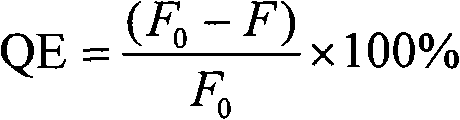Method for distinguishing fungi and bacteria
A technology for bacteria and fungi, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of complicated preparation, high cost, etc., to reduce drug resistance, simple sample processing, and fast processing. Effect
Active Publication Date: 2010-09-15
INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
View PDF4 Cites 4 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Although the existing detection methods have certain sensitivity and selectivity, the shortcomings of high cost, complicated preparation, long-term processing and special requirements for instruments limit the large-scale application of these methods
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
Embodiment 2
Embodiment 3
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
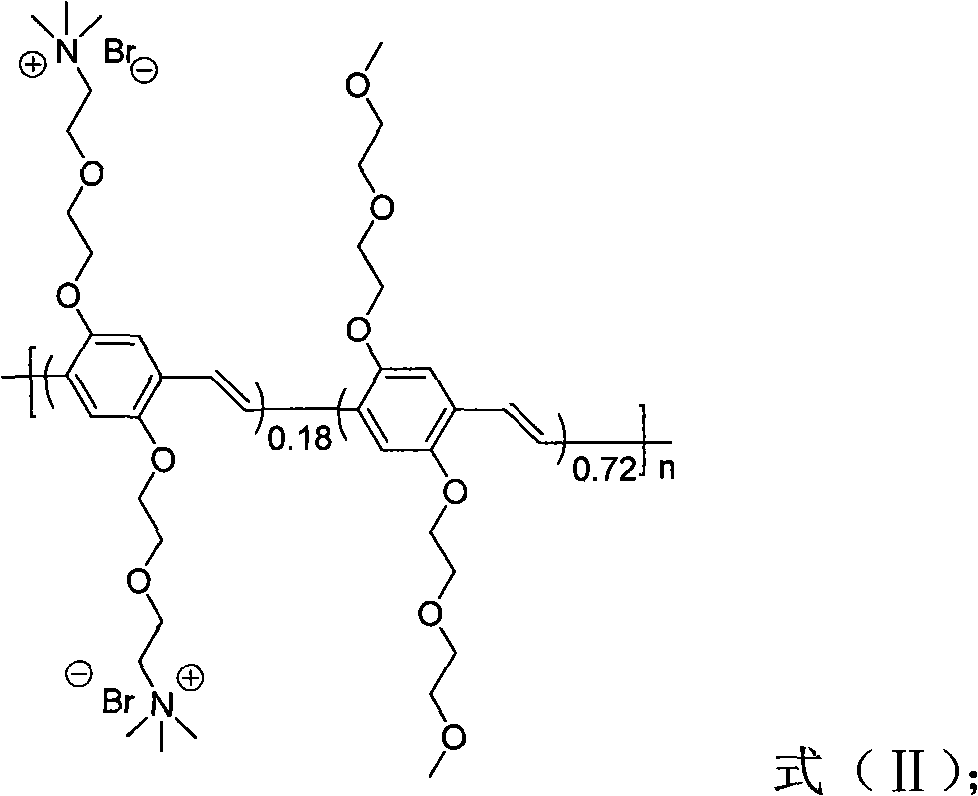
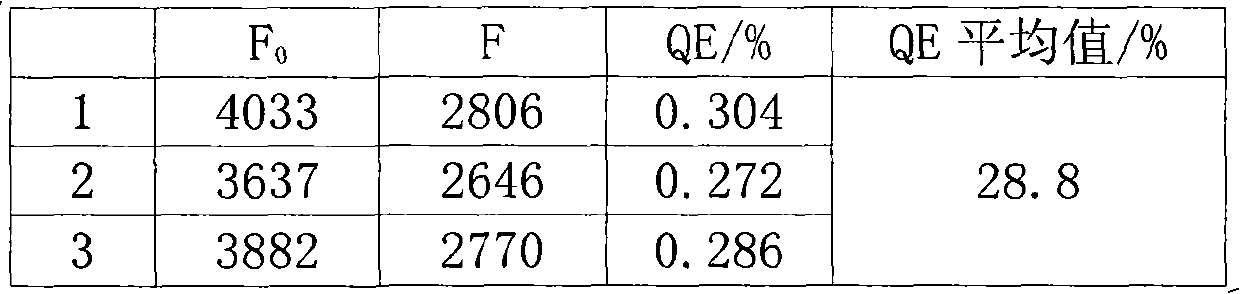
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing fungi and bacteria, which comprises the following steps of: detecting whether the bacteria to be detected can induce the compounds expressed by the formulas (I and II) to cause fluorescence resonance energy transfer; if the bacteria to be detected can induce the compounds expressed by the formulas (I and II) to cause fluorescence resonance energy transfer, determining that the bacteria to be detected is bacteria; and if the bacteria to be detected cannot induce the compounds expressed by the formulas (I and II) to cause fluorescence resonance energy transfer, determining that the bacteria to be detected is fungi. The method has the advantages of high speed, visibility and convenience and the like. The method can be used for distinguishing the types of the infectious pathogenic bacteria, instructing the administration of the doctors aiming at different patients, improving the therapeutic efficiency and reducing the occurrence of drug resistance caused by incorrect use of antibiotic. The method also has application value in aspects of food safety, environmental monitoring and the like.
Description
technical field The present invention relates to a method for differentiating fungi and bacteria. Background technique The detection of pathogenic bacteria is of great significance in the fields of medical treatment, food safety and environmental science. Since deep fungal infections are occult and have no characteristic clinical manifestations, the quick distinction between fungi and bacteria has important guiding significance for physicians to administer more targeted drugs clinically. In deep fungal infections, Candida albicans is the most common pathogen, accounting for about 40% of all types of fungi; while in blood-borne infections caused by bacteria, Escherichia coli is the most common type of bacteria, among which E.coli O157:H7 occupies a considerable proportion in various bacterial infections. At present, the traditional methods for the detection of pathogenic bacteria mainly include microbial culture methods, membrane filtration methods, and biochemical detecti...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): C08G61/02C12Q1/04G01N21/64
Inventor 王树杨琼朱春雷
Owner INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com