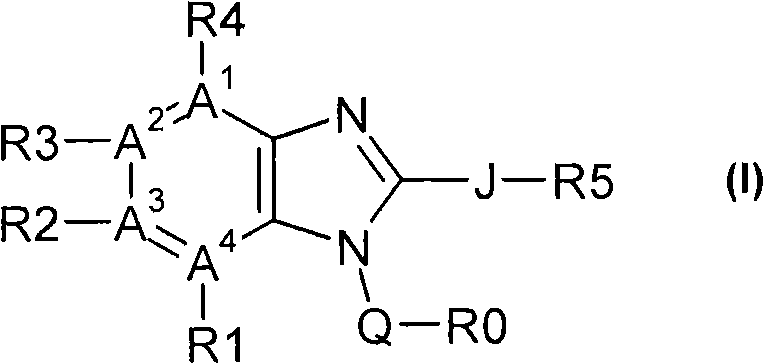
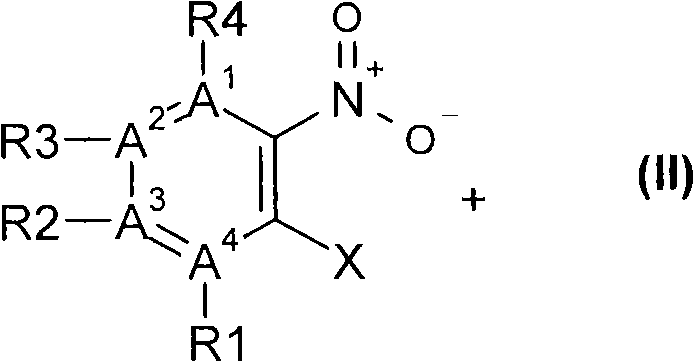
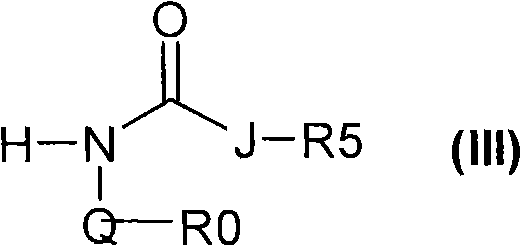
A regioselective copper catalyzed synthesis of benzimidazoles and azabenzimidazoles
A compound and heteroaryl technology, applied in the field of regioselective synthesis of compounds of formula I, can solve the problems of copper-catalyzed cross-coupling not showing universal applicability, poor cost-effectiveness, hindering optimization, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0188] During the preparation of compounds of formula I, it is often advantageous or necessary to introduce functional groups which reduce or prevent undesired or side reactions in the various synthetic steps in the form of precursor groups which are subsequently converted into the desired functional groups, or by means of suitable Protecting group strategies for synthetic problems to temporarily block functional groups. Such strategies are well known to those skilled in the art (see eg Greene and Wuts, Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, Wiley, 1991 or P. Kocienski, Protecting Groups, Thieme 1994). As an example of a precursor group there may be mentioned the cyano group, which can be converted in a subsequent step into a carboxylic acid derivative or into an aminomethyl group by reduction. A protecting group can also have the meaning of a solid phase, and cleavage from a solid phase means removal of the protecting group. The use of such techniques is known to those skil...
Embodiment 1
[0209] Example 1: 2-Methyl-1-phenyl-1H-benzimidazole.
[0210]
[0211] A solution containing 2-iodonitrobenzene (125 mg, 0.5 mmol), N-phenylacetamide (81 mg, 0.6 mmol), CuI (4.8 mg, 0.025 mmol), N-methylethyl ether in anhydrous toluene (3 mL) The reaction tube of diamine (4.4 μL, 0.05 mmol), potassium phosphate (212 mg, 1 mmol) was purged with dry argon for 3 minutes. The mixture was then heated at 100 °C for 18 h. After cooling, the reaction was hydrolyzed with 3 mL of water and filtered through Varian cartridge Chem Elut 12198007, washing with ethyl acetate. The crude mixture was dissolved in 10 mL of glacial acetic acid and refluxed for 30 minutes in the presence of iron powder (279 mg, 5 mmol). The acid was removed under reduced pressure, the residue was suspended in saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and extracted with ethyl acetate. The obtained crude product was purified by preparative HPLC to obtain the title compound (82 mg, 73% yield) as a yellow solid. mp...
Embodiment 2
[0212] Example 2: 5-Chloro-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-benzimidazole.
[0213]
[0214] The title compound was prepared according to a method similar to that described in Example 1, using 4-chloro-1-bromo-2-nitrobenzene (118 mg, 0.5 mmol) and N-phenylacetamide (81 mg, 0.6 mmol) as starting materials , the title compound was obtained as a yellow solid (68 mg, 56% yield). mp 109-111℃. 1 HNMR (DMSO) δ2.52(s, 3H), 7.22(d, J=8.6Hz, 1H), 7.34(d, J=8.6Hz, 1H), 7.48-7.59(m, 5H), 7.86(s, 1H); 13 C NMR δ13.5, 112.2, 116.4, 123.9, 126.9, 127.9, 129.7, 130.1, 133.9, 138.5, 154.0, 157.0. HRMS (FAB): C 14 h 12 N 2 Cl[M+H + ], calculated value: 243.0689; measured value: 243.0684.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com