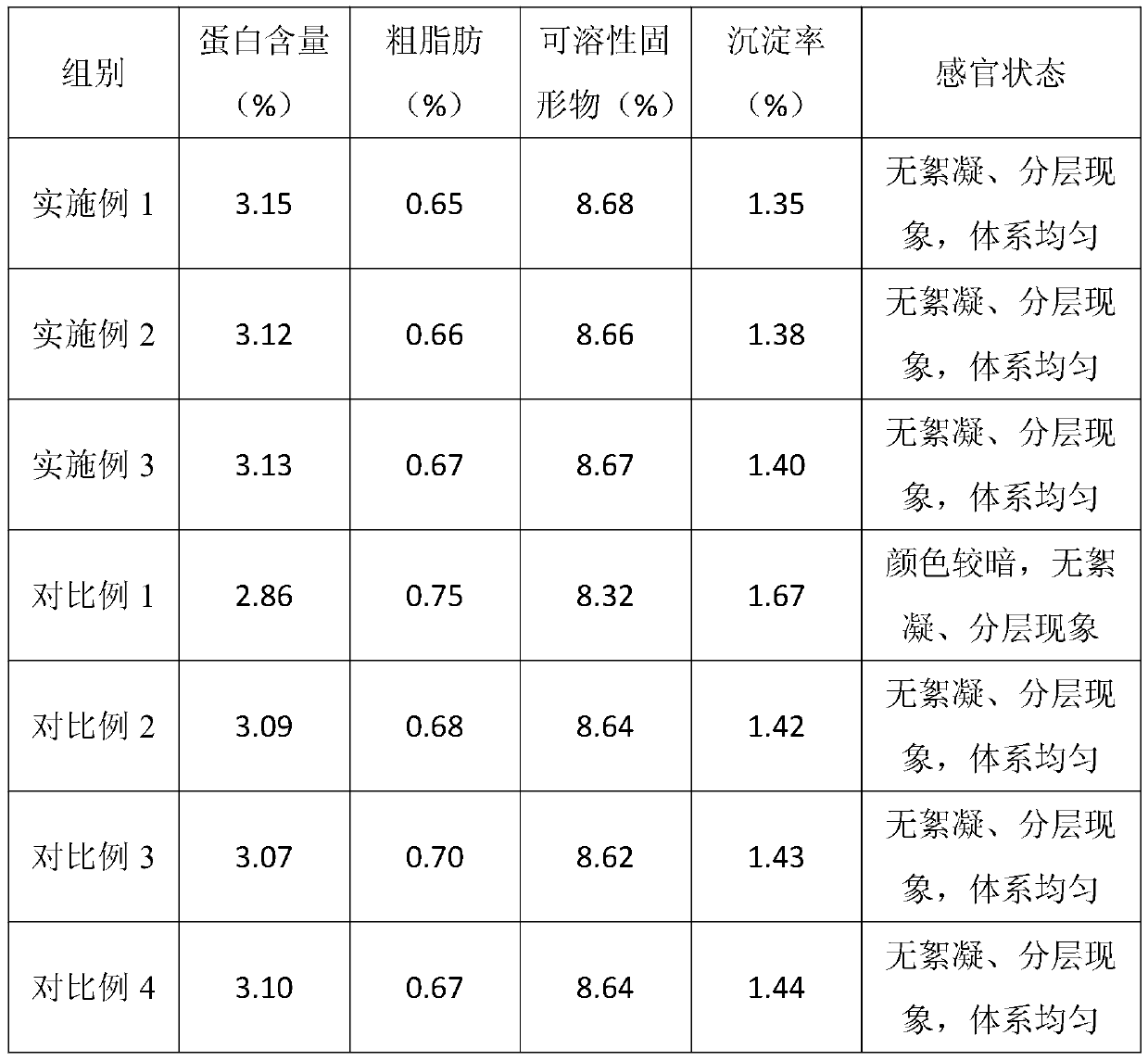
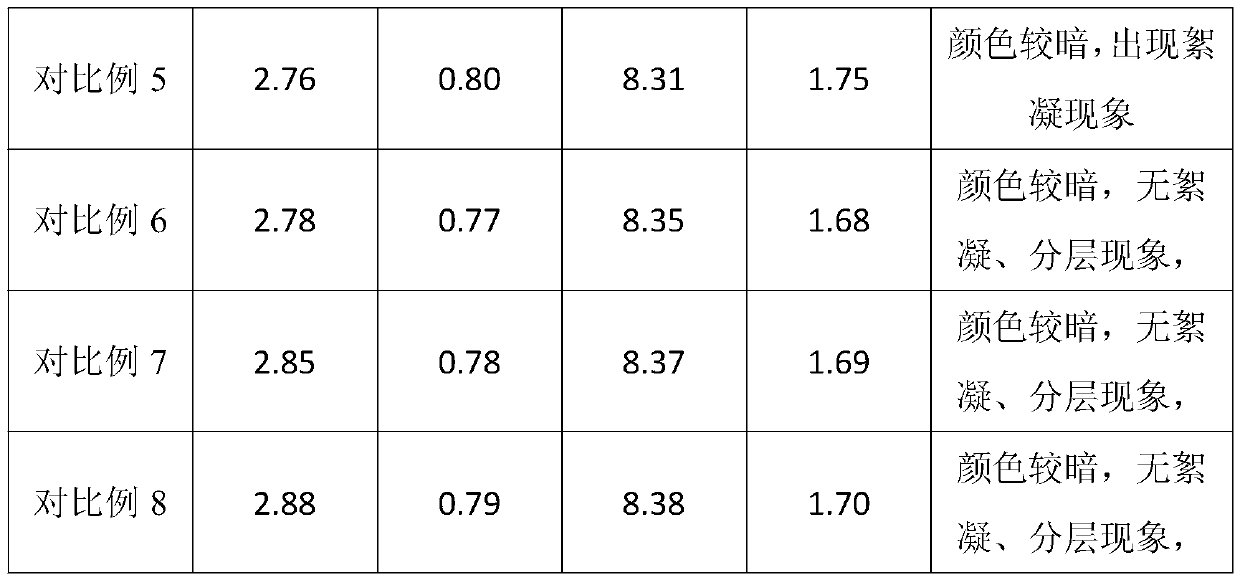
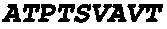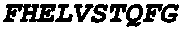Patents
Literature
40 results about "Fungal protease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
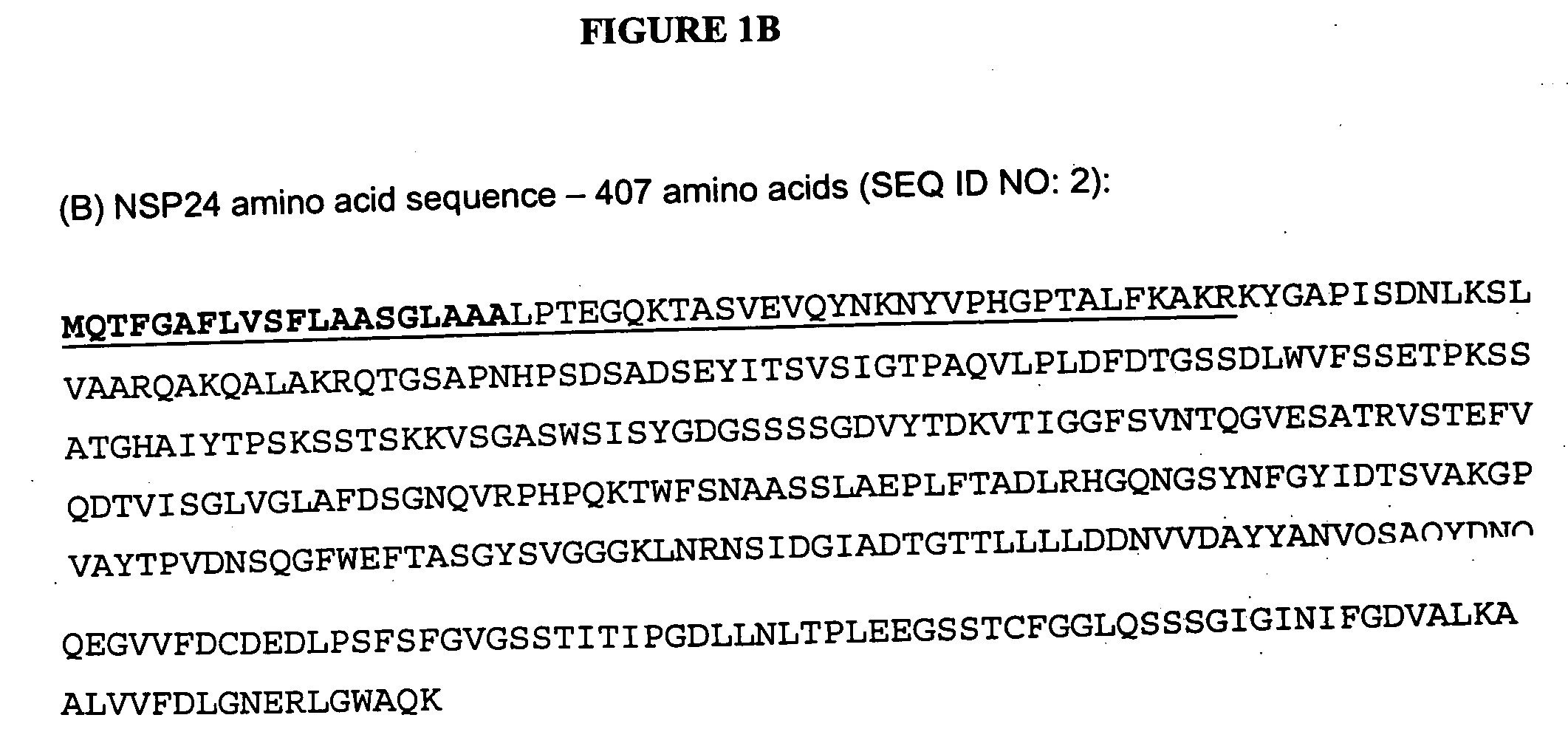
Fungal Protease (HUT) is an enzyme derived from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae var. The enzyme exhibits both exo- and endo- peptidase activities.
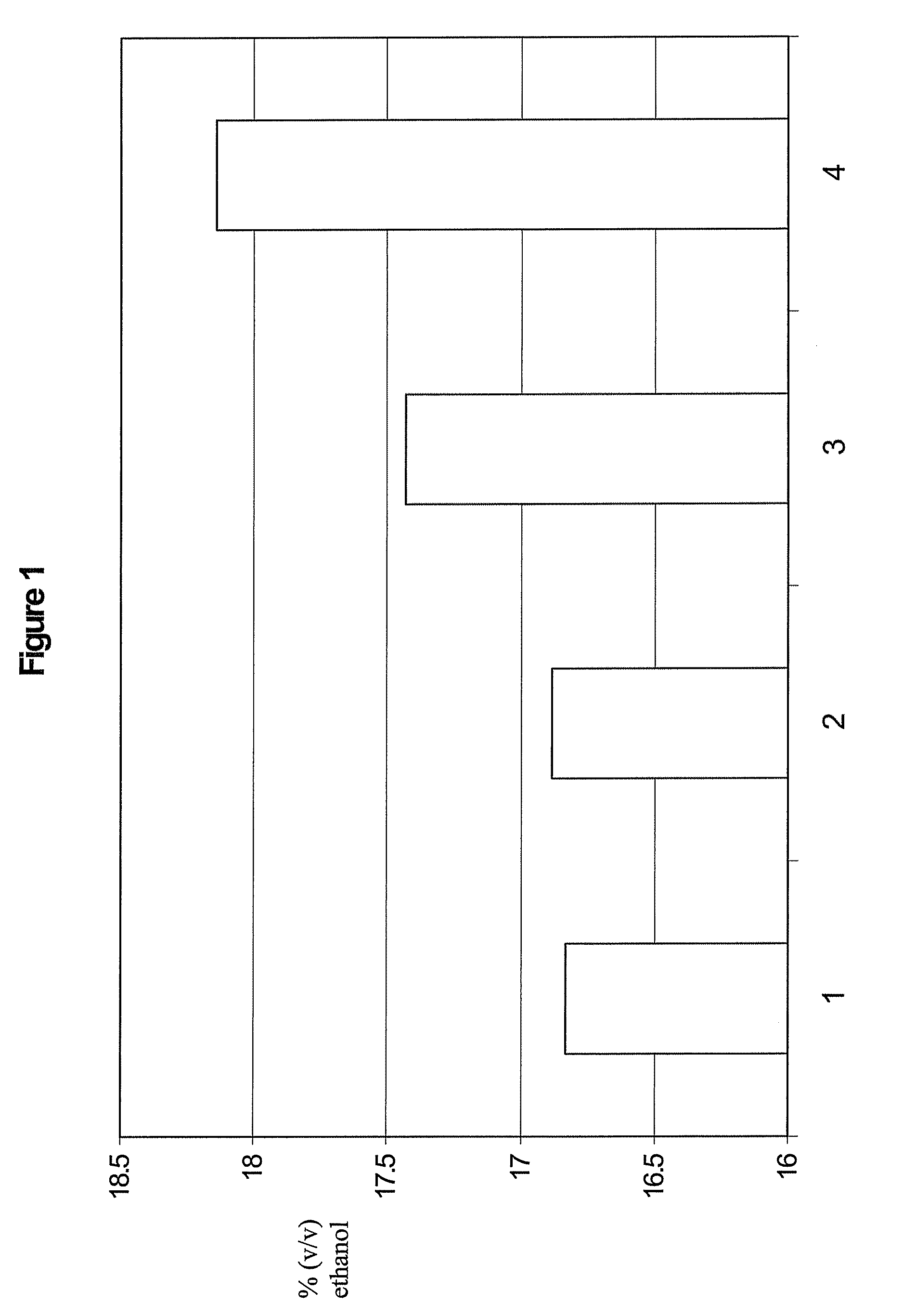
Acid fungal protease in fermentation of insoluble starch substrates
The invention is directed to methods of producing ethanol and decreasing residual starch production in a no cook fermentation comprising contacting granular starch containing substrates with a granular starch hydrolyzing enzyme, a protease, and a fermenting microorganism under suitable fermentation conditions at a temperature below the starch gelatinization temperature of the starch substrate to produce ethanol, wherein the ethanol production is increased and the amount of residual starch is decreased compared to a substantially similar method conducted without the protease.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Enzyme compositions comprising a glucoamylase, an acid stable alpha amylase, and an acid fungal protease
The present invention relates to an enzyme blend composition comprising a glucoamylase, an acid stable alpha amylase, and an acid fungal protease. The present invention is further directed to a method for producing end products such as alcohols from fermentable sugars, comprising the steps of: (a) contacting a slurry comprising a milled grain that contains starch with an alpha amylase to produce a liquefact; (b) contacting the liquefact with a glucoamylase, an acid stable alpha amylase, and an acid fungal protease, to produce fermentable sugars; and (c) fermenting the fermentable sugars in the presence of a fermenting organism to produce end products.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Process for preparation of protein-hydrolysate from milk protein
The present invention provides a process for the preparation of protein hydrolysate from milk protein by treating milk protein with fungal protease at a pH of 7.5-8.5, a temperature of 40±5° C. for a time period of 30 min to 2 hours, followed by heating at 65-70° C. for at least 3 min, separating the clarified supernatant by a known manner and drying the clarified liquor thus obtained to get the protein hydrolysate.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Peptide product
a peptide product is made by enzymatically hydrolyzing a protein, such as whey protein concentrate, in two stages. A fungal protease is used to hydrolyze the protein in each stage. The hydrolyzed protein is dried to form a peptide product. The peptide product is non-allergenic and lacks the bitter taste that some other peptide products have. If can be used to make milk replacement products and various other food products.
Owner:SAWHILL ROBERT +1
Acid fungal protease in fermentation of insoluble starch substrates
The invention is directed to methods of producing ethanol and decreasing residual starch production in a no cook fermentation comprising contacting granular starch containing substrates with a granular starch hydrolyzing enzyme, a protease, and a fermenting microorganism under suitable fermentation conditions at a temperature below the starch gelatinization temperature of the starch substrate to produce ethanol, wherein the ethanol production is increased and the amount of residual starch is decreased compared to a substantially similar method conducted without the protease.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Dietary supplements containing natural ingredients
InactiveUS7229651B2Reduced activityReduce oxidationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLingonberry extractDietary supplement
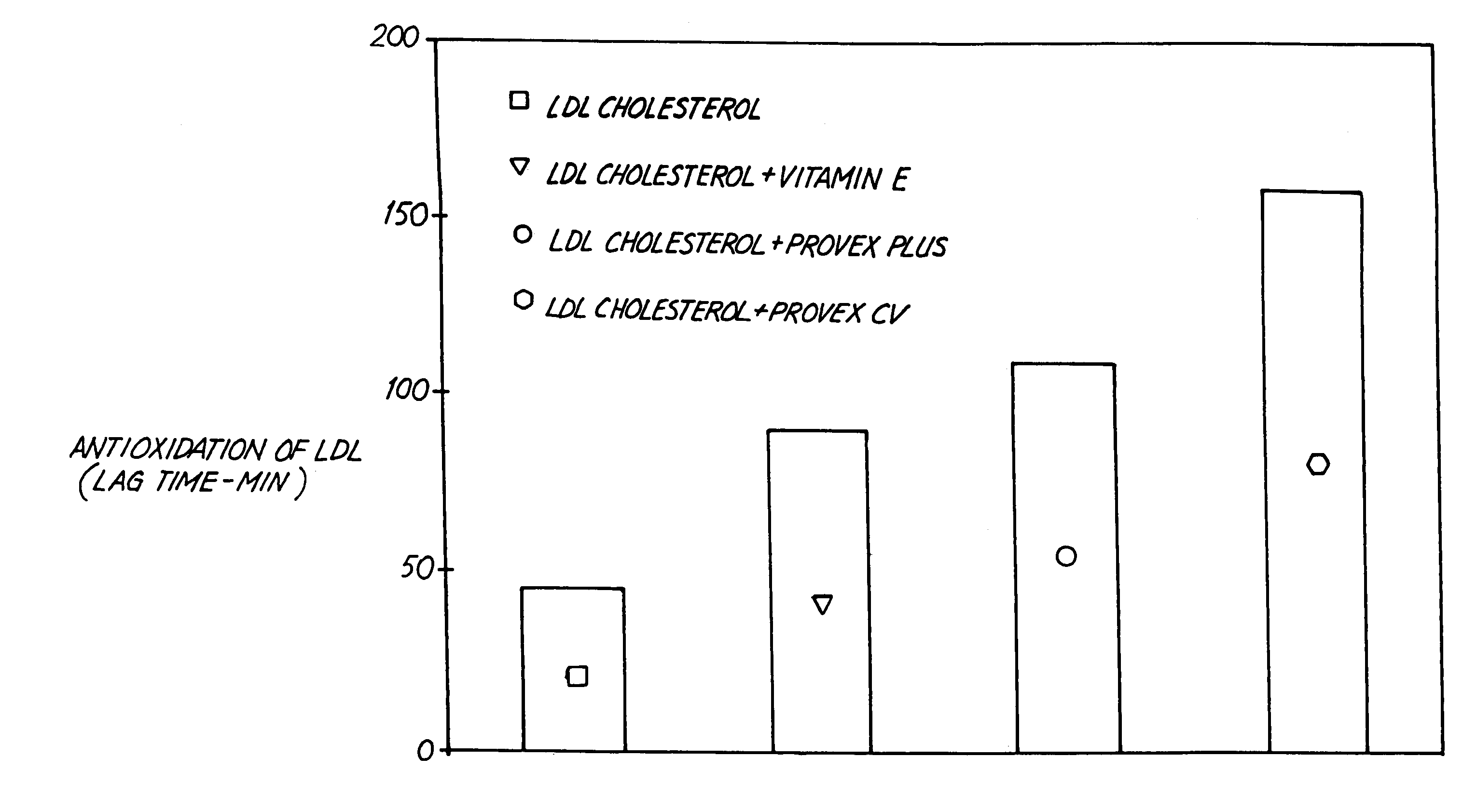
The invention provides a dietary supplement comprising at least one flavonoid source and an enzyme, that is effective for inhibiting in vivo platelet activity and LDL cholesterol oxidation in a mammal at a dosage of about 30 mg / Kg or less. The supplement may contain flavonoid sources found in grape seed extracts, grape skin extracts, bilberry extracts, ginkgo biloba extracts or the flavonoid quercetin. The supplement may also contain fungal proteases, acid stable proteases and bromelain. The invention further provides a method for using the dietary supplement and an article of manufacture containing the supplement.
Owner:MELALEUCA INC
Process for preparation of protein-hydrolysate from milk protein
InactiveUS20020132288A1High degree of hydrolysisMilk preparationButtermilkProtein hydrolysatesFungal protease
The present invention provides a process for the preparation of protein hydrolysate from milk protein by treating milk protein with fungal protease at a pH of 7.5-8.5, temperature of 40±5° C. for a time period of 30 min to 2 hours; heating at 65 -70° C. for at least 3 min, separating the clarified supernatant by a known manner and drying the clarified liquor thus obtained to get the protein hydrolysate.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Enzyme blends for fermentation
The present invention relates to an enzyme blend composition comprising a glucoamylase, an acid stable alpha amylase, and an acid fungal protease. The present invention is further directed to a method for producing end products such as alcohols from fermentable sugars, comprising the steps of: (a) contacting a slurry comprising a milled grain that contains starch with an alpha amylase to produce a liquefact; (b) contacting the liquefact with a glucoamylase, an acid stable alpha amylase, and an acid fungal protease, to produce fermentable sugars; and (c) fermenting the fermentable sugars in the presence of a fermenting organism to produce end products.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Soluble soy protein with superior functional properties
InactiveUS20050053705A1Function increaseSubstantial antioxidant propertyCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsFruit juiceHydrolysate
The present invention utilizes a novel enzyme cocktail comprising a fungal protease enzyme or a mixture of fungal protease enzymes having both endo and exo-peptidase activities to hydrolyze soy proteins while substantially avoiding free amino acids and low-molecular weight peptides which impart a bitter or undesirable flavor to the hydrolysate. The hydrolysate, and more preferably the soluble soy protein contained therein, is used in a food product such as, for example, high protein content beverages, sports beverages, balanced nutritional beverages, fruit juice mixes, health / nutrition bars, salad dressings, meat products, snacks, desserts, confectionaries, nutritional supplements, and the like. The soy protein hydrolysate, and more preferably the soluble soy protein contained therein, according to the present invention is particularly useful when the required dose is as high as about 2.5 to about 6.5 grams of soy protein per normal serving of a food product.
Owner:KRAFT FOODS GRP BRANDS LLC
Process for the preparation of protein hydrolysate from legumes
InactiveUS20020132287A1Low mineral contentHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesProtein hydrolysatesSlurry
The present invention provides a process for the preparation of protein hydrolysate from soy flour, which comprises preparing aqueous slurry of defatted soy flour having 6-12% w / v of solid content, hydrolyzing the said slurry using fungal protease at pH 7-8 and temperature 43±5° C. to get 20-40% degree of hydrolysis (DH), further hydrolyzing using papain at temperature 53±5° C. under stirring till completion of hydrolysis to 30-45% DH, inactivating residual enzyme in a known manner, separating the solids and drying the clarified supernatant thus obtained to get protein hydrolysate.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Expression and high-throughput screening of complex expressed DNA libraries in filamentous fungi
InactiveUS8680252B2Decrease protease activityBacteriaHydrolasesCDNA libraryHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention provides a method for the expression and subsequent screening of DNA libraries, particularly synthetic, genomic, and cDNA libraries, in filamentous fungal hosts. In particular, the invention provides vectors, host strains, and a method for the expression and screening of complex DNA libraries, including, but not limited to, combinatory (combinatorial) libraries expressing one, two or more variable constituents and / or prepared from two or more sublibraries (e.g., for the expression and screening of immunoglobulin (including fragments and derivatives of whole immunoglobulin proteins) and other receptor or complex DNA libraries or libraries of libraries). The invention is useful for the expression and screening for a large variety of proteins and protein complexes, including human proteins. The present invention also relates to novel fungal protease sequences.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Macadamia nut drink and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a macadamia nut drink, which belongs to the technical field of drink preparation. The macadamia nut drink comprises the following materials: macadamia nut, xylitol, sorbitan, sucrose, citric acid, lactic acid, an emulsifier, a stabilizer, fungal protease, papain, aminopeptidase, and lactic acid bacteria; and the weight ratio of papain, aminopeptidase and lactic acid bacteriais: (0.1-0.2): (0.008-0.02): (0.2-0.3). The macadamia nut drink is obtained by the steps of pressing, pulping, enzymatic hydrolysis, debittering, blending, homogenization, fermentation, sterilizationand the like. The macadamia nut drink improves the nutrient content and stability of macadamia nut drink by using a reinforcing system composed of papain, aminopeptidase and lactic acid bacteria.
Owner:SOUTH ASIAN TROPICAL AGRI SCI RES INST OF GUANGXI
Soluble soy protein with superior functional properties
The present invention utilizes a novel enzyme mixture comprising a fungal protease or a mixture of fungal proteases with both endo- and exo-peptidase activities to hydrolyze soy protein while substantially avoiding free amino acids and low molecular weight Peptides, two substances that can impart a bitter or unpleasant flavor to hydrolysates. The hydrolyzate, more preferably the soluble soy protein it contains, can be used in food products such as high protein beverages, sports drinks, balanced nutritional drinks, juice mixes, health / nutrition bars, salad dressings, meat products , snacks, sweets, confectionery, nutritional supplements, etc. The soy protein hydrolyzate, more preferably the soluble soy protein it comprises, is particularly useful in accordance with the present invention when dosages up to about 2.5 to about 6.5 grams of soy protein per common serving of food product are desired.
Owner:KRAFT FOODS INC
Process for preparation of protein hydrolysate from soy flour
The present invention provides a process for the preparation of protein hydrolysate from soy flour, which comprises preparing aqueous slurry of defatted soy flour having 6-12% w / v of solid content, hydrolyzing the said slurry using fungal protease at pH 7-8 and temperature 43 + / -5 deg.C to get 20-40% degree of hydrolysis (DH), further hydrolyzing using papain at temperature 53 + / -5 deg.C under stirring till completion of hydrolysis to 30-45 % DH, inactivating residual enzyme in a known manner, separating the solids and drying the clarified supernatant thus obtained to get protein hydrolysate.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for preparing biological zinc from oysters
InactiveCN105476014ANutrient release is completely more thoroughUniform molecular weight suitable forFood scienceSolubilityOyster
The invention discloses a method for preparing biological zinc from oysters. The method comprises the following steps: removing shells of living oysters, grinding fresh oyster meat by a colloid mill to obtain meat pulp, adding cellulase, fungal proteinase and lipase for enzymolysis, performing fine filtering, separating to obtain filter liquor rich in biological zinc, separating the filter liquor with a molecular sieve, performing vacuum concentration, and performing spray drying to obtain 100-150-mesh biological zinc dry powder. The biological zinc drying powder has the characteristics of being high in water solubility, uniform in molecular weight, high in biological activity, free from activation, direct and fast in absorption, free of fishy smell of the oysters, and the like, and is a good functional factor in healthy products having high additional values.
Owner:GUANGXI PANDA BIOTECH DEV CO LTD
Enzyme formulation for use as food supplement
ActiveUS20160114012A1Lower drug concentrationAffect occurrencePeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemFood supplementMedicine
The present document describes an enzyme formulation comprising an enzyme mixture comprising from about 5% to about 45% (wt / wt) of a fungal protease enzyme; and from about 1.5% to about 50% (wt / wt) of at least one polysaccharide digesting enzyme; in combination with an acceptable pharmaceutical carrier. The present document also describes the use of the formulation of the present invention for the prevention or treatment of digestive disorder.
Owner:BRYSON PATENTS
Application of domestic silkworm cocoon antifungal protease inhibitor in fungus prevention and preparation method of domestic silkworm cocoon antifungal protease inhibitor
ActiveCN105175534AInhibitory activityKeep aliveAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologySpore germination
The invention discloses an application of a domestic silkworm cocoon antifungal protease inhibitor in fungus prevention and a separation method of the domestic silkworm cocoon antifungal protease inhibitor. The separation method comprises the following steps: layering and cutting a silkworm cocoon into pieces, then adding 100mm of Tris-HCL buffer solution with pH of 7.5, and extracting for 30 minutes under the condition that the temperature is 37 DEG C and the rotation speed is 220 r / pm, centrifuging for 15 minutes under the rotation speed of 10000rpm, filtering supernatant by utilizing a 0.22-micrometer filter membrane, to obtain the domestic silkworm cocoon antifungal protease inhibitor. The prepared protease inhibitor can inhibit the activity of fungal protease secreted by Tritirachium album limber, can inhibit the spore germination of silkworm pathogenic fungal beauveria bassiana and still can maintain the activity after being incubated for 10 minutes in boiled water. The prepared domestic silkworm cocoon antifungal protease inhibitor belongs to the natural, high-activity and high-stability antifungal protease and is non-toxic and harmless; and meanwhile, the silk used in the method is rich in resource, and a novel way is provided for diversified development of the silk.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
A fungal protease and use thereof
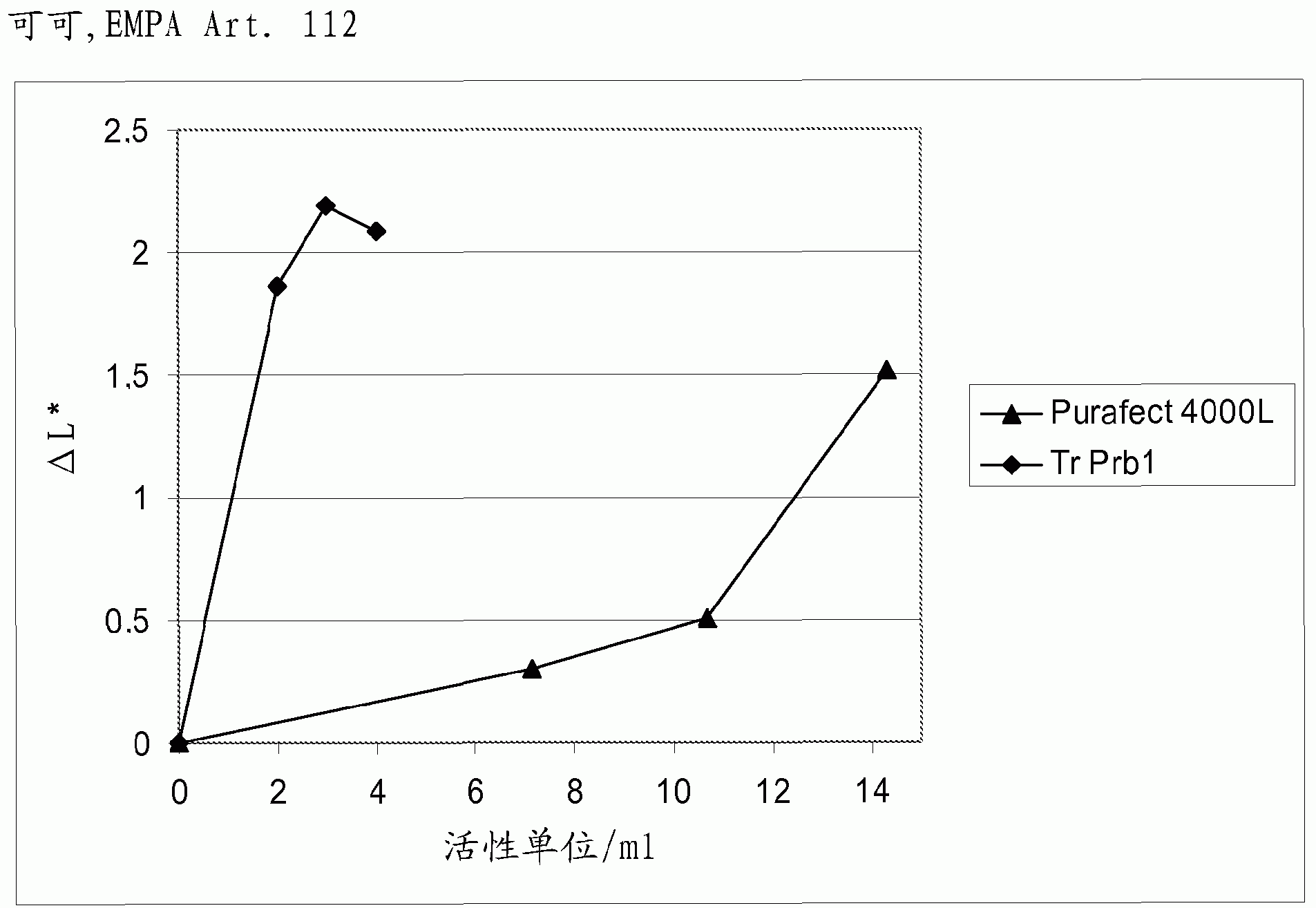
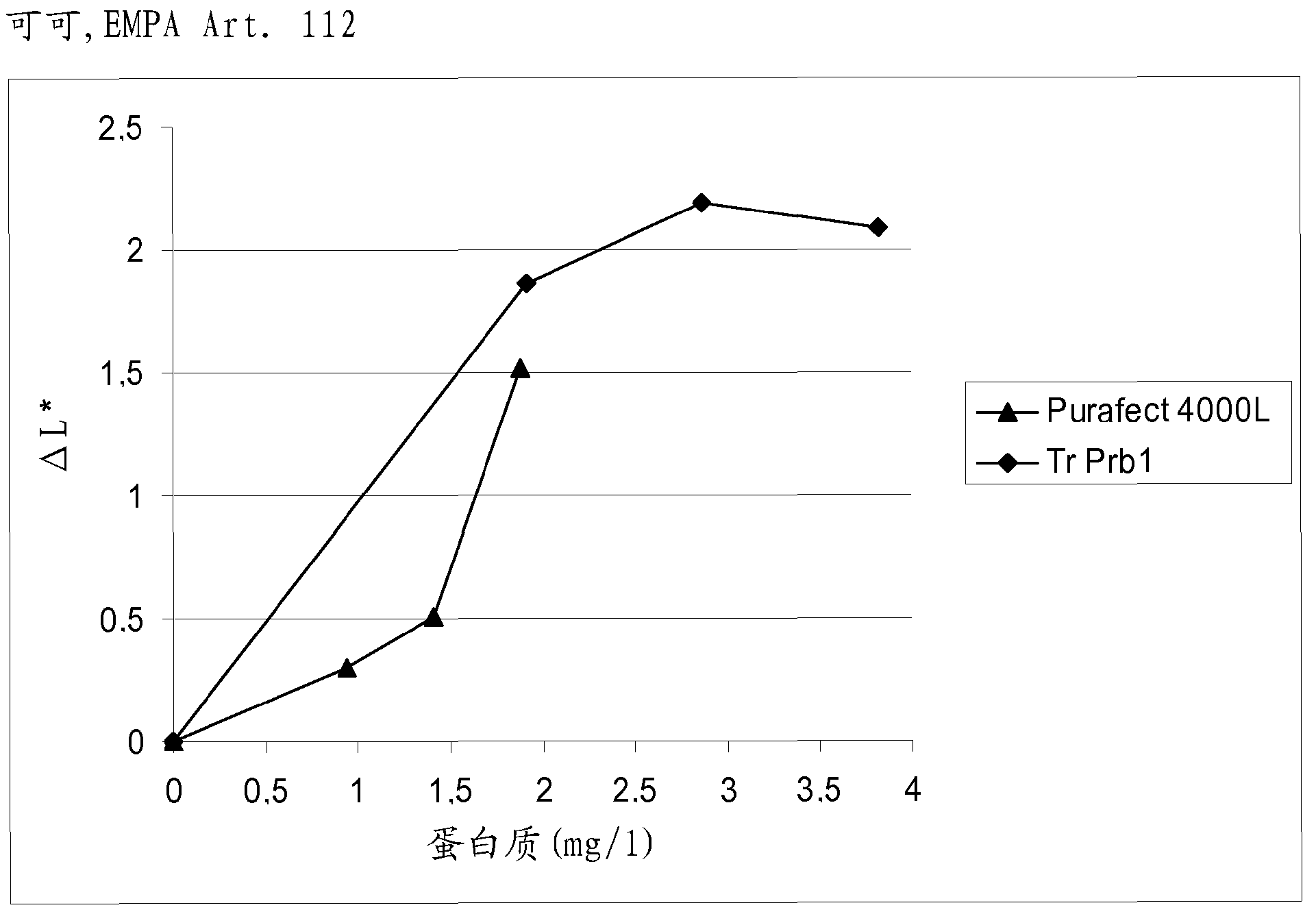
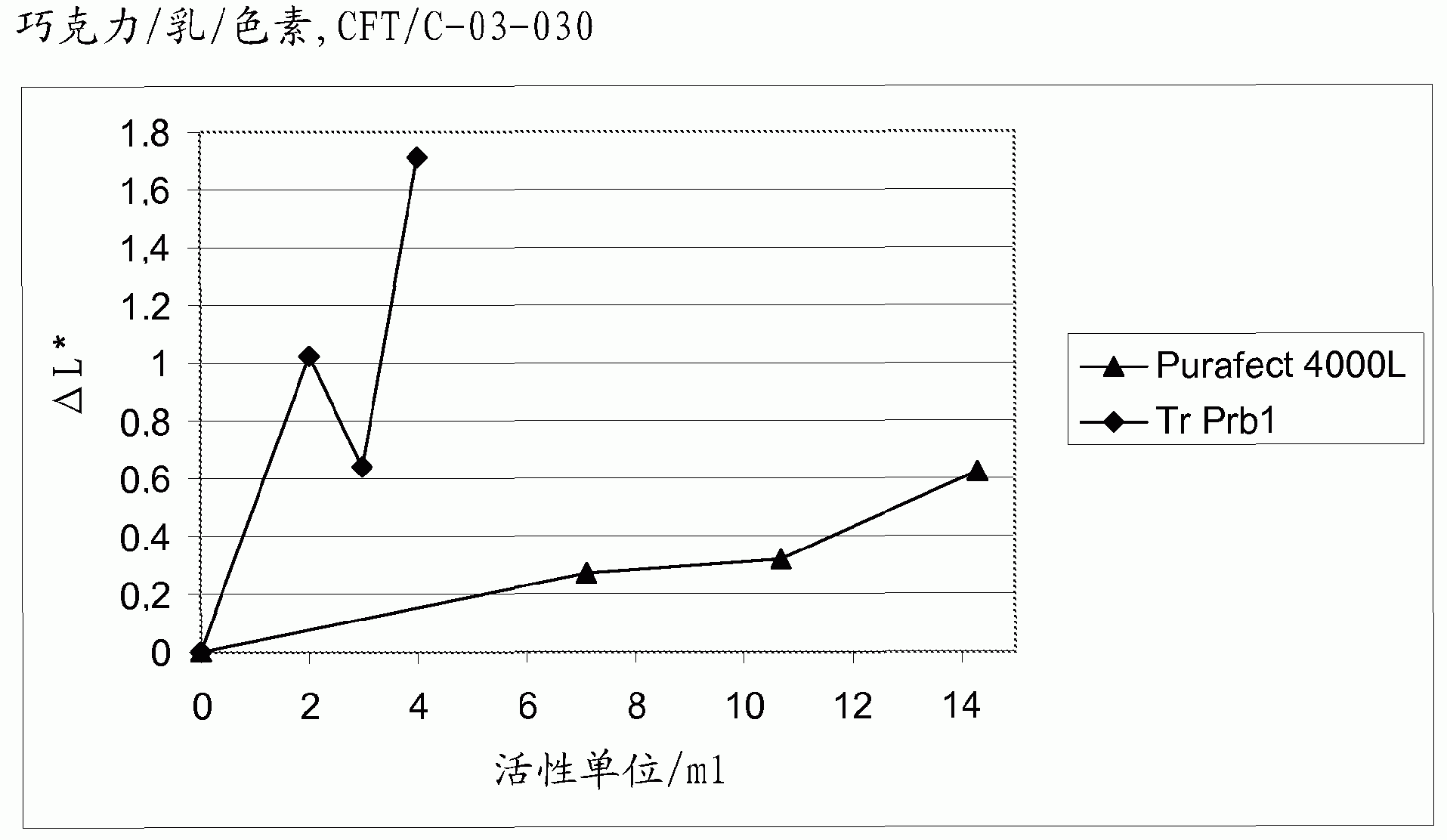
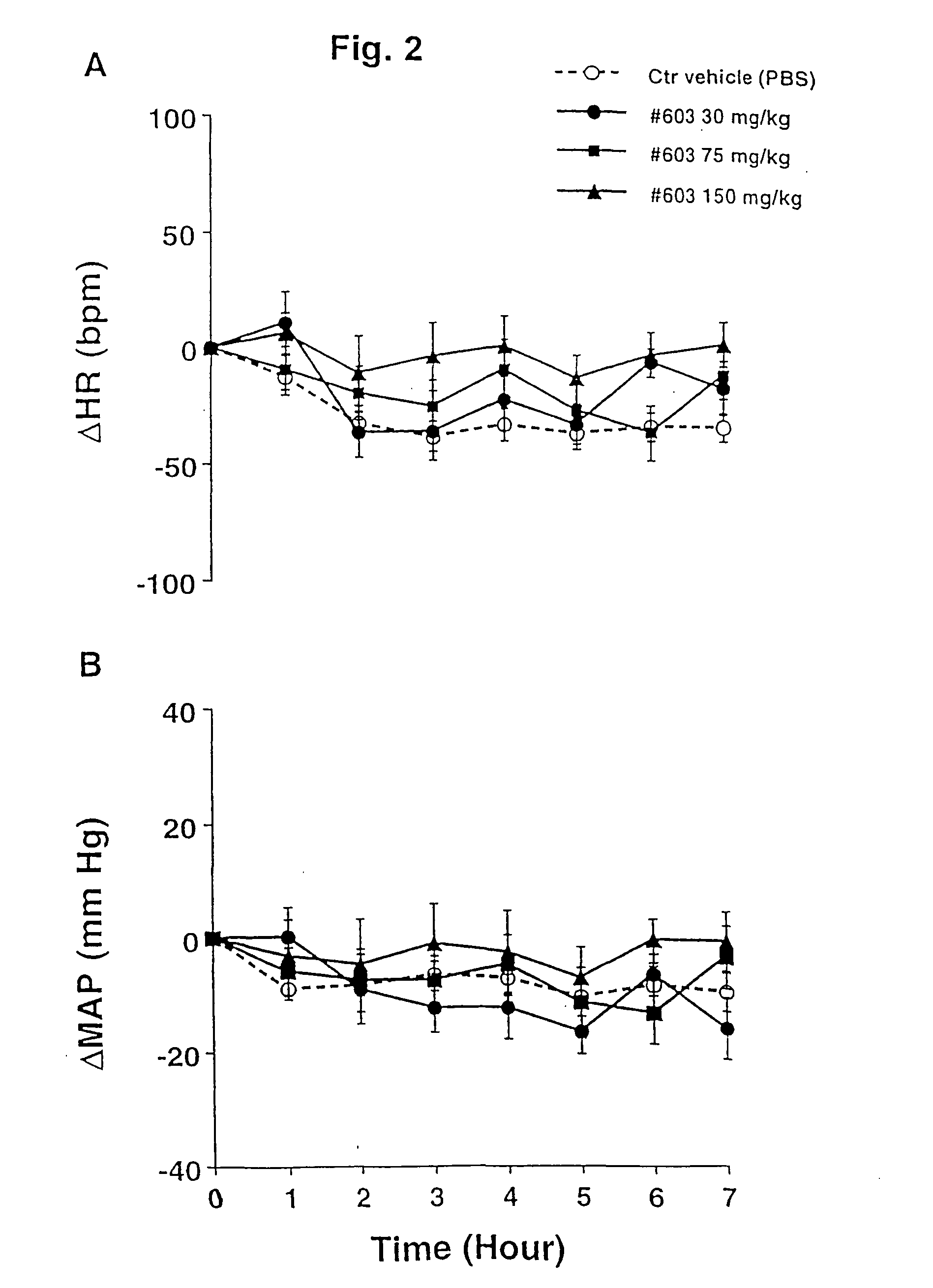
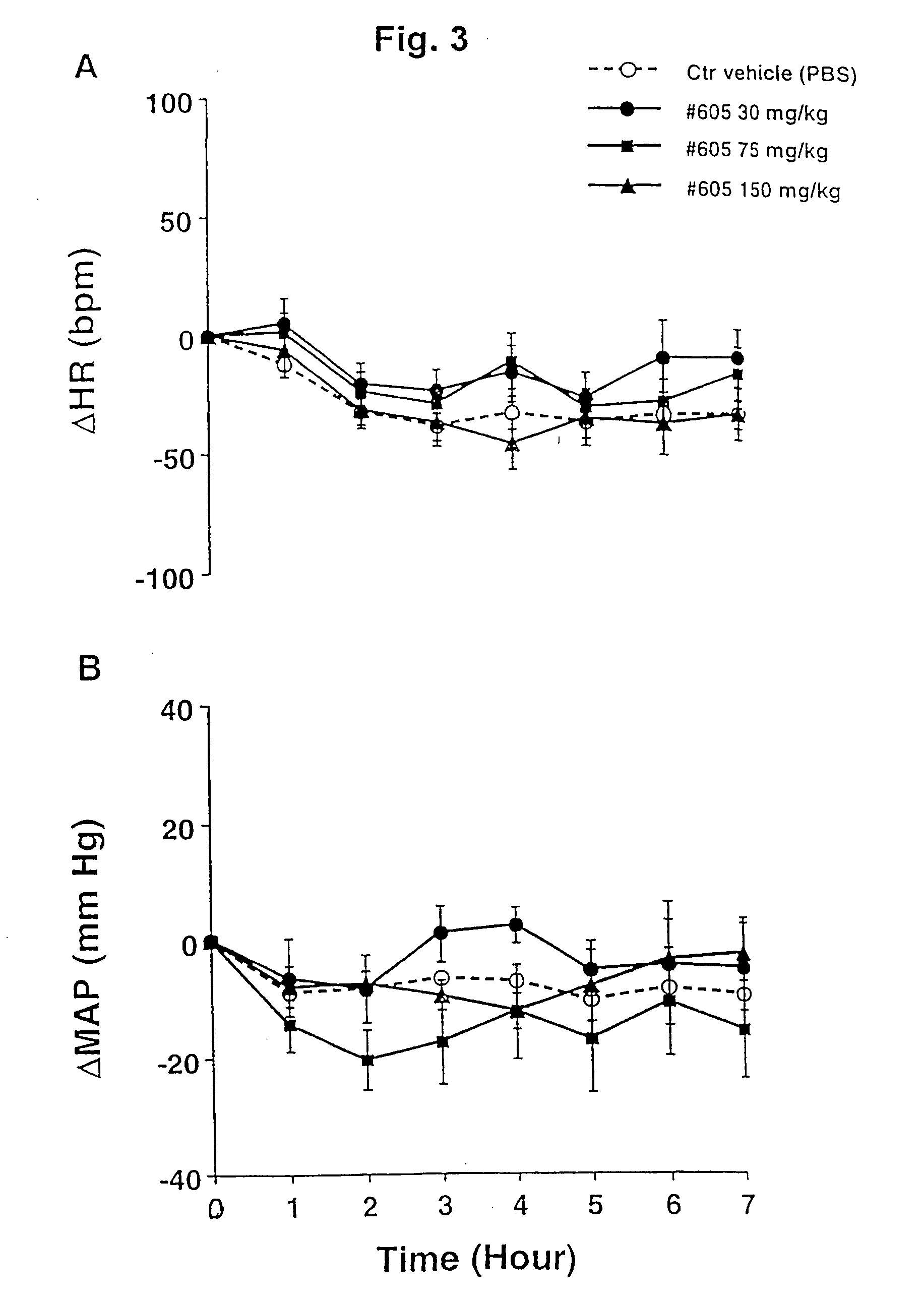
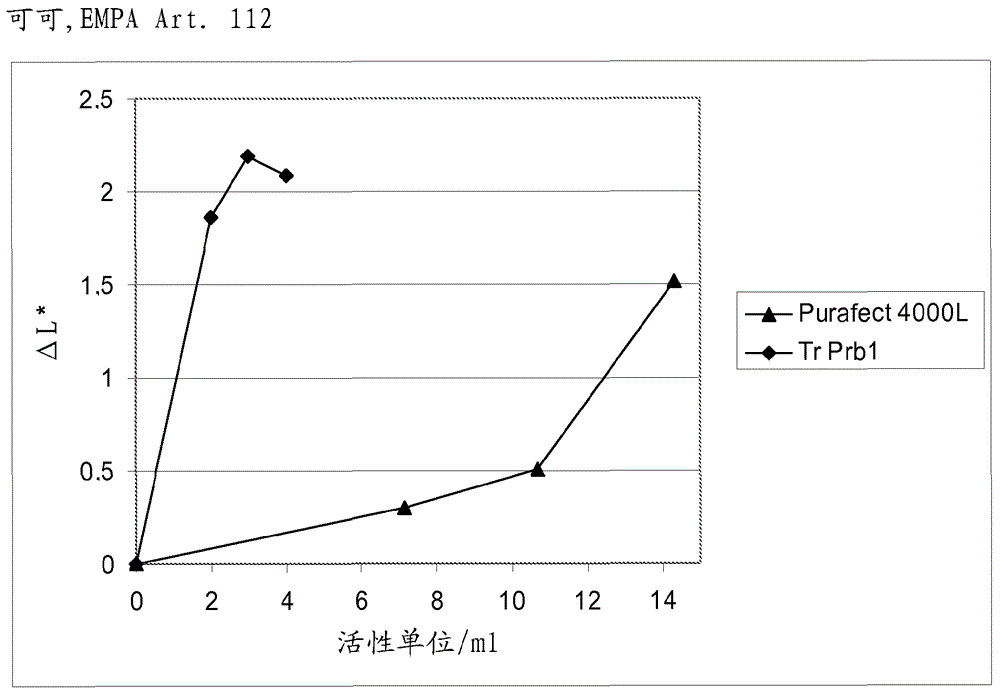
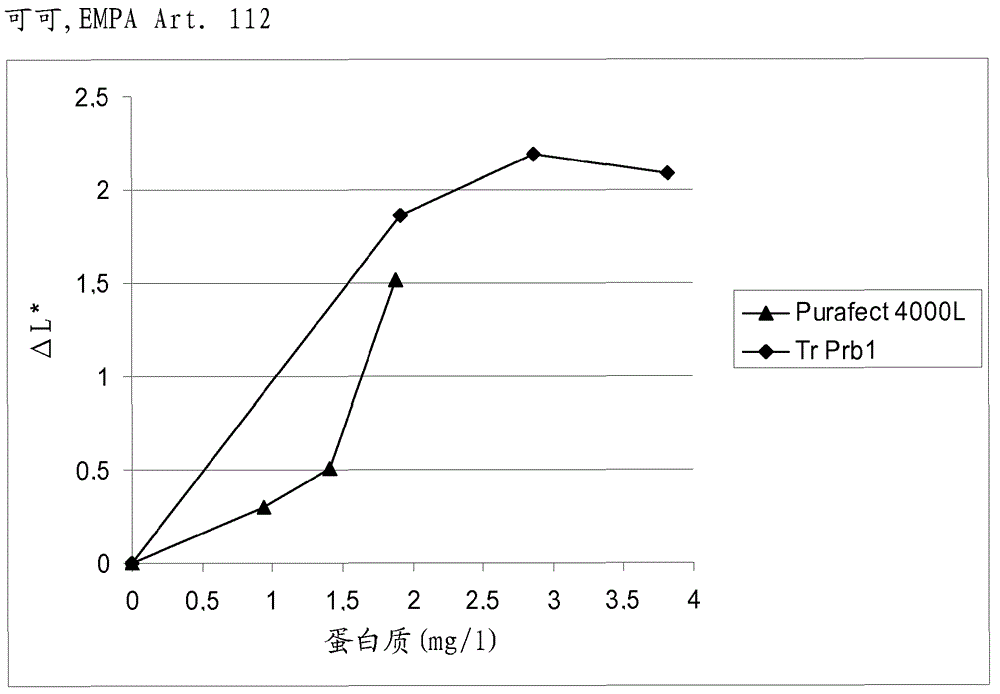
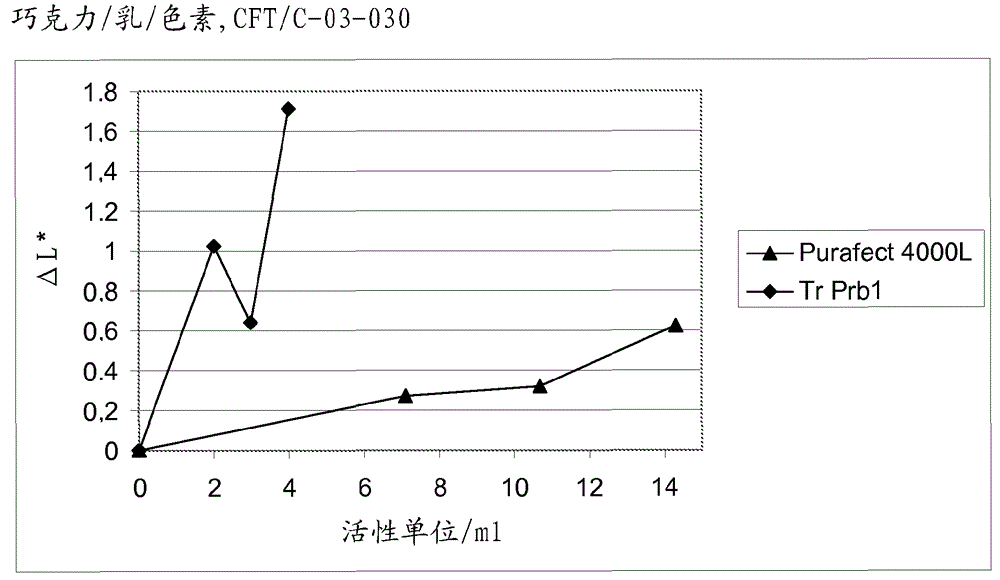
The present invention is related to a fungal serine protease enzyme useful in modification, degradation or removal of proteinaceous material, which enzyme comprises an amino acid sequence of the mature Tr Prb 1 enzyme having an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 10 or a variant thereof having similar activity. The serine protease is obtainable from Trichoderma. Also disclosed are nucleic acid sequences encoding said protease, such as plasmid pALK2650 comprising the nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO: 10 of the full length enzyme deposited in E. coli RF8052 under accession number DSM 22635. Said protease is useful as an enzyme preparation applicable in detergent compositions and for treating fibers, for treating wool, for treating hair, for treating leather, for treating food or feed, or for any applications involving modification, degradation or removal of proteinaceous material at low or moderate temperature ranges.
Owner:AB ENZYMES GMBH
Process for preparation of protein hydrolysate from milk protein
InactiveCN1494384AIncrease the degree of hydrolysisAnimal proteins working-upProtein hydrolysatesFungal protease
The present invention provides a process for the preparation of protein hydrolysate from milk protein by treating milk protein with fungal protease at a pH of 7.5-8.5, temperature of 40+ / -5 deg.C for a time period of 30 min to 2 hours; heating at 65-70 deg.C for at least 3 min, separating the clarified supernatant by a known manner and drying the clarified liquor thus obtained to get the protein hydrolysate.
Owner:科学和工业研究委员会
Process for the preparation of protein hydrolysate from legumes
Owner:RAO APPU RAO GOPALA RAO APPU +7
Dietary supplements containing natural ingredients
InactiveUS20080031861A1Reduced activityReduce oxidationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMammalAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a dietary supplement comprising at least one flavonoid source and an enzyme, that is effective for inhibiting in vivo platelet activity and LDL cholesterol oxidation in a mammal at a dosage of about 30 mg / Kg or less. The supplement may contain flavonoid sources found in grape seed extracts, grape skin extracts, bilberry extracts, ginkgo biloba extracts or the flavonoid quercetin. The supplement may also contain fungal proteases, acid stable proteases and bromelain. The invention further provides a method for using the dietary supplement and an article of manufacture containing the supplement.
Owner:PERKES LYNN
Process for preparation of protein hydrolysate from milk protein
InactiveCN1225185CIncrease the degree of hydrolysisAnimal proteins working-upProtein hydrolysatesFungal protease
The present invention provides a process for the preparation of protein hydrolysate from milk protein by treating milk protein with fungal protease at a pH of 7.5-8.5, temperature of 40+ / -5 deg.C for a time period of 30 min to 2 hours; heating at 65-70 deg.C for at least 3 min, separating the clarified supernatant by a known manner and drying the clarified liquor thus obtained to get the protein hydrolysate.
Owner:科学和工业研究委员会
Enzymatic treatment of whey proteins for the production of antihypertensive peptides, the resulting products and treatment of hypertension in mammals
InactiveUS20050003999A9Lower blood pressureSuppressing angiotensin-converting enzymePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMammalFungal protease
Enzymatic digests of whey protein concentrates were prepared using animal, bacterial and fungal proteases, and evaluated for antihypertensive activities. ACE-inhibitory activity and antihypertension activity were obtained with a hydrolysate of whey protein isolate prepared with a porcine trypsin.
Owner:DAVIS MARTIN E +5
A fungal protease and use thereof
The present invention is related to a fungal serine protease enzyme useful in modification, degradation or removal of proteinaceous material, which enzyme comprises an amino acid sequence of the mature Tr Prb1 enzyme having an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 10 or a variant thereof having similar activity. The serine protease is obtainable from Trichoderma. Also disclosed are nucleic acid sequences encoding said protease, such as plasmid pALK2650 comprising the nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO: 10 of the full length enzyme deposited in E. coli RF8052 under accession number DSM 22635. Said protease is useful as an enzyme preparation applicable in detergent compositions and for treating fibers, for treating wool, for treating hair, for treating leather, for treating food or feed, or for any applications involving modification, degradation or removal of proteinaceous material at low or moderate temperature ranges.
Owner:AB ENZYMES GMBH
A kind of macadamia nut beverage and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a macadamia nut beverage, which belongs to the technical field of beverage preparation. The macadamia nut beverage includes the following raw materials: macadamia nuts, xylitol, sorbitol, sucrose, citric acid, lactic acid, emulsifier, stabilizer, fungal protease, papain, aminopeptidase, lactic acid bacteria; the papaya The weight ratio of protease, aminopeptidase and lactic acid bacteria is: (0.1-0.2): (0.008-0.02): (0.2-0.3). The macadamia nut beverage is prepared through steps such as pressing, pulping, enzymatic hydrolysis, debittering, blending, homogenizing, fermenting, and sterilizing. The invention improves the nutritional content and stability of the macadamia nut drink by adopting a reinforcing system composed of papain, aminopeptidase and lactic acid bacteria.
Owner:SOUTH ASIAN TROPICAL AGRI SCI RES INST OF GUANGXI
Dietary supplements containing natural ingredients
InactiveCN101849675BOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFood additiveAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a dietary supplement comprising at least one flavonoid source and an enzyme, that is effective for inhibiting in vivo platelet activity and LDL cholesterol oxidation in a mammal at a dosage of about 30 mg / Kg or less. The supplement may contain flavonoid sources found in grape seed extracts, grape skin extracts, bilberry extracts, ginkgo biloba extracts or the flavonoid quercetin. The supplement may also contain fungal proteases, acid stable proteases and bromelain. The invention further provides a method for using the dietary supplement and an article of manufacture containing the supplement.
Owner:MELALEUCA INC
Regulated PepC expression
The present invention relates to a recombinant fungal host cell comprising at least one first polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide of interest; and one or more second polynucleotide encoding a fungal PepC protease, wherein the one or more second polynucleotide is operably linked to a regulated heterologous promoter, as well as a method for producing a polypeptide of interest, comprising cultivating said fungal host cell.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Antimicrobial nano-surfactant and methods
PendingUS20220265707A1Low viscosityImprove solubilityBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsActive agentPhosphorus acid
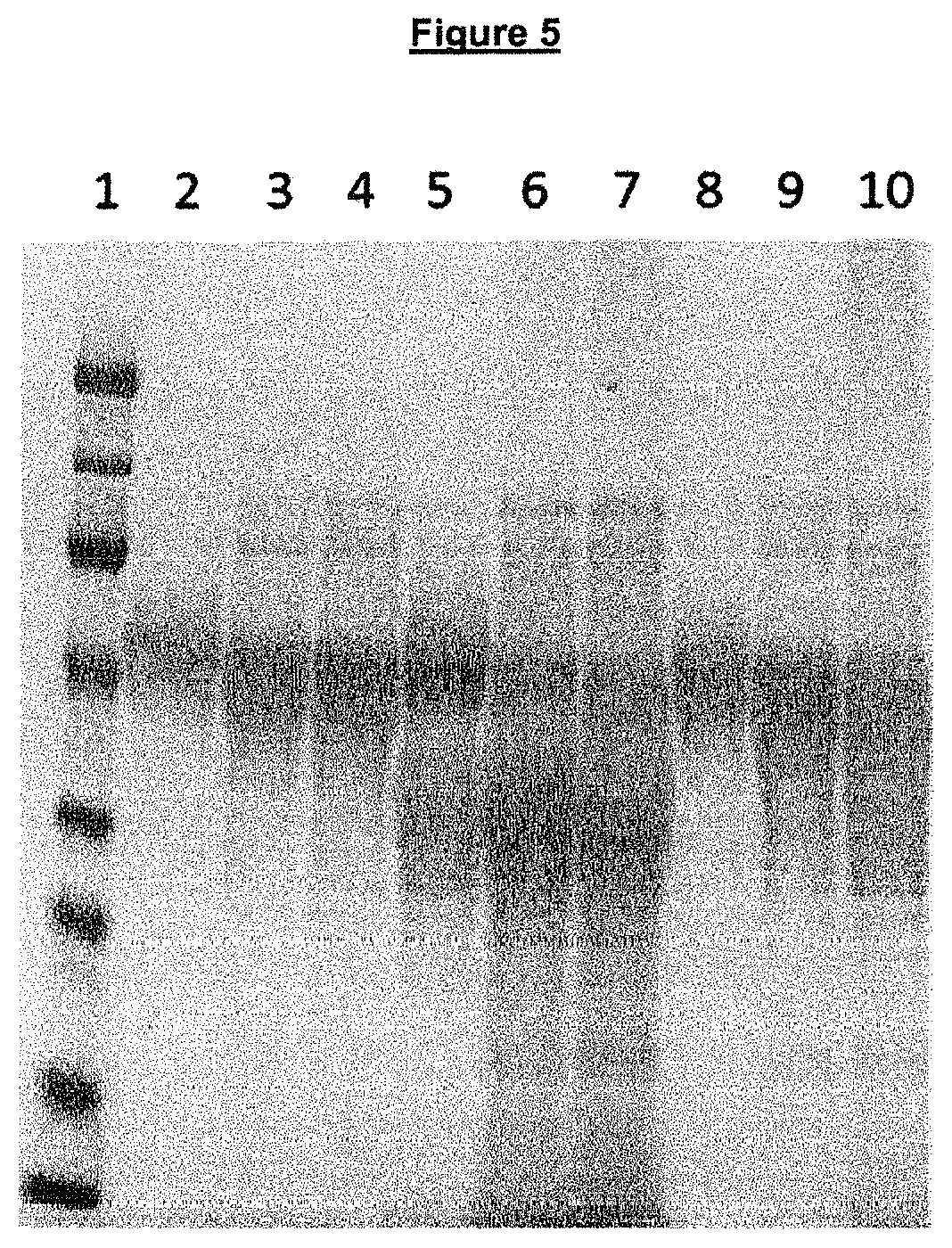
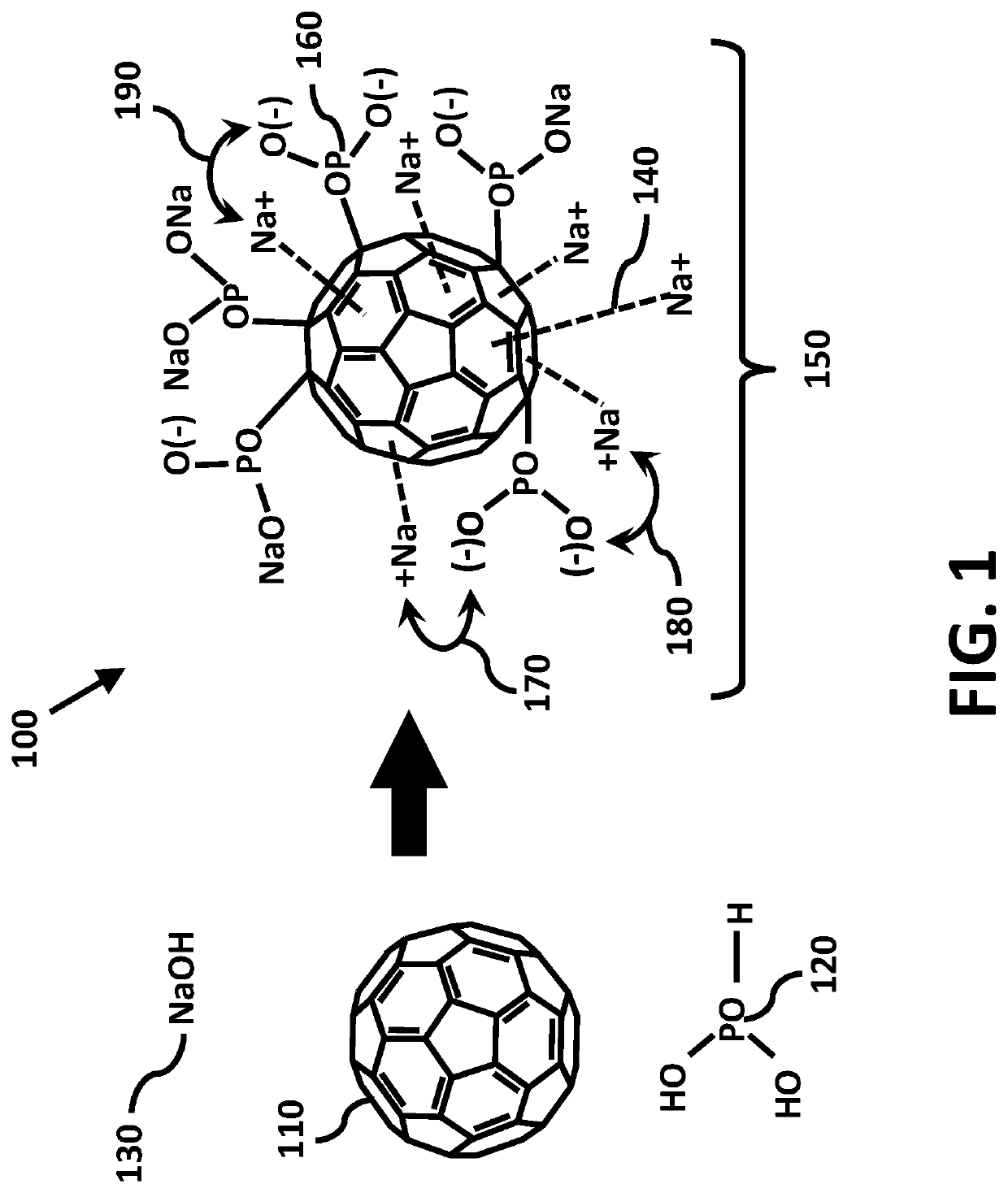
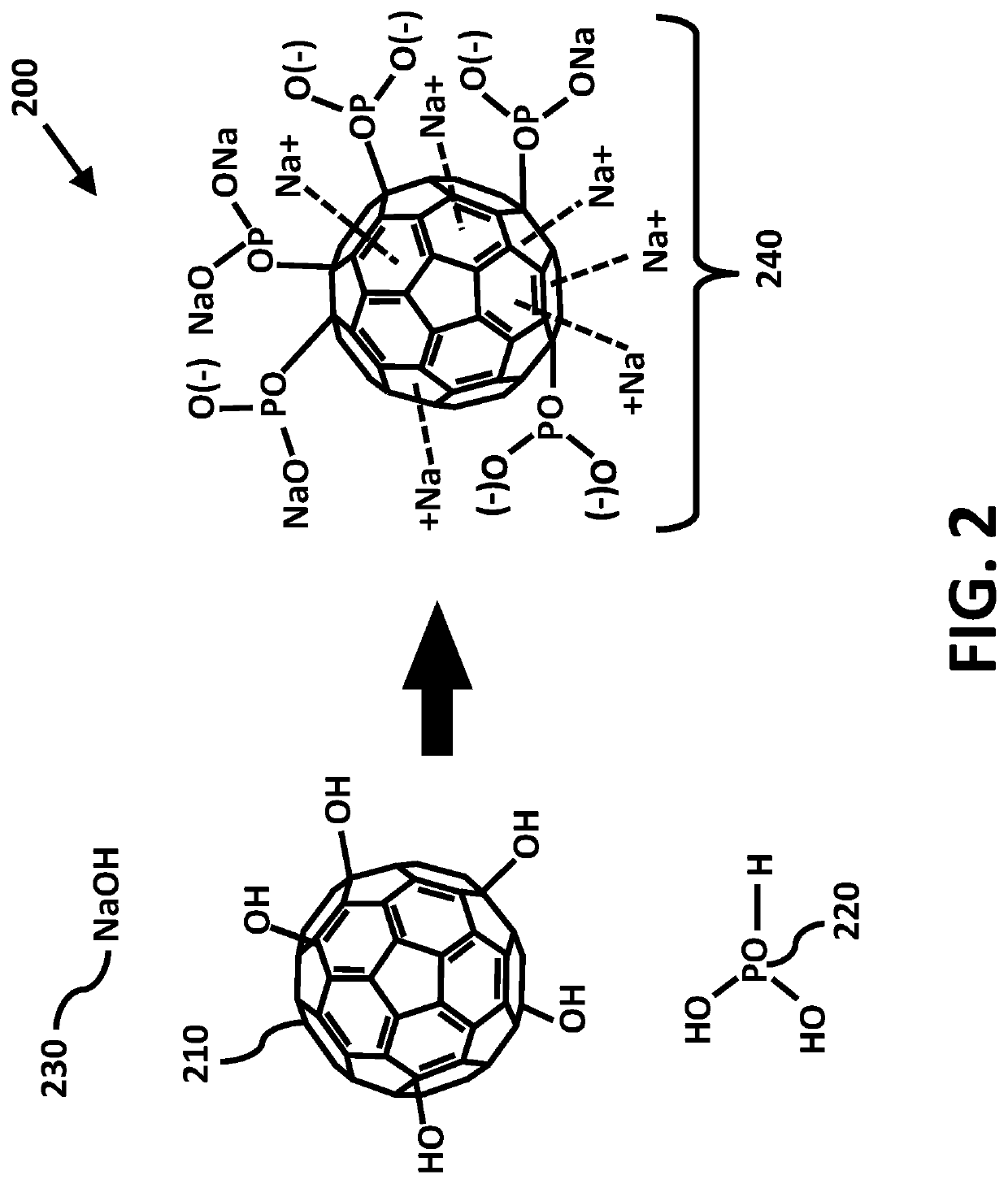
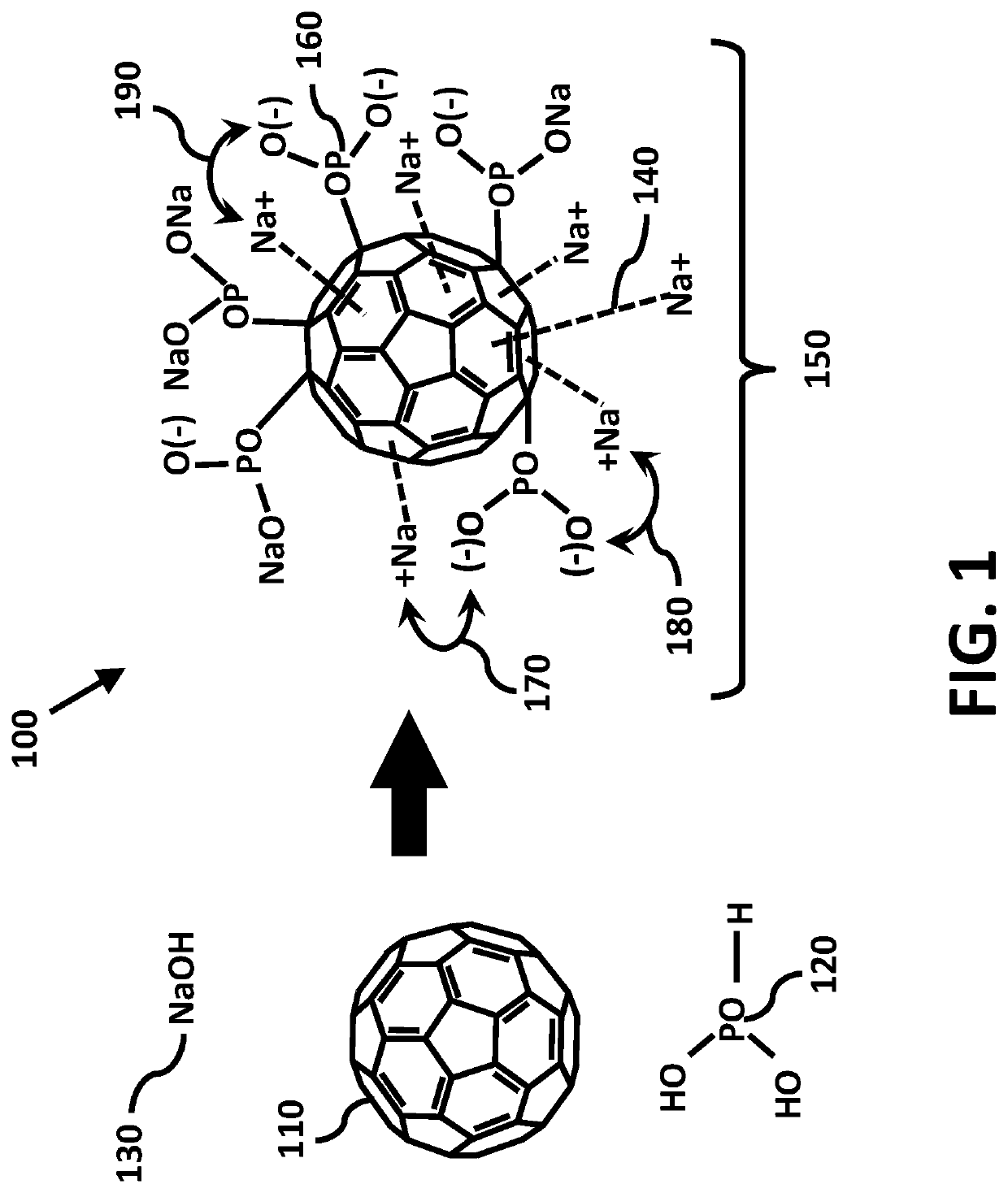
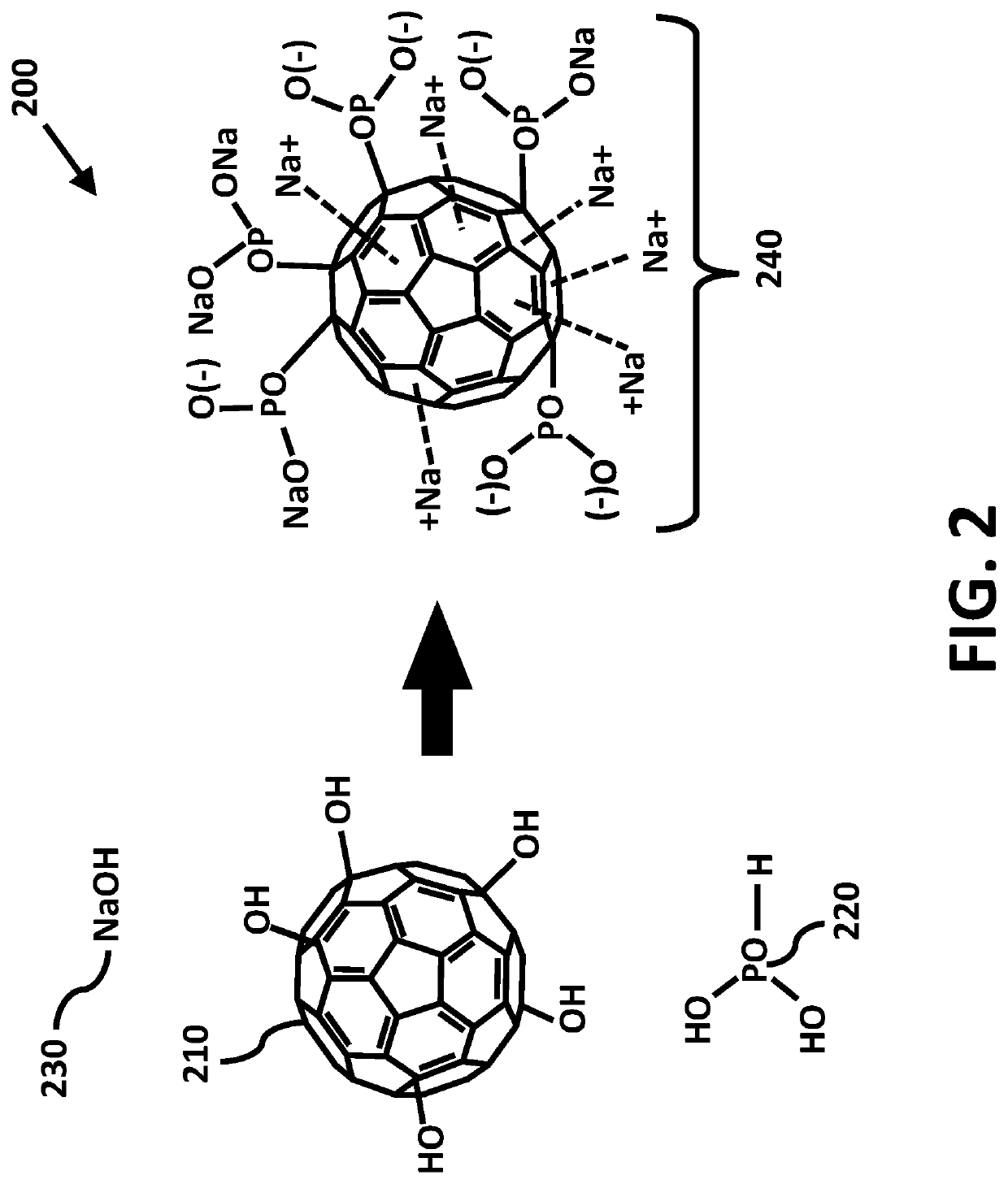
An antimicrobial composition of buckminsterfullerene with saponified phosphorus acid functional groups is provided to disassemble or make virus particles inert, and to inhibit viral and fungal proteases using catalytic desulfurization. This composition is formulated to prevent or to treat novel corona viruses including emerging strains of SARS-Cov-2, as well as fungal pathologies such as valley fever and respiratory ailments such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) and pneumonia. Virus particles are implicated in the development of cancers. The antiviral properties further enable the composition to prevent conditions leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation, neoplasms, degenerative malignancy, and to help treat chronic inflammatory diseases associated with or leading to induce cancer in virus infected cells. The composition can be produced at low temperatures through reactive shear mixing. Delivery methods include ingestion, topical application, inhalation, or injection when used as a medicament or as a food supplement.
Owner:EXOTHULE INC
Antimicrobial nano-deliverant and methods
PendingUS20220265850A1Low viscosityImprove solubilityBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsPhosphorus acidNeoplasm
An antimicrobial composition of buckminsterfullerene with saponified phosphorus acid functional groups is provided to disassemble or make virus particles inert, and to inhibit viral and fungal proteases using catalytic desulfurization. This composition is formulated to prevent or to treat novel corona viruses including emerging strains of SARS-Cov-2, as well as fungal pathologies such as valley fever and respiratory ailments such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) and pneumonia. Virus particles are implicated in the development of cancers. The antiviral properties further enable the composition to prevent conditions leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation, neoplasms, degenerative malignancy, and to help treat chronic inflammatory diseases associated with or leading to induce cancer in virus infected cells. The composition can be produced at low temperatures through reactive shear mixing. Delivery methods include ingestion, topical application, inhalation, or injection when used as a medicament or as a food supplement.
Owner:EXOTHULE INC
A kind of method that utilizes oyster to prepare biological zinc
InactiveCN105476014BNutrient release is completely more thoroughUniform molecular weight suitable forFood scienceSolubilityOyster
The invention discloses a method for preparing biological zinc from oysters. The method comprises the following steps: removing shells of living oysters, grinding fresh oyster meat by a colloid mill to obtain meat pulp, adding cellulase, fungal proteinase and lipase for enzymolysis, performing fine filtering, separating to obtain filter liquor rich in biological zinc, separating the filter liquor with a molecular sieve, performing vacuum concentration, and performing spray drying to obtain 100-150-mesh biological zinc dry powder. The biological zinc drying powder has the characteristics of being high in water solubility, uniform in molecular weight, high in biological activity, free from activation, direct and fast in absorption, free of fishy smell of the oysters, and the like, and is a good functional factor in healthy products having high additional values.
Owner:GUANGXI PANDA BIOTECH DEV CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com