Human Scurfin protein span with membrane penetration sequence, fragment and preparation method
A technology of sequence and fusion protein, applied in the biomedical field of genetic engineering and protein transduction, can solve the problems of mutation, difficulty in amplification and low transfection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
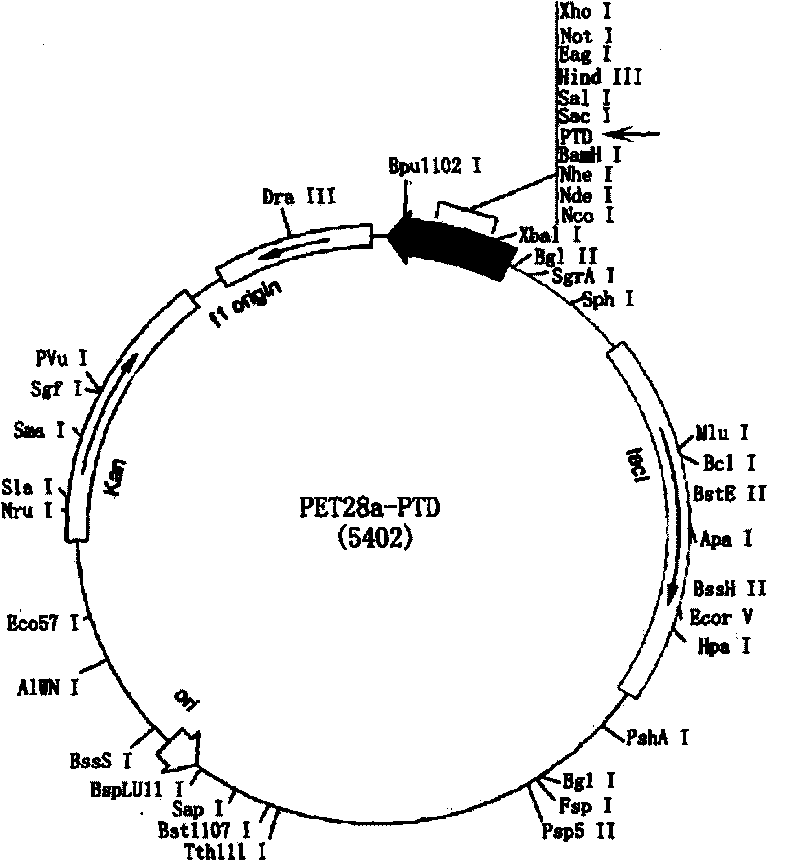
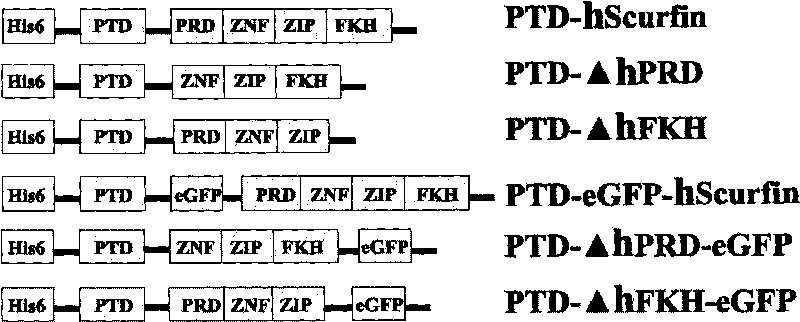
[0087] The PTD-hScurfin, PTD-ΔhFKH and PTD-ΔhPRD fusion proteins described in the specific embodiments have the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3.
[0088] The present invention provides a method for producing PTD-hScurfin, PTD-ΔhFKH and PTD-ΔhPRD fusion proteins, the method comprising the following steps:
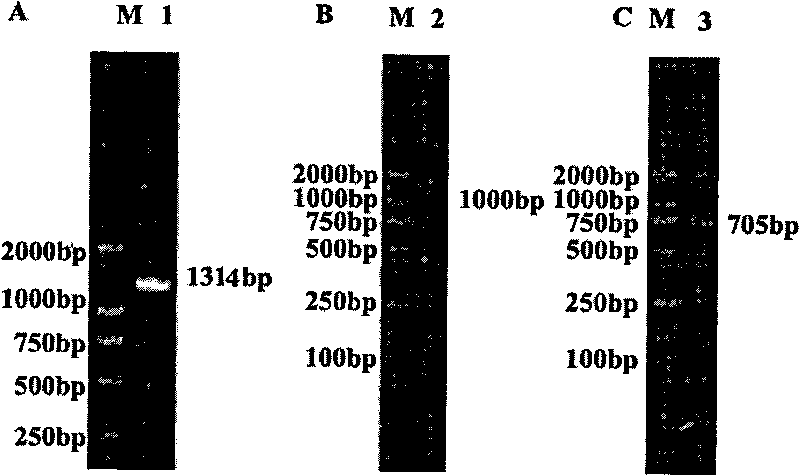
[0089] 1. Obtain the gene sequences encoding PTD-hScurfin, PTD-ΔhFKH and PTD-ΔhPRD fusion proteins;
[0090] 2. inserting the sequence obtained in step 1 into a suitable vector to obtain the corresponding nucleic acid construct;
[0091] 3. transforming suitable engineered expression bacteria with the nucleic acid construct obtained in step 2;
[0092] 4. Under appropriate culture conditions, induce the transformed engineered expression bacteria in step 3, and purify PTD-hScurfin, PTD-ΔhFKH and PTD-ΔhPRD fusion proteins therefrom.
[0093] 5. PTD-hScurfin, PTD-ΔhFKH and PTD-ΔhPRD fusion proteins or fusion proteins carrying eGFP as a tracer were observed by conf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com