Method for judging formation time of fragmental rock based on structural thermal evolution history
A technology of clastic rock and thermal evolution, applied in the direction of material inspection, soil material testing, etc., can solve the problems that cannot represent the sedimentary age, is difficult to apply, and the paleontological fossils in the gravel are scarce.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
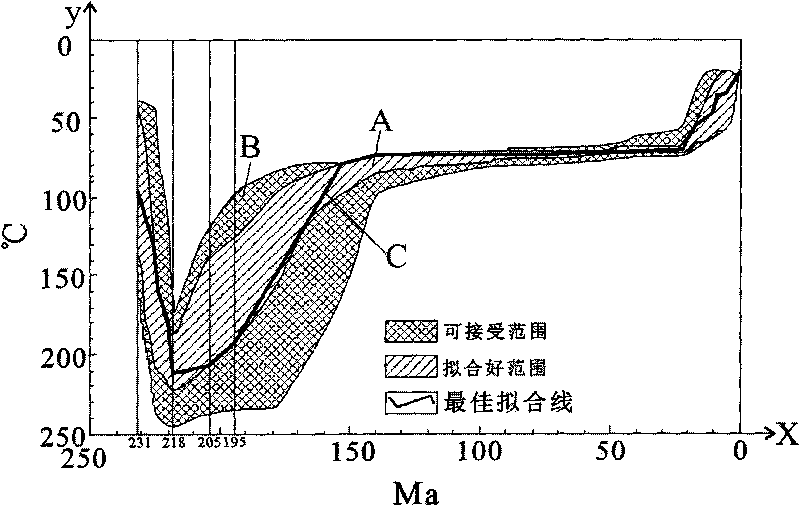
[0025] Embodiment one, sample is Kongtong mountain conglomerate
[0026] A method for judging the formation age of clastic rocks based on tectonic thermal evolution history, comprising the following steps:
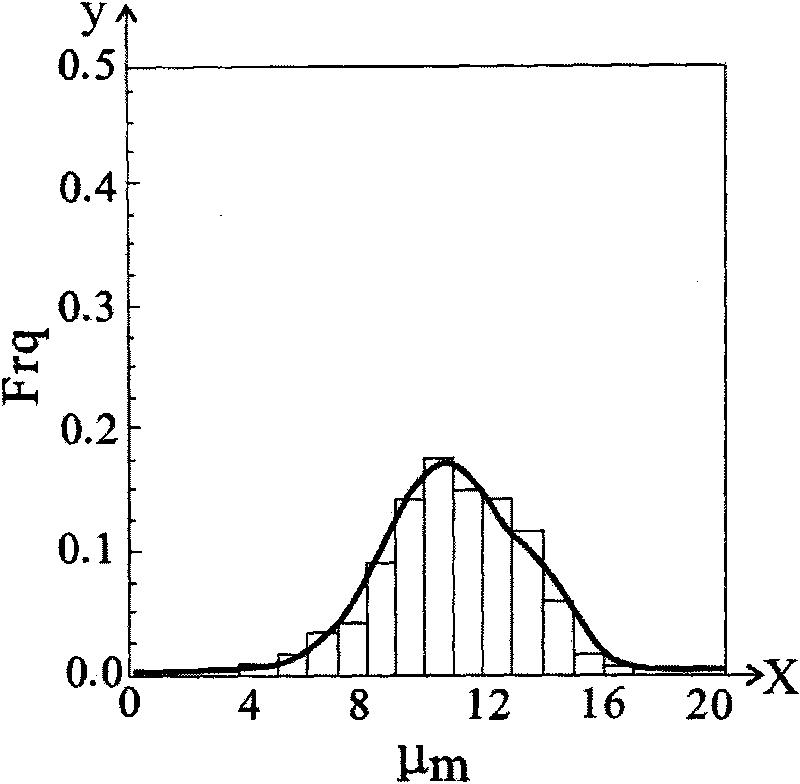
[0027] The first step is to conduct a fission track test on the sandstone interlayer sample in the Kongtong Mountain conglomerate, and obtain the fission track combination age (Pooled age) and error (AgeErr) of apatite and zircon in the sample, and the fission track median value Age (Central age) and error (Age Err), statistical test probability P(χ 2 )% and apatite fission track length (L (μm)) and length error, see Table 1, to obtain apatite single fission track length (L (μm)), apatite single fission The maximum diameter of the track etching image (Kin Par) and the angle between the single fission track direction of apatite and the crystallization C-axis (C-axis) are shown in Table 2, and the age of the apatite single particle (Age) and error (Age Err), apatite single...
Embodiment 2
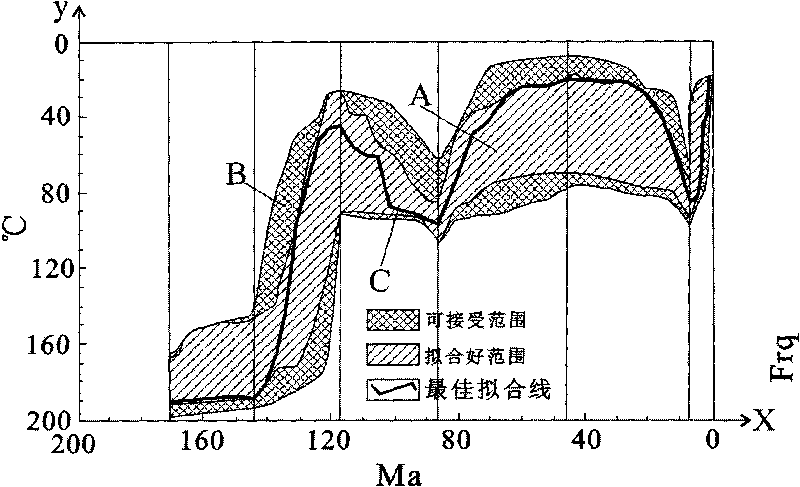
[0040] Example 2, the sample is the clastic rock of Liupan Mountain in Longde
[0041] A method for judging the formation age of clastic rocks based on tectonic thermal evolution history, comprising the following steps:
[0042] The first step is to conduct a fission track test on the clastic rock samples from Liupanshan in Longde, and obtain the fission track combination age (Pooled age) and error (Age Err) of apatite and zircon in the sample, and the median value of the fission track Age (Central age) and error (Age Err), statistical test probability (P(χ 2 )%) and apatite fission track length (L (μm)) and length error, see Table 4, obtain apatite single fission track length (L (μm)), apatite single The maximum diameter (Kin Par) of the fission track etching image and the angle (C-axis) between the direction of the single fission track of apatite and the crystallization C axis (C-axis) are shown in Table 5, and the age (Age) and error (Age) of the apatite single particle ( ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment three, the sample is carbon mountain clastic rock
[0058] A method for judging the formation age of clastic rocks based on tectonic thermal evolution history, comprising the following steps:
[0059] The first step is to conduct fission track test on the carbon mountain clastic rock sample, and obtain the fission track combination age (Pooled age) and error (±1σ) of apatite and zircon in the sample, and the fission track median age (Central age) and error (±1σ), statistical test probability P(χ 2 ) and apatite fission track length (L(μm)) and length error (±1σ) (Table 7), to obtain apatite single fission track length (L(μm)), apatite intersecting the polished surface The largest diameter (Kin Par) of the single fission track etching image of apatite and the angle between the direction of a single fission track of apatite and the crystallization C axis (C-axis) (Table 8), and the age of apatite single particle (Age) and Error (±1σ), apatite single particle ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com