Digital content distributed authorization method
A digital content, distributed technology, applied in the direction of program/content distribution protection, electrical digital data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of not maintaining the flexibility and high scalability of P2P file sharing systems, high computing and storage overhead, and rights. Manage out-of-control issues to improve scalability, reduce response time, and protect copyrights
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
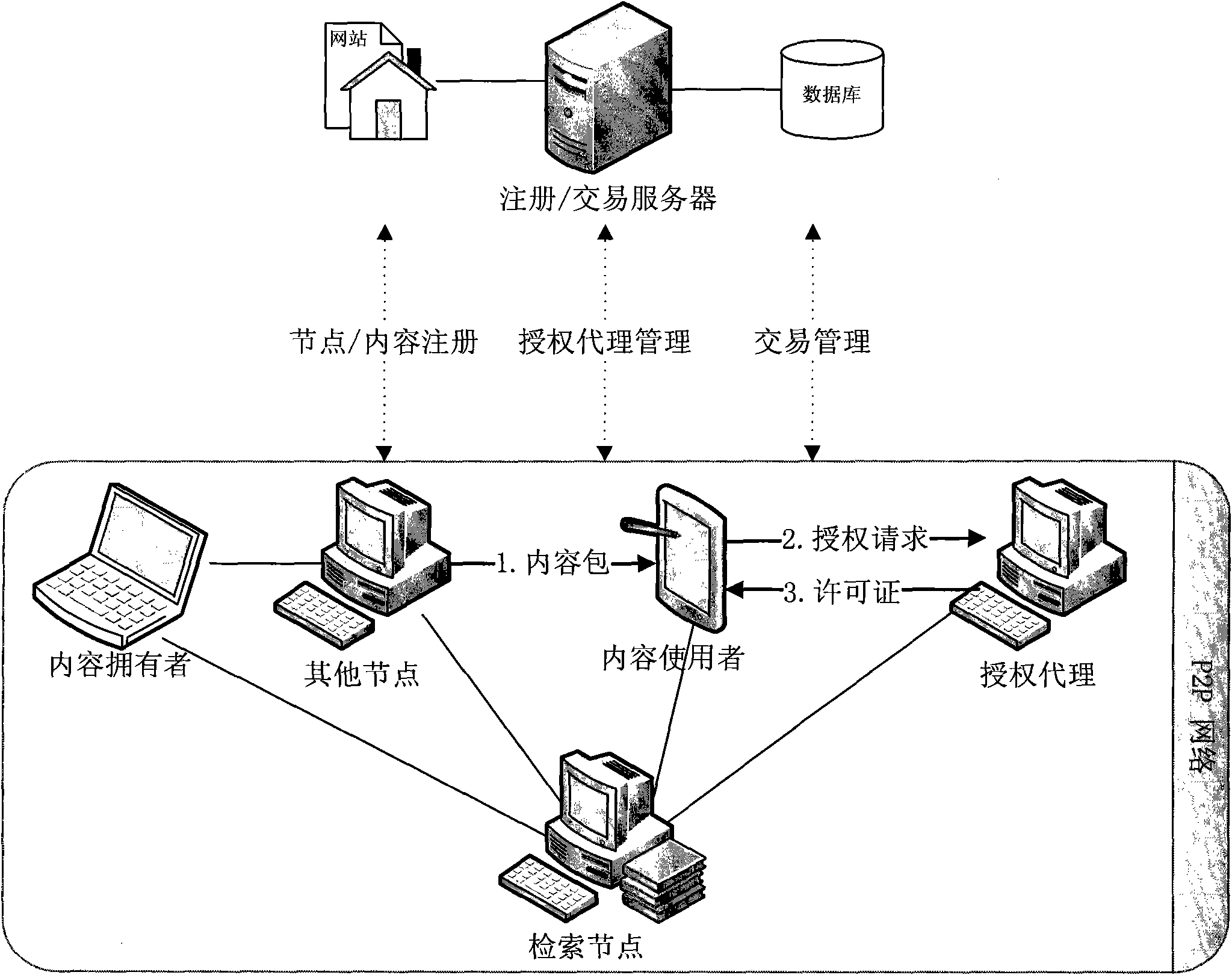
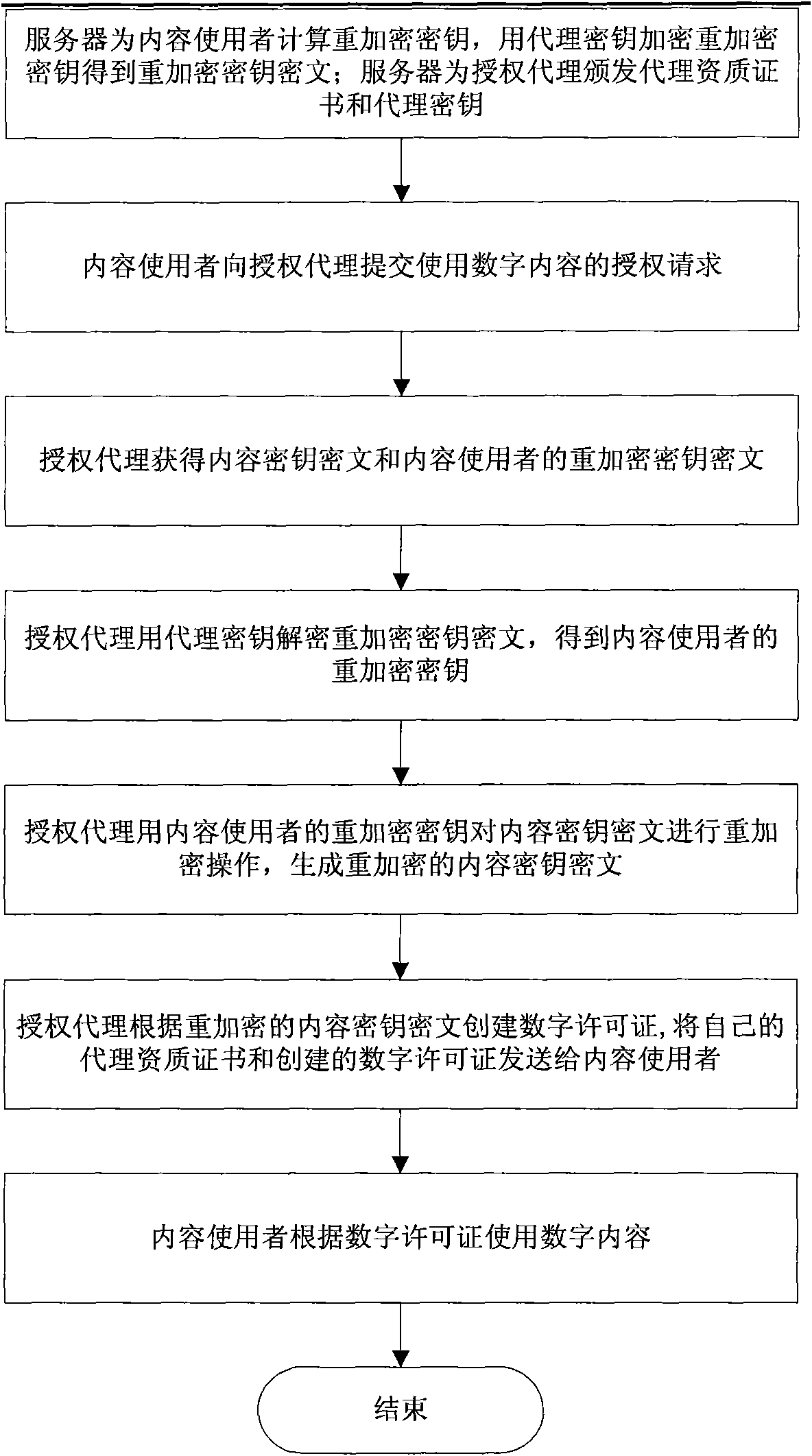
[0046] This embodiment proposes a digital content distributed authorization method for the application scenario of digital content transactions in a P2P network, which can use a variety of proxy re-encryption algorithms, which are characterized in that the re-encryption key is based on the private key of the principal (server) and the private key of the user (content consumer).
[0047] The following is an example of a proxy re-encryption algorithm based on the El Gamal algorithm proposed by the document "Proxy Cryptography Revisited" (Anca Ivan; Yevgeniy Dodis, Proc. 10th annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), 2003), to illustrate the implementation method. The re-encryption operation is recorded as RE(r, c), which means that the ciphertext c is re-encrypted with the re-encryption key r.
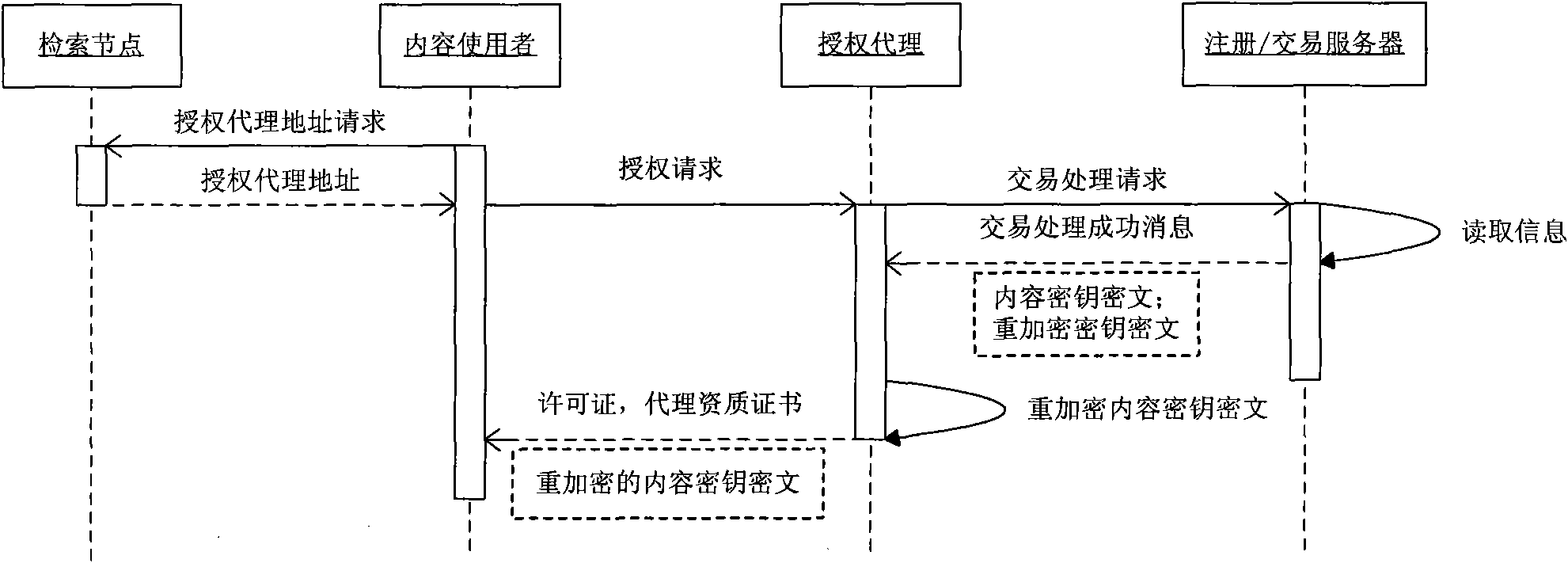
[0048] see figure 1 , the participants of this system include content owner A, content user B, authorized agent P, retrieval node X and trusted registration / trans...
no. 2 example
[0081] The above-mentioned first embodiment requires the server to know the private key of the content user, and the re-encryption key is generated according to the private key of the server and the private key of the content user. This embodiment proposes a digital content distributed authorization method for the application scenario of digital content transactions in a P2P network, which can use a variety of proxy re-encryption algorithms, which are characterized in that the re-encryption key is based on the private key of the principal (server) and the public key of the user (content consumer). By using this type of algorithm, the server does not need to know the content user's private key, and the re-encryption key is generated based on the server's private key and the content user's public key.
[0082] Below is the literature "Improved proxy re-encryption schemes with applications to secure distributed storage" (Giuseppe Ateniese; Kevin Fu; Matthew Green; Susan Hohenberg...
no. 3 example
[0114] The above-mentioned first and second embodiments require the server to read the database information during the digital content authorization process, and transmit the content key ciphertext and the re-encryption key ciphertext to the authorization agent. In order to further reduce the server's overhead in the authorization process, this embodiment proposes a digital content distributed authorization method for the application scenario of digital content transactions in a P2P network: content key ciphertext and re-encryption key ciphertext are submitted by content users When the authorization request is sent to the authorized agent, there is no need for the server to read the database after the transaction is successfully processed, and then send it to the authorized agent.
[0115] In addition, similar to the first and second embodiments, in order to prevent content users from repeatedly paying for authorizations that have already been paid for when applying for authori...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com