Keratin derivatives and methods of making the same
A technology of keratin and derivatives, applied in the field of preparation and use of said soluble keratin derivatives
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
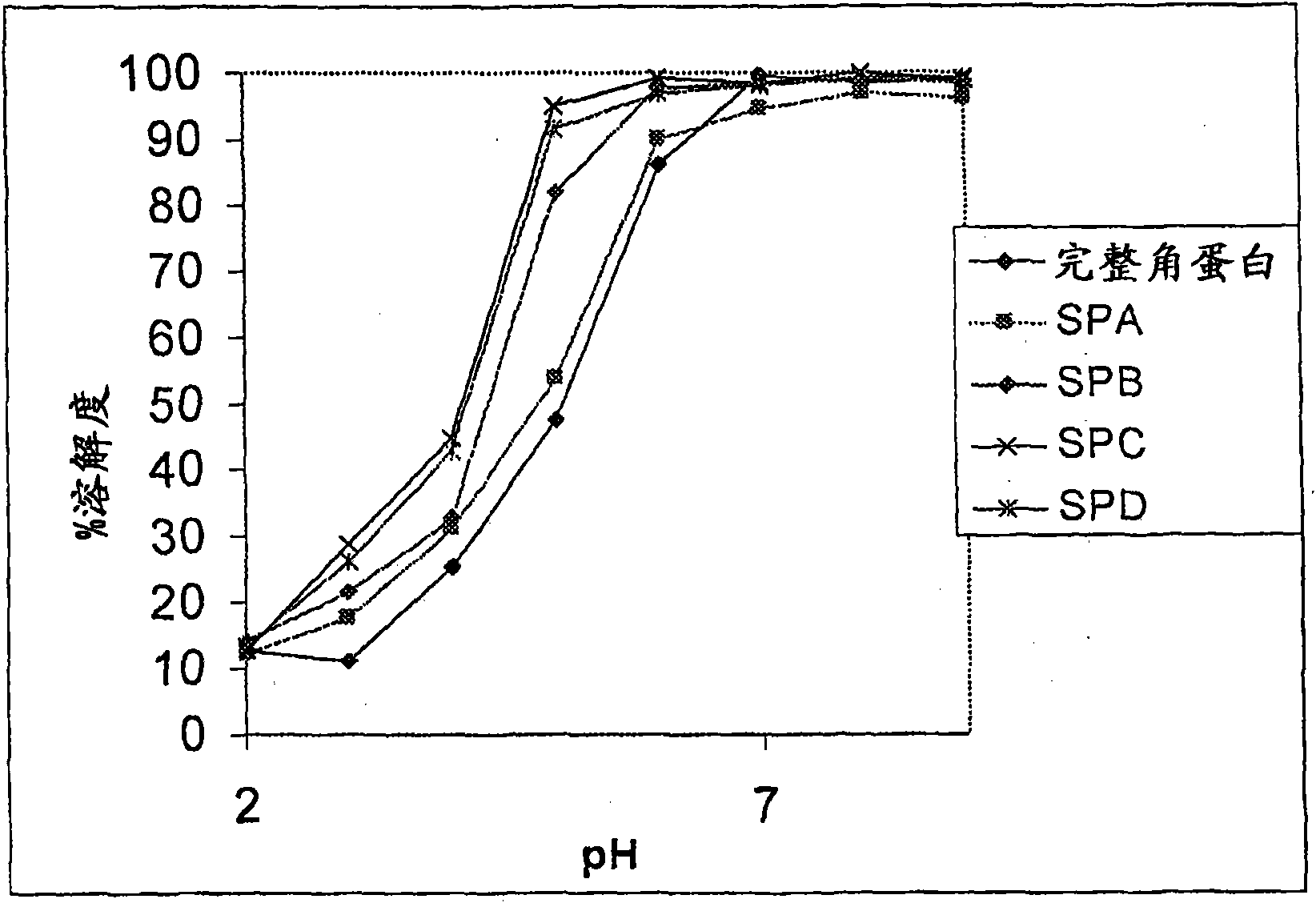
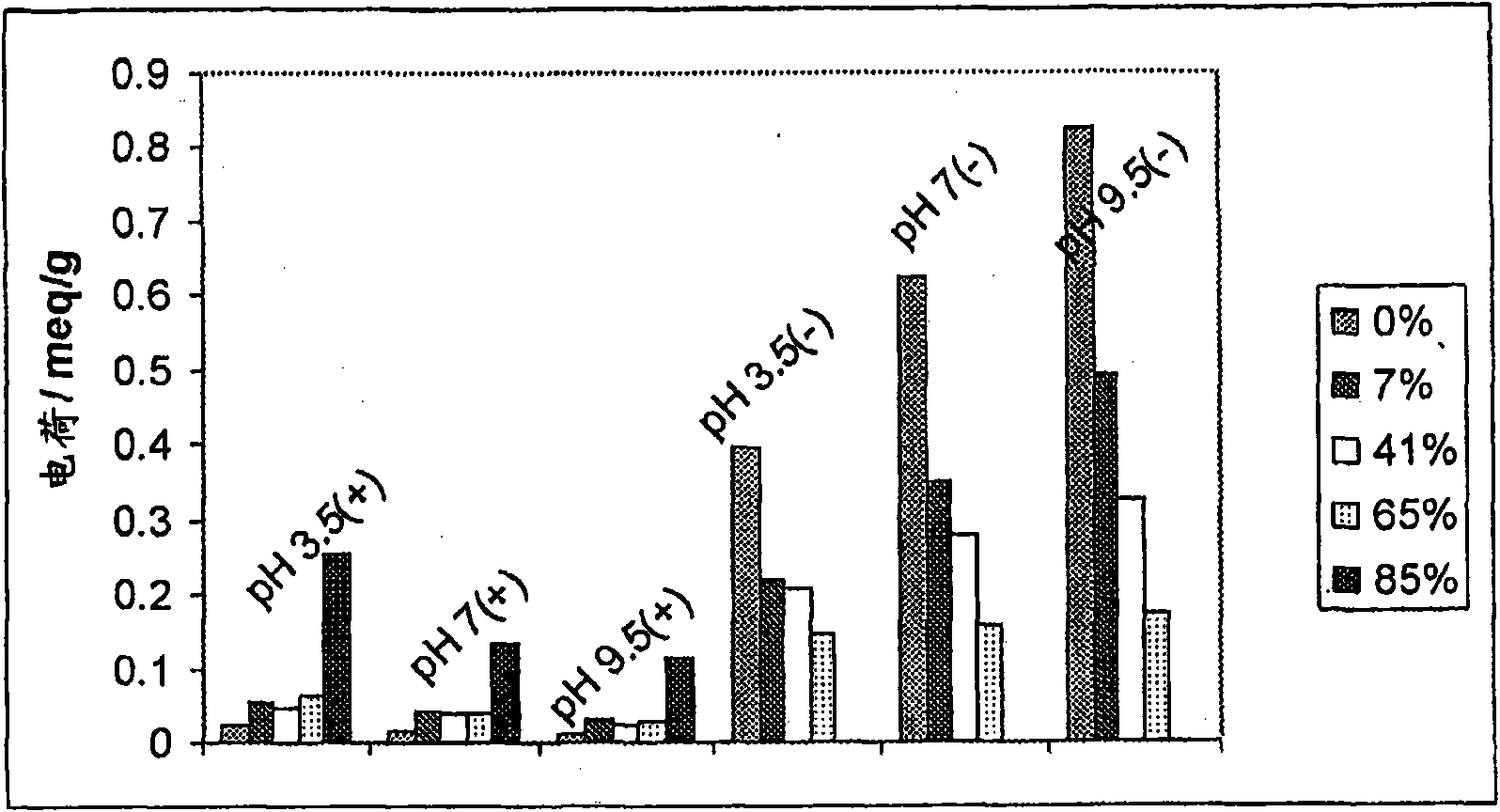
[0148] Example 1 Manufacture of succinylated keratin derivatives
[0149] This example describes studies directed at the derivatization of soluble keratin. It describes a method for succinylation of soluble keratin and properties of the resulting derivatives.
[0150] Succinylation of intact soluble keratin intermediate filament proteins was performed by adding succinic anhydride to the reaction. Succinic anhydride reacts with primary amino groups (lysine and amino terminus) and to a lesser extent with hydroxyl amino acids (serine, threonine and tyrosine) in intact soluble keratin IFP to generate carboxylic acid functionality. As should be understood, in the case of a lysine group, this means that an amino acid, which is sometimes positive, has been replaced by a negatively charged carboxyl group. This should make intact soluble keratin IFP more negative in character.
[0151] More specifically, the method is accomplished by the following steps:
[0152] (i) Cool 100 g o...
Embodiment 2
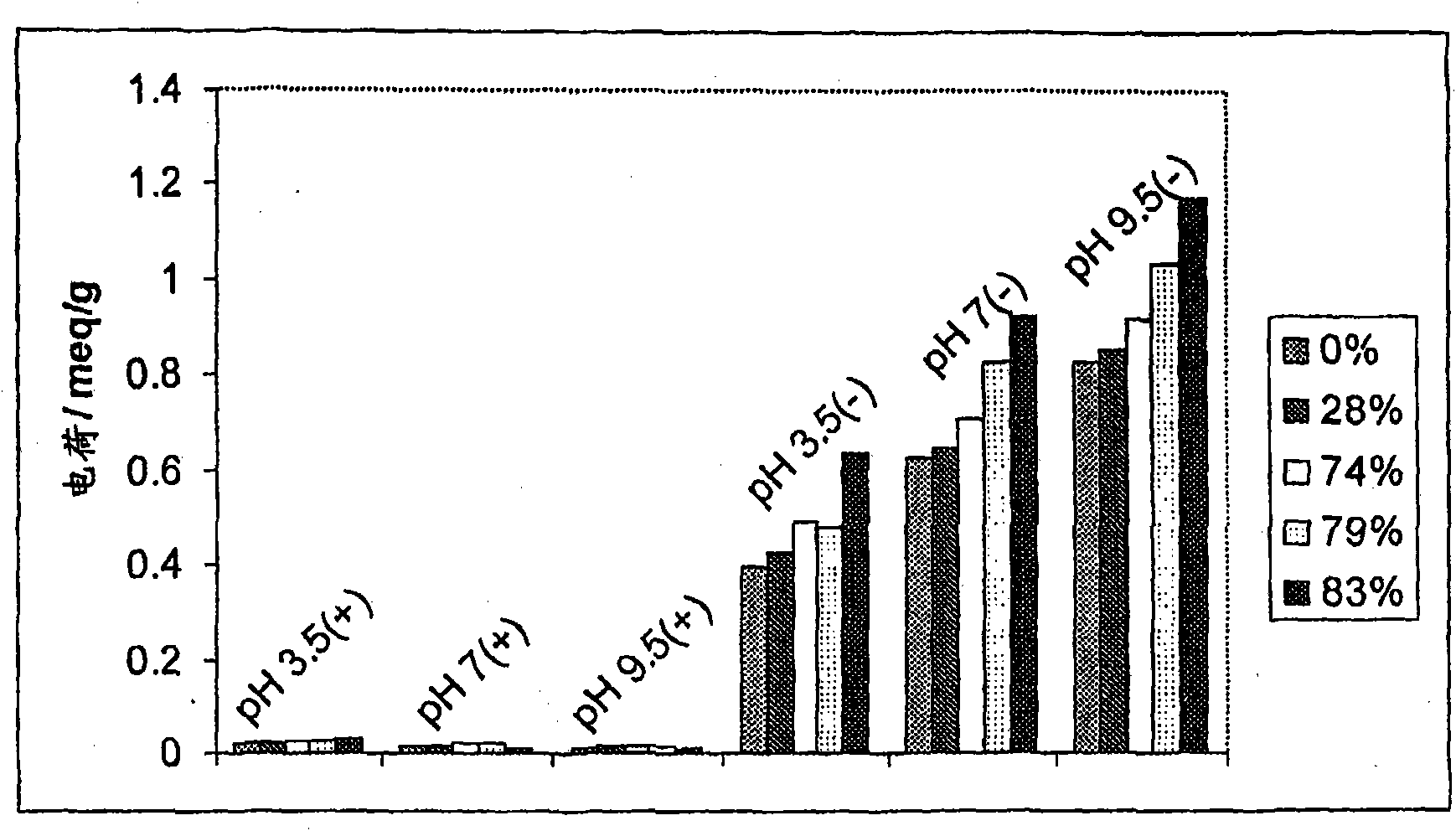
[0174] Example 2 - Manufacture of quaternized keratin derivatives
[0175] This example describes studies directed at the derivatization of soluble keratin. It describes a method for the quaternization of soluble keratin.
[0176] Quaternization of soluble keratin is performed by adding positively charged quaternary ammonium salts to the lysine groups and terminal amine groups in the soluble keratin. The reaction was found to be reproducible each time the experiment was performed under the same conditions with compounds having the same properties. More specifically, quaternization of soluble keratin can be performed using the following methods:
[0177] (i) Add varying amounts (0.625ml (0.5g) in QuatA, 1.25ml (1 g), 2.5 ml (2 g) in QuatC, 5 ml (4 g) in Quat D) Glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride was added.
[0178] (ii) The bottle was sealed and shaken well before placing in a pre-heated shaking incubator at 40°C for 18 hours.
[0179](iii) After 18 hours, samples were rem...
Embodiment 3
[0198] Example 3 - Fatty Acid Substitution
[0199] Alternative approaches for the chemical modification of soluble keratin are described.
[0200] In the first method, fatty acid chlorides are used to form the following schematic Figure 4 Fatty acid keratin derivatives (FAP) shown in:
[0201]
[0202] Reaction 4
[0203] where R = keratin or peptide substrate, X = NH or O, [] n = Repeated fatty acid chains.
[0204] More specifically, the reaction of intact soluble keratin intermediate filament protein (IFP) with long fatty acid chains to form the first sample (FAP1) was performed using the following method:
[0205] (i) at 35°C in N 2 Add 0.41 g of oxalyl chloride dropwise over 10 min to anhydrous CH 2 CI 2 0.5 g lauric acid in (10 ml);
[0206] (ii) Stir the reaction mixture at 35°C for 2 hours, then remove the solvent under vacuum;
[0207] (iii) Dissolving the obtained solid in 10ml of acetone and gradually adding it dropwise to 25ml or 250ml of 5% keratin s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com