Method for reducing CPU power consumption in embedded system
A technology of an embedded system and an implementation method, which is applied in the field of embedded system power consumption control and embedded system, and can solve the problems of high average power consumption of the system, high CPU power consumption, and current consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] In order to understand the technical content of the present invention more clearly, the following examples are given in detail.
[0035] First define the three states that the CPU is in during system operation, running state, stop state, and sleep state.
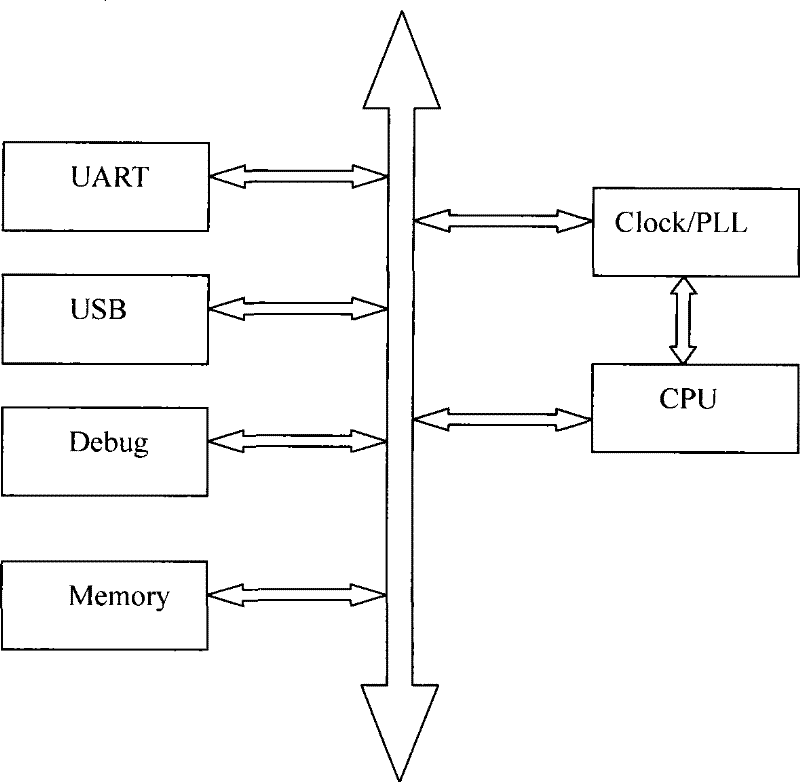
[0036] (1) Running state - indicates that the CPU is currently powered and can execute instructions normally. Of course, at this time, there must be a stable Clock provided to the CPU. Compared with the other two states, the CPU consumes the most power at this time.
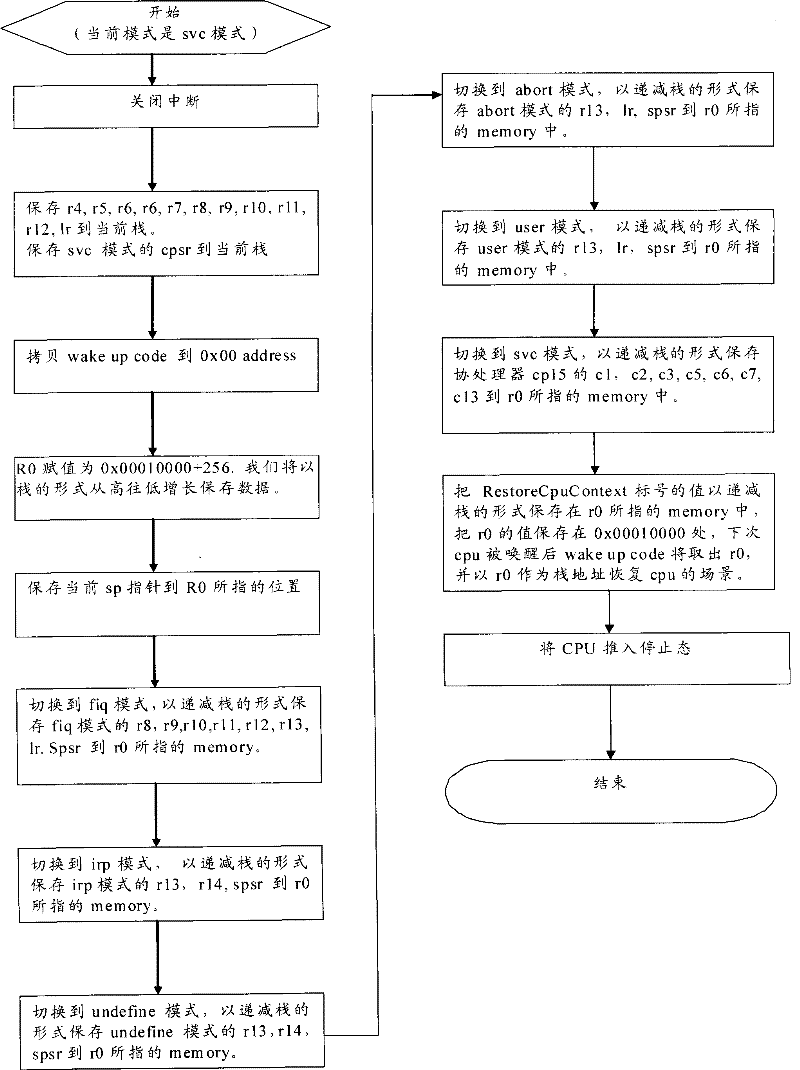
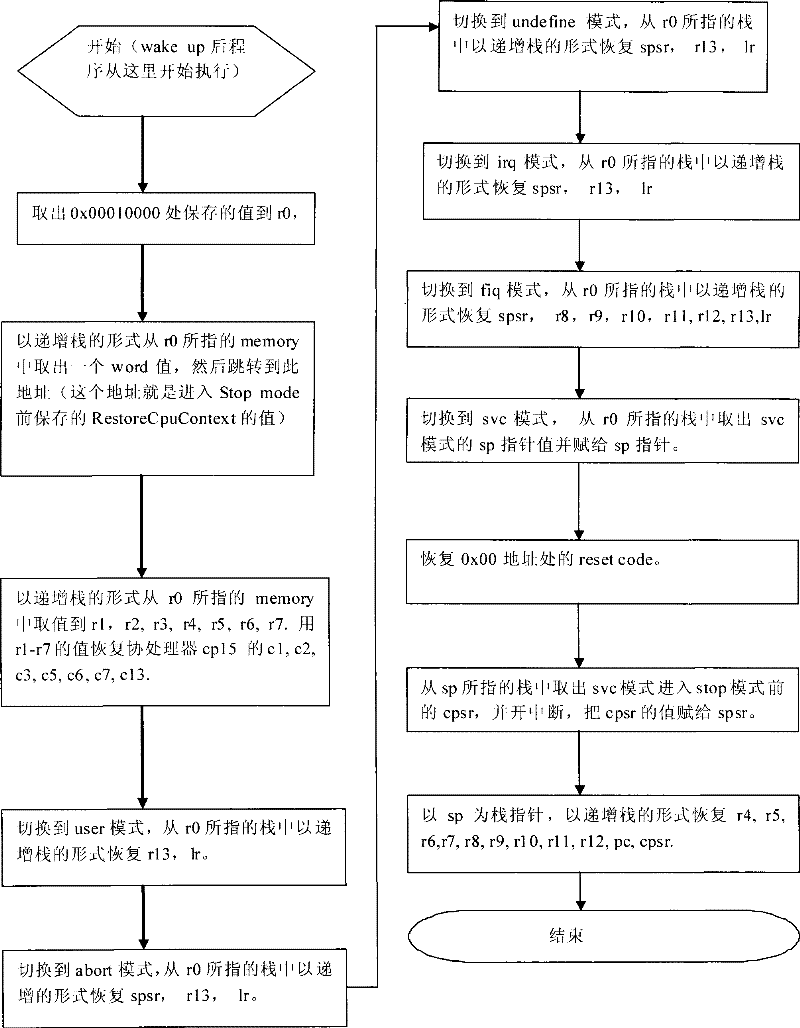
[0037] (2) Stopped state - the CPU is completely powered off, there is neither Clock nor power supply. Compared with the other two states, the CPU power consumption is the smallest at this time. At this time, all the scenes before the CPU power off are lost. After restarting, you need to reset the previous state. The scene is restored.
[0038] (3) Sleep state - SOC is still supplying power to CPU, but not sending Clock to CPU. The CPU power consumptio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com