Co-graduation surface full-spectrum target
A full-spectrum, target technology, applied in spectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromator, optical radiation measurement, measurement device, etc. problems, to reduce the influence of measurement accuracy, expand the test range, and simplify the structure of the instrument
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
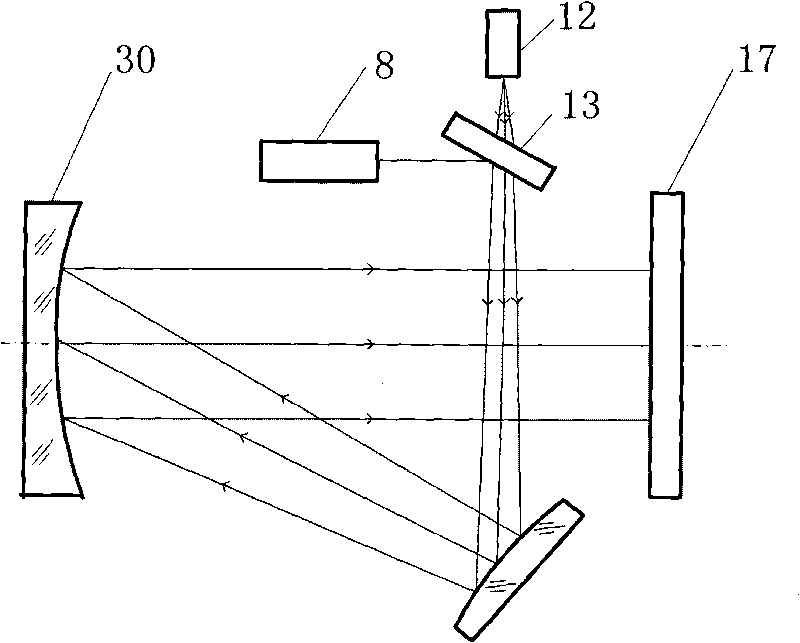
[0043] The structure of Embodiment 1 of the present invention is as follows Figure 8 As shown, the 0.5 μm-14 μm co-divided full-spectrum ZnS cross-divided target 25 includes: a ZnS substrate 8, a four-quadrant detector 22 and a star point hole 9, wherein the four-quadrant detector 22 is fabricated on the ZnS substrate 8, The star point hole 9 is located at the center of the ZnS substrate 8 .
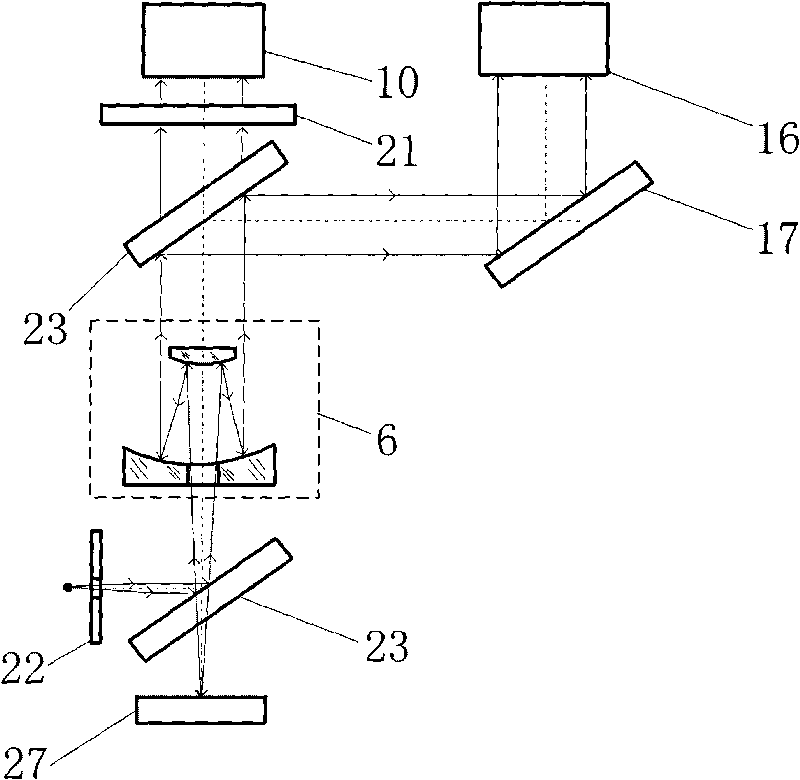
[0044] Measure the parallelism of visible light axis, infrared light axis, laser emitting axis and laser receiving axis: place the full-spectrum light source 1 at the focal point of the parabolic reflector 7, and the reflected parallel beam evenly irradiates the ZnS reticle target 25, ZnS reticle The reticle target 25 is placed at the focal point of the image space of the optical collimation system 6. After the parallel beam of the full-spectrum light source 1 is imaged by the ZnS cross reticle target 25 and the optical collimation system 6, a parallel beam is emitted, which is imaged b...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The structure of the second embodiment of the present invention is as Figure 9 As shown, the 0.5 μm ~ 14 μm co-divided full-spectrum ZnS cross-reticle target 26 includes: ZnS substrate 8, chromium thin film layer 33, four-quadrant detector 22 and star point hole 9, wherein the chromium thin film layer 33 is plated on the ZnS On the area outside the dividing line of the substrate 8, the four-quadrant detector 22 is fabricated on the chromium thin film layer 33, and the star point hole 9 is located at the center of the ZnS substrate 8.
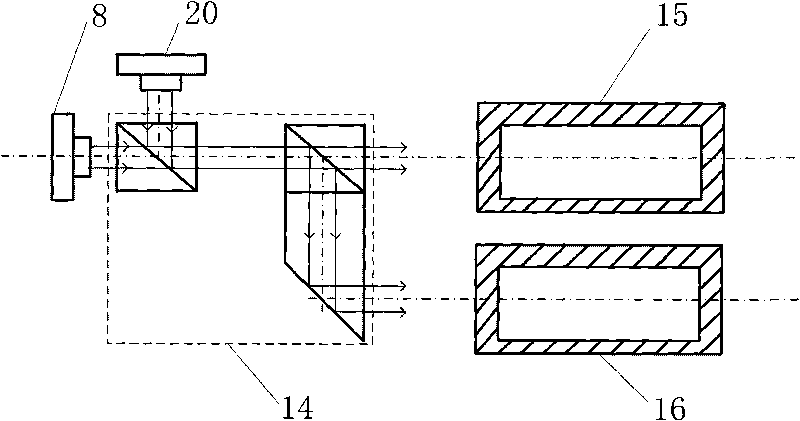
[0053] Measure the parallelism of visible light axis, infrared light axis, laser emitting axis and laser receiving axis: take the cross reticle 34 of the ZnS cross reticle target 26 as the alignment target, when the center of the imaging spot coincides with the center of the observation screen, it proves that the visible light system 16 is parallel to the optical axis of the infrared system 15 . A star point hole 9 is formed in the cent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com