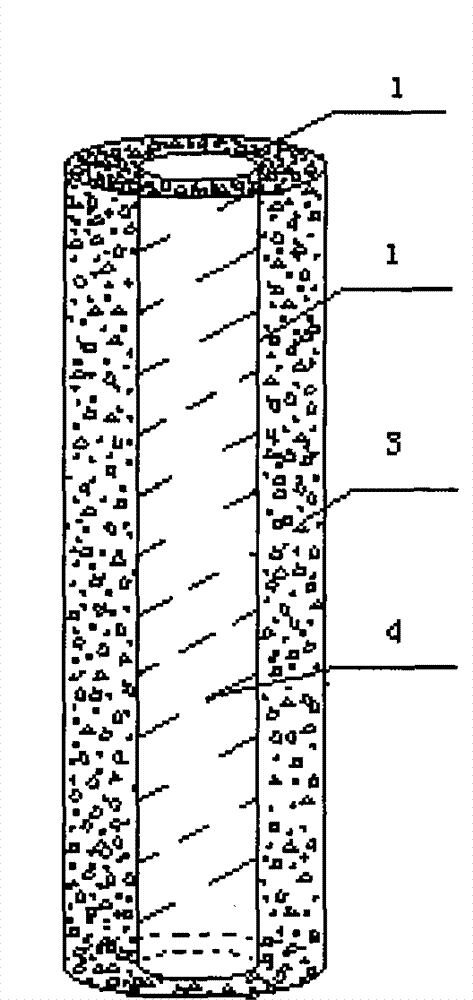
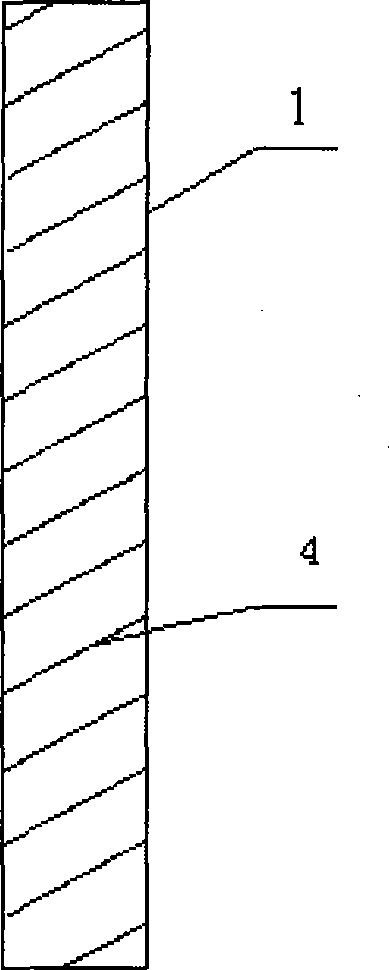
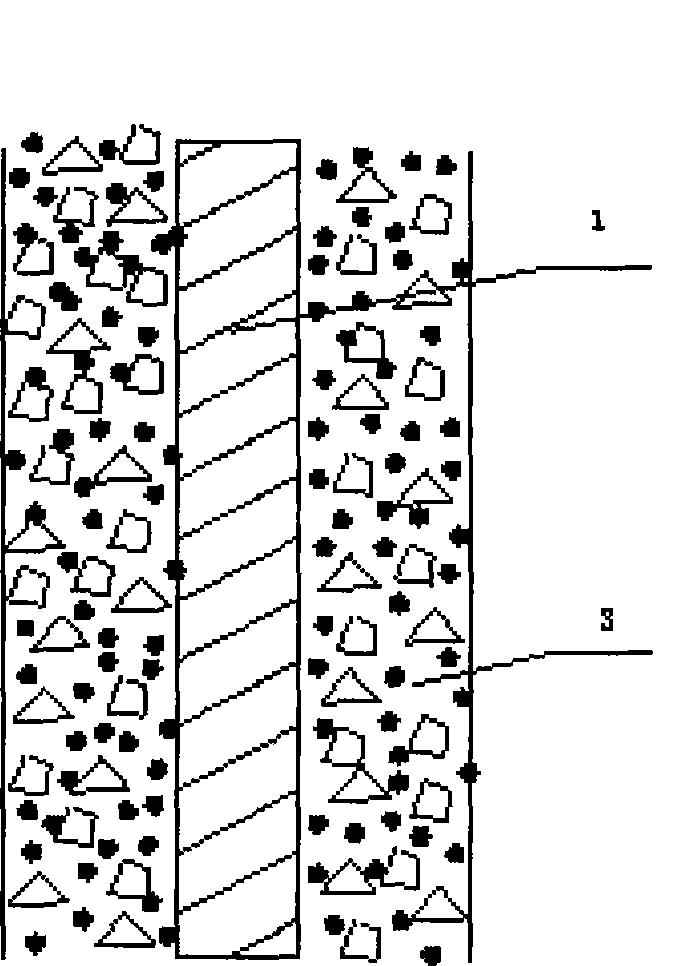
[0014] 3) The process of making and installing the reinforcement cage is complicated:
[0027] (4) Multiple high-pressure injections of cement slurry are required
[0029] 4. Problems and deficiencies in the above process
On the other hand, the unreasonable adjustment of mud consistency and mud material selection for the retaining wall is the direct factor leading to the failure of reducing the water loss of plastic soil (controlling the seepage reduction of the hole wall) and the failure to quickly form a stable hole wall mud skin around the hole wall
Thirdly, when the hole is formed, the mud delivery rate of the mud pump is not increased, the hole is not formed quickly, and the time for forming the hole is not shortened, which is the indirect cause of swelling, quicksand and soil collapse.
Fourth, a certain number of alloy blades are not welded on the outside of the straightener, and the sweeping effect does not work when drilling or pulling out, which is an improper control factor
[0049] The concrete in the pile body is discontinuous after solidification, and the broken pile phenomenon that the pile body is partially filled with mud, uncured concrete and soil is mostly caused by: the distance between the bottom end of the conduit and the bottom of the hole is greater than 1.0m, that is, the exit of the conduit is too close to the bottom of the hole; the concrete pouring process Diluted by the water in the mud, the amount of water in the water-cement ratio in the concrete increases, delaying the age of concrete solidification; affected by groundwater activities or poor sealing of the conduit, groundwater immerses in the concrete to change the water-cement ratio, resulting in slow piles. Condensation; the lifting and pulling speed of the conduit is greater than the concrete pouring speed, and the bottom of the conduit is exposed to the concrete surface in the hole, that is, the conduit is lifted too fast; or temporary power failure, long intervals of concrete mixing cause slag inclusion, and mud sediment deposits in the pile hole Layers; when pouring concrete, instead of pouring it from the conduit, the concrete is poured directly from the orifice, resulting in concrete segregation, resulting in looseness and voids in individual piles.
[0050] ③ Poor compactness of pile concrete
[0052] ④ thick mud skin around the pile
[0055] ①The process of making steel cages is complicated:
However, cast-in-situ piles belong to the field operation process. Therefore, the mix ratio of concrete will change due to factors such as mixing location, humidity in the air, moisture content and particle size of sand and gravel, and different batches of cement. The mix ratio of the concrete in it is substantially different from the mix ratio provided by the laboratory
[0071] 2) Problems and deficiencies in the construction technology of special cast-in-place piles
[0073] ① Unable to determine the fullness and compactness of the cement slurry in the sand
[0079] The proportion of cement particles is larger than that of cement slurry. Under the action of gravity and during the process of cement gel production, cement particles are mostly deposited in the middle and lower parts of the pile body. Therefore, the strength of the pile body in the middle and lower parts of the pile body is greater than that of the pile body. The strength of the middle and upper parts, the compactness of the upper part is poor, and the coagulation strength is low
The strength of the main stress-bearing part of the pile body (pile top) is low
[0080] 3) Problems and deficiencies in construction workers of advanced micro piles (small piles without sand)
[0082] ① Unable to determine the fullness and compactness of the cement slurry in the gravel
[0089] ④ Poor bonding between step-by-step concrete and steel pipes
This kind of pile is only suitable for projects with relatively low loads in engineering applications.
[0091] ⑤ The strength of concrete is difficult to meet the design requirements
[0092] Due to the lack of intermediate particles and the cement solidification body cannot fill all the coarse particle spaces, the strength of the step-by-step concrete is tested under the same cement content. The results of the pressure test show that the unconfined compressive strength does not meet the design requirements
[0093] ⑥ The construction process is cumbersome and labor-intensive
[0097] Through the above brief introduction, the construction process of cast-in-situ piles is complicated, lacks clear indicators, has no obvious effect, is not high in safety, is difficult to master, low in economy, high in mechanical cooperation, high in labor intensity, many testing items, complex in management, and difficult to supervise. Many contents, changeable process control factors, strong comprehensiveness, lack of understanding and utilization of natural geotechnical engineering conditions, weak improvement, non-uniform quality caused by non-standardized process flow, etc. have become obstacles to the development of cast-in-place pile technology
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More