Automatic compensating circuit for uncooled semiconductor laser wavelength temperature-following drift
An automatic compensation and laser technology, applied to semiconductor lasers, lasers, laser components, etc., can solve the problems of small number of channels, complexity, and low total transmission rate, so as to increase the number of channels and total transmission rate, reduce complexity and cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
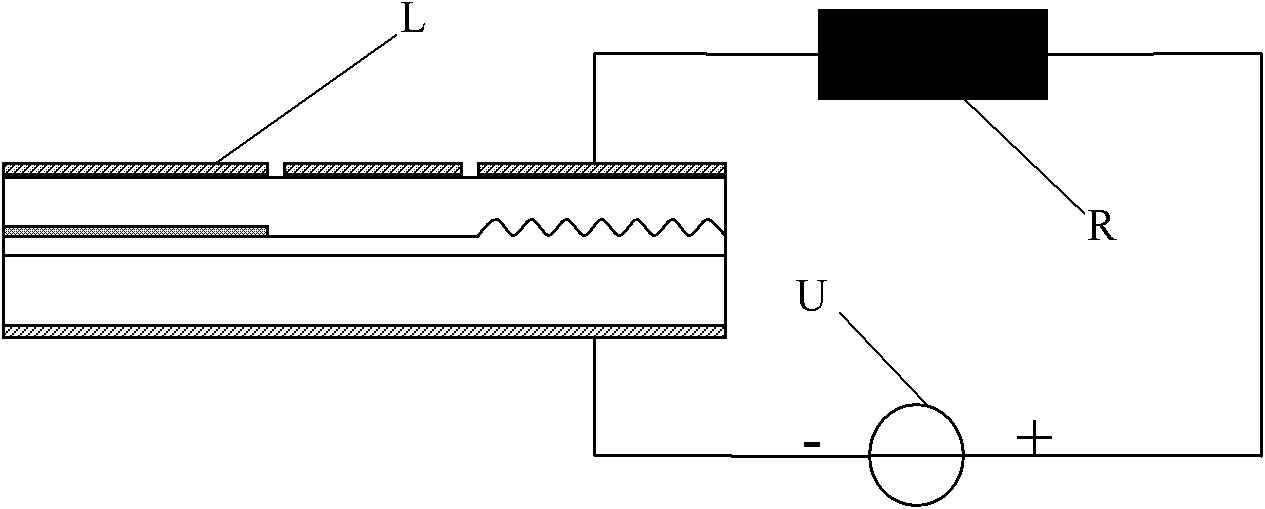
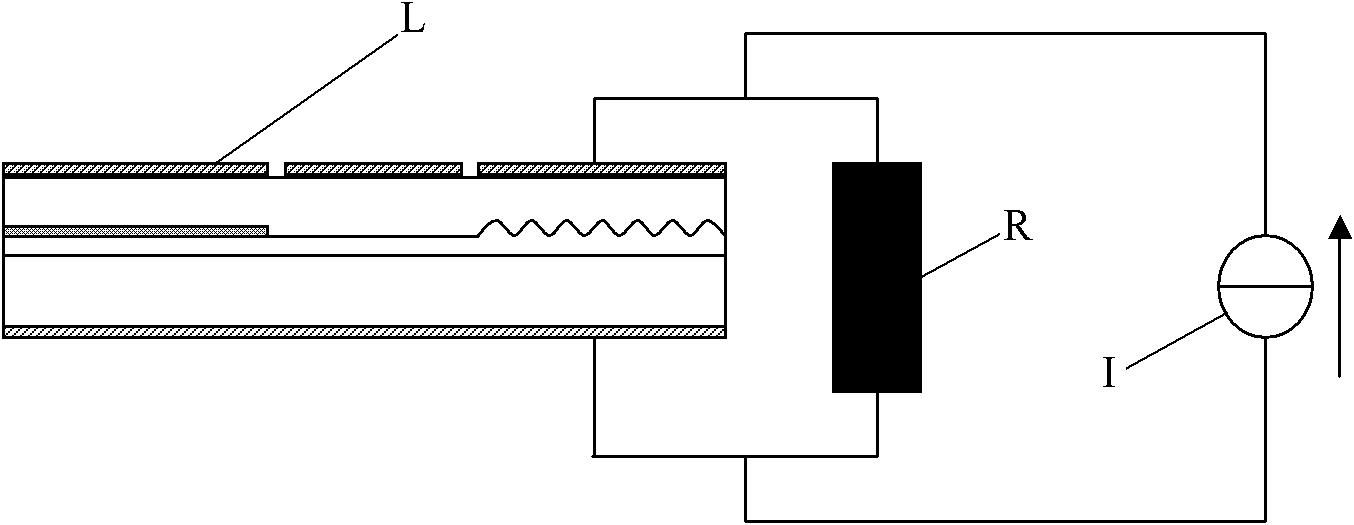
[0017] Here is a specific example of a constant voltage source driving a series circuit:
[0018] The relationship between the resistance value R of the thermistor and the temperature can be expressed as:
[0019] R=R 0 gexp(Bg(1 / (T+273)-1 / 293))+R C
[0020] In the above formula, T is the temperature in Celsius, R 0 is the resistance value of the thermistor at a temperature of 20°C. B is the material constant of the negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor, also known as the thermal index, and the B value range is generally between 2000K and 6000K. R C Indicates a fixed-value resistor that can be connected in series according to actual needs. R can be determined by experiments and calculations 0 , B and R C , to meet the temperature compensation requirements.
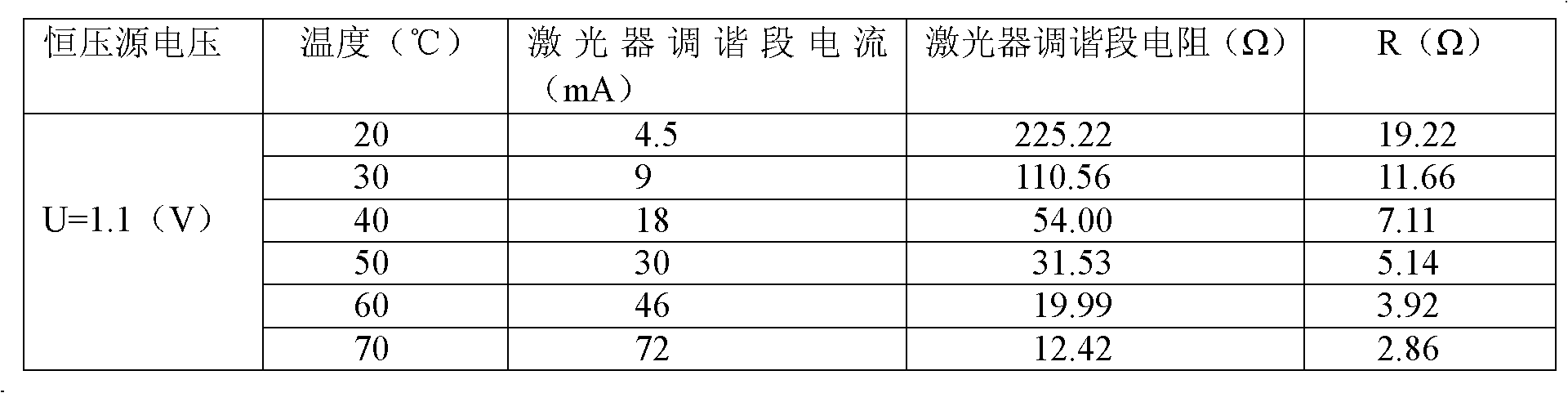
[0021] First of all, it is necessary to determine the R value corresponding to the wavelength temperature drift that can be compensated at different temperatures. The relevant data are as follows:
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com