Method for storing and refreshing peach
A storage and preservation technology, which is applied in the fields of fruit and vegetable preservation, fruit/vegetable preservation through freezing/refrigeration, food preservation, etc. It can solve the problem of quality decline, fruit disease resistance and storage resistance decline, affecting sales and edible value to prevent chilling damage, maintain postharvest quality, and prolong the storage period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] experiment material:
[0016] The eight-ripe "August crisp" (Prunus persica L.cv.Bayuecui) peach fruit was used as the experimental material. The fruit comes from the Agricultural Picking Garden in Pinggu District, Beijing. The fruits were immediately transported to the Postharvest Physiology and Pathology Laboratory of the Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences after harvesting.
[0017] Test treatment:
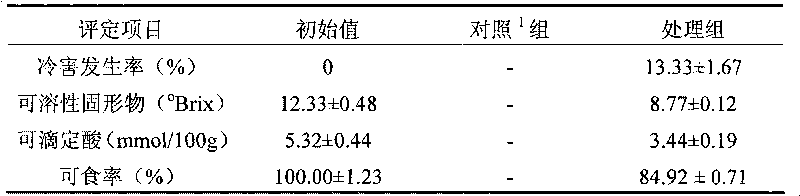
[0018] The above-mentioned eight-ripe "August Crisp" peach fruit was soaked in 1% (volume percent concentration) sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution for 2 minutes to carry out surface disinfection, rinsed and dried naturally for subsequent use. Peach fruits were randomly divided into 2 groups. One group was directly stored at 5°C for 30 days as a control; the other group was exercised at 0°C and relative humidity of 90-95% for 5 days, and then transferred to 5°C and relative humidity of 90-95%. Store for 25 days. The experimental treatment combinations...
Embodiment 2
[0025] experiment material:
[0026] The eight-ripe "August Crisp" (Prunus persica L.cv.Bayuecui) peach fruit was used as the experimental material. The fruit came from the Agricultural Picking Garden in Pinggu District, Beijing. After the fruit was harvested, it was immediately transported to the Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences. and pathology laboratory.
[0027] Test treatment:
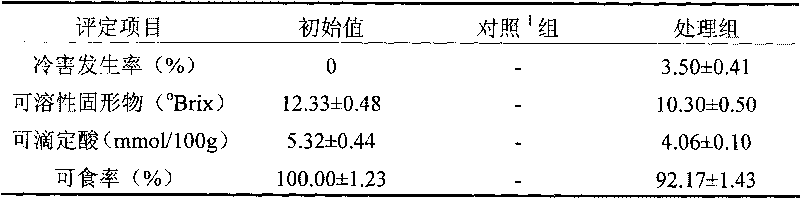
[0028] The above-mentioned eight-ripe "August Crisp" peach fruit was soaked in 1% (volume percent concentration) sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution for 2 minutes to carry out surface disinfection, rinsed and dried naturally for subsequent use. Peach fruits were randomly divided into 2 groups. One group was directly stored at 5°C for 30 days as a control; the other group was trained at 0°C and relative humidity of 90-95% for 7 days, and then transferred to 5°C and relative humidity of 90-95%. Store for 23 days. The experimental treatment combinations are shown in Table 2.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0035] experiment material:
[0036] The eight-ripe "August crisp" (Prunus persica L.cv.Bayuecui) peach fruit was used as the experimental material. The fruit comes from the Agricultural Picking Garden in Pinggu District, Beijing. The fruits were immediately transported to the Postharvest Physiology and Pathology Laboratory of the Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences after harvesting.
[0037] Test treatment:
[0038] The above-mentioned eight-ripe "August Crisp" peach fruit was soaked in 1% (volume percent concentration) sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution for 2 minutes to carry out surface disinfection, rinsed and dried naturally for subsequent use. Peach fruits were randomly divided into 2 groups. One group was directly stored at 5°C and a relative humidity of 90-95% for 30 days as a control group; the other group was exercised at 0°C and a relative humidity of 90-95% for 10 days and then transferred to 5°C. Continue to store for 20 days. The experimental ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com