Fastener installing tool
A technology for installing tools and fasteners, applied in the direction of threaded fasteners, connecting components, screws, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and high cost, expensive and difficult realization of quenching and tempering, and reduce the molded load , Elimination of complexity, the effect of high-intensity capabilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0076] The purpose of the first experiment was to determine whether a collar manufactured to size HS5CF-R12 could be used as a headed collar to meet the Grade 8 value. The HS5CF-R12 fastener is a commercially available Grade 5 molded type fastener manufactured by Huck International, Inc. of Waco, Texas, USA.
[0077] The experiments involved testing the outside diameter (OD), hardness, swage load, tensile strength and preload of standard quenched and tempered Grade 8 collars and comparing them to Grade 5 collars such as cold heading collars. The results are expressed quantitatively in Table 1 below.
[0078] Table 1: Grade 5 Collars as Headed Collars
[0079]
[0080] As shown in Table 1, the two collars "A" and "B" have 18% lower molded loads than the current standard HS8CF-R12 collar, and both meet the Grade 5 minimum industry tensile strength and preload requirements. Experiments have revealed that the collar, such as the cold heading collar, collar "A", has two outs...
example 2
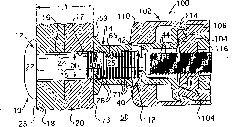
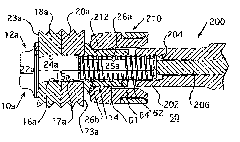
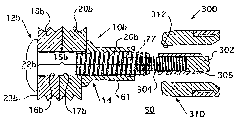
[0085] The second experiment arose out of a desire to develop an economical way to improve the life of safety tools and to reduce the cost of manufacturing Grade 8 collars. Specifically, the goal of the experiment was to determine whether a thinner walled, as-headed collar could increase snub load, reduce swage load and maintain the same tensile strength as a standard quenched and tempered collar and preload. The detent load is the load at which the collar 14 initially engages the pin lock slots 26, 26a, 26b, 26c, 26d. After this moment, plate (eg, workpieces 18, 20; 18a, 20a; 18b, 20b; 18c, 20c) clearance pullout is restricted because the collar 14 is seized on the pins 12, 12a, 12b, 12c, 12d. If the gap is maintained after the snub, the clamping force is reduced because instead of stretching the pins 12, 12a, 12b, 12c, 12d, the collar elongates to make the gap disappear.
[0086] HSCF-R20 made from the same processing sequence and raw material (50KSI tensile strength) were...
example 3
[0103] In addition to the results of the first two experiments, the third experiment also tested the effect of increasing the stiffness of the collar while reducing the wall thickness of the collar in an attempt to find the best balance of high strength and low mold load. Gap pullout results in less than optimal clamping force at the joint. However, as demonstrated in Example 2, increasing the collar stiffness also increased the mold force of the mounting collar. Reducing the collar wall thickness disproportionately lowers the mold force more than the stop (gap pull-out) load. Correspondingly, combining the findings of the preceding experiments, the installation is improved by balancing the increase in collar stiffness with a decrease in collar wall thickness to maintain the same tensile strength and preload, and increasing the stop load while reducing the molded load. Tool life, this experiment is expected to overcome known fastener design limitations. The purpose of this e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com