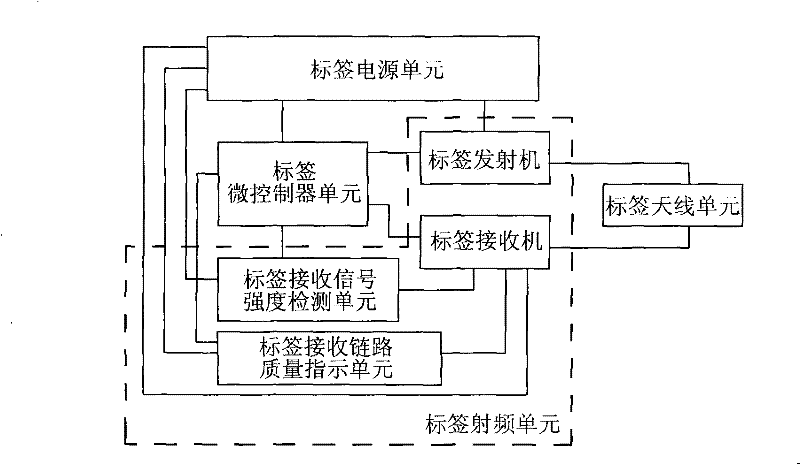
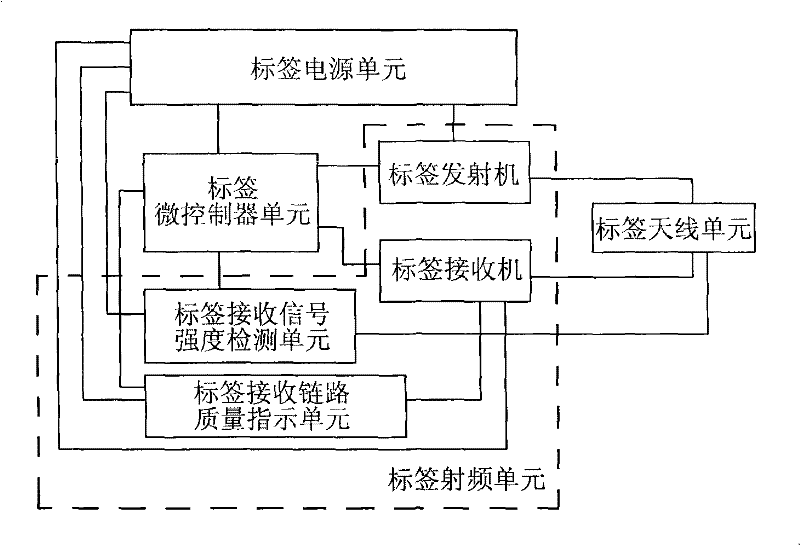
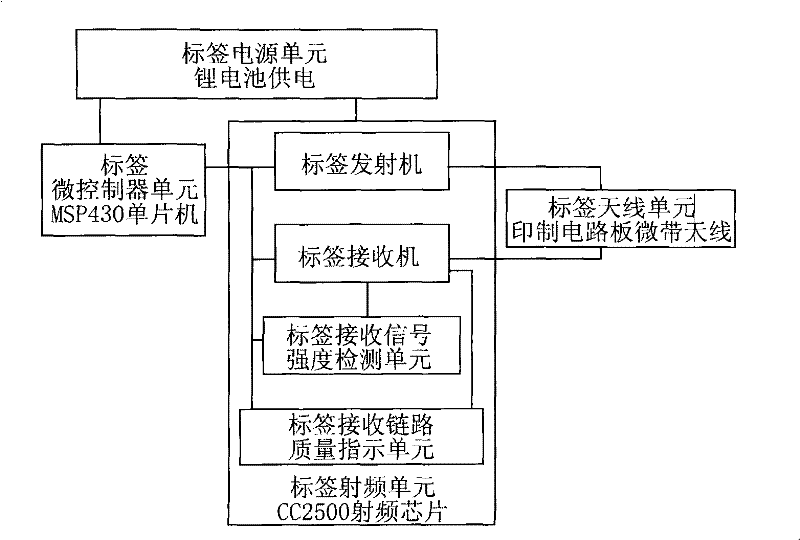
The current
radio frequency identification technology usually has three schemes. The first scheme is passive
radio frequency identification (passive RFID). In this scheme, the radio frequency identification tag is passive and does not contain a battery itself. When it is outside, the radio frequency tag is in a passive state. When it is within the reading and writing range of the reader, the radio frequency tag extracts the power required for its work from the
radio frequency energy emitted by the reader. The
data transmission from the radio frequency tag to the reader It is necessary to use the carrier wave emitted by the reader, and the reflection technology of load modulation is generally used to modulate the data of the radio frequency tag onto the carrier wave emitted by the reader and reflect it back to the reader. The
disadvantage is that the communication distance is relatively short, and passive radio frequency identification can achieve The maximum communication distance is usually less than 5 meters
The second scheme is semi-passive radio frequency identification (semi-passive RFID). In this scheme, the radio frequency tag is semi-passive, it contains a battery, and the radio frequency tag does not need to extract the energy required for its work from the
radio frequency energy emitted by the reader. However, the
data transmission from the RF tag to the reader still needs the carrier wave emitted by the reader. The semi-passive RF tag still uses the load-modulated reflection technology to modulate the RF tag data to the reader just like the passive RF tag. The transmitted carrier wave is reflected back to the reader. Compared with the first solution, the maximum communication distance that the second solution can work has been improved, usually up to 10 meters to 15 meters, but it is still difficult to meet the requirements of 20 meters to 50 meters. Requirements for communication distance of meters or more
The third solution is active radio frequency identification (active RFID). In this solution, the radio frequency tag is active and contains a battery. The radio frequency tag does not need to extract the power required for its work from the
radio frequency energy emitted by the reader. The
data transmission from the tag to the reader does not need the carrier wave transmitted by the reader. The active radio frequency tag can generate the carrier wave and modulate the tag data to the carrier wave, and then transmit it to the reader through the
transmitter. The
transmitter is an active
transmitter, so the transmitter can work at a large transmission power, and usually can reach a communication distance of 20 meters to 50 meters or more, which can fully meet the requirements of long-distance communication, but its
disadvantage is that it needs battery power. High
power consumption and short service life
In order to solve the problem of large power consumption of active radio frequency tags, one method in the prior art is to make active radio frequency tags work in a
sleep state at ordinary times, and the active radio frequency tags receive the
radio frequency signal emitted by the reader and convert it into a DC
signal To judge whether to enter the coverage area of the reader and wake up the radio frequency tag to enter the working state and start transmitting the tag ID information. This is mentioned in the invention patent with the application number 200710119625.x. The
disadvantage of this wake-up method is that there is an external radio frequency interference
signal Caused by false wake-up, if there is always an interference
signal in the industrial, scientific and medical frequency band (ISM: Industrial, Scientific and Medical frequency band), the radio frequency tag will judge that it is always in the coverage area of the reader and will always be in the state of false transmission, resulting in The power consumption is very large, and the battery of the tag will be exhausted quickly. In addition, the RFID tag must detect a large enough DC signal to be woken up, which requires that the RFID tag must receive a large enough RF signal from the reader. The maximum transmission signal of the reader is limited by international standards. For example, in the UHF 902MHz to 928MHz frequency band, the maximum transmission power of the reader is 4 watts, which further limits the maximum read and write distance of active radio frequency tags. less than 20 meters
Another method in the existing technology is to let the active radio frequency tag work in the periodic transmission or reception state, and the active radio frequency tag wakes up from the
sleep state to transmit or receive once at a certain
periodic interval and check whether it has received the read or write The response signal returned by the reader, the RF tag judges whether it has entered the coverage area of the reader according to whether it has received the response signal from the reader. The working cycle will cause active radio frequency tags to frequently check whether they enter the coverage area of the reader, resulting in too much power consumption, and the radio frequency tags have to use high-capacity batteries to achieve several years or longer use time
If the radio frequency tag adopts a very long working cycle, the average power consumption will become lower, but when the radio frequency tag does not receive a response signal from the reader in the previous cycle, the radio frequency tag must wait for one cycle before it can perform the next check and work The longer the period, the longer the
waiting time for the RFID tag to perform the next inspection, causing the reader to read and write the RFID tag
too slowly, if the RFID tag moves out of the reader coverage area before starting the next inspection , the RF tag will be missed
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More