Method for binding pathologic protein by using conjugated polyelectrolyte
A technology of conjugated polyelectrolytes and proteins, which is applied in the field of or inferior forms of proteins, conjugated polyelectrolytes as new therapeutic agents, can solve the problems of lack of reliable methods for capturing misfolded proteins, and no effective treatment methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0104] Example 1. Capture and detection of PrP-amyloid in solution using conjugated polyelectrolytes protein. Surface Inspection Using Fluorescence Microscopy
[0105] Tubes containing PrP and PrP-amyloid samples, the latter being PrP Sc - or PrP res -like protein. PrP-amyloid was prepared by dialyzing 1 mg / ml recHuPrP90-231 in 3M guanidinium hydrochloride against water. Another experimental protocol was the preparation of PrP-amyloid by shaking in test tubes under conditions of high salt concentration. To this solution containing PrP and PrP-amyloid was added conjugated polyelectrolyte PTAA (10 μg / ml), allowing PTAA to capture, bind and stain PrP-amyloid. The PTAA / PrP-amyloid former is then left to settle to the bottom of the test tube, whereupon it can be easily separated from the sample and, if necessary, detected. Other methods of collecting PTAA / PrP-amyloid are, but not limited to, filtration, centrifugation, capture on hydrophobic surfaces, capture on surfaces wit...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Example 2: Filtration, capture
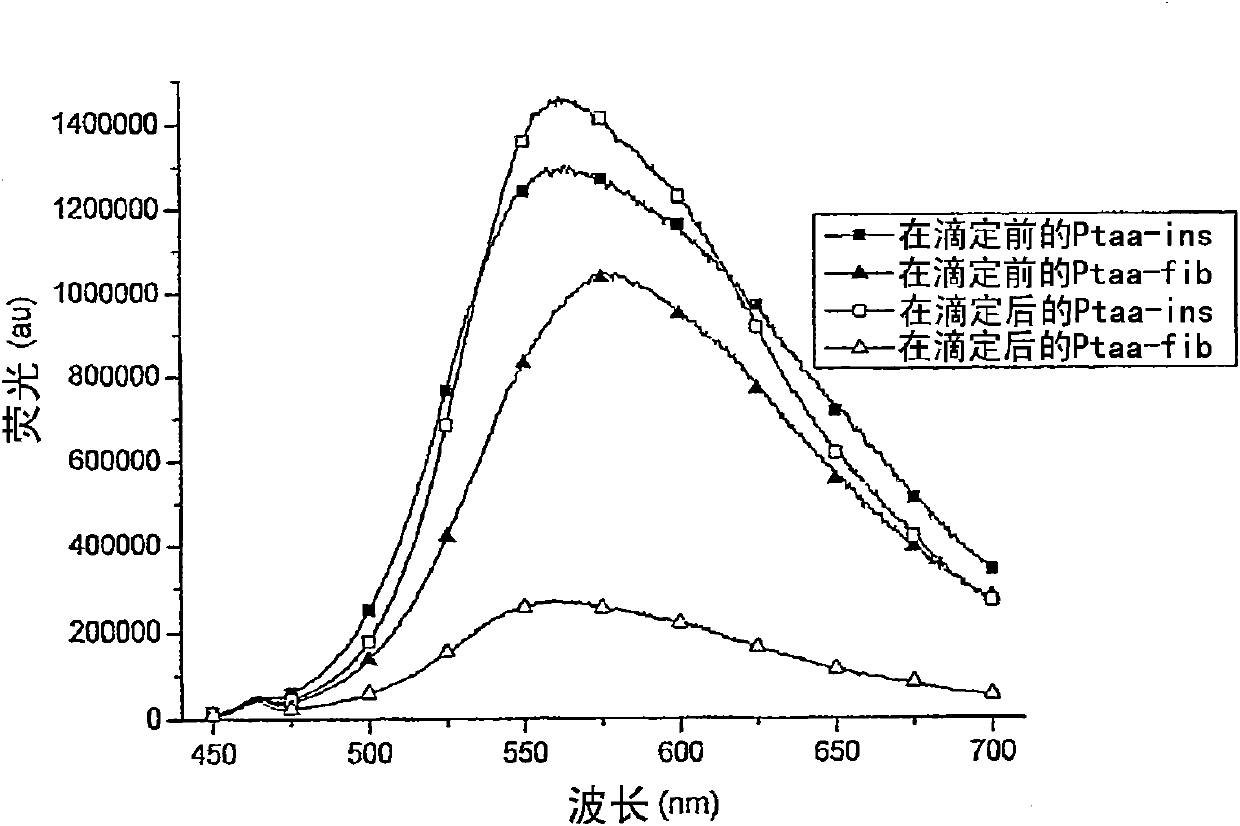
[0107] Filtration of the polymer-insulin sample was performed in order to separate native and fibrillar insulin and thereby purify the fibril insulin. The samples tested were native insulin and fibril insulin, with or without PTAA. Initially, the concentration of PTAA was 0.5 mg / ml, the concentration of insulin was 2 mg / ml, and the samples contained 10 μl of PTAA + 25 μl of insulin in 1 ml of 20 mM pH 8 phosphate buffer. For all samples, fluorescence measurements were taken before and after filtration, and the filters were turned on for visual inspection. The filter used was 0.22 μm Millex-gu, and 1 ml of each sample was filtered through the filter.
[0108] Fluorescence spectra of PTAA-native insulin (PTAA-ins) and PTAA-fibril insulin (PTAA-fib) before and after filtration through a 0.22 μm filter are shown in Figure 9 middle. Before filtering, the spectra looked as expected. After filtration, it was apparent that samples contai...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Capture and detection of insulin-amyloid in solution using conjugated polyelectrolytes. profit Solution detection with fluorescence measurement
[0114] In test tubes, samples containing native insulin containing 0, 1, 5, 50 and 100% fibrils were mixed with PTAA (0.05 mg / ml, 10 μl) and 965 μl of 20 mM phosphate buffer pH 7.0 (2 mg / ml, 25 μl). Fibrillar insulin was produced by incubating native insulin at pH 2 for 8 hours at 65°C. The samples were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 minutes, the supernatant was removed, new buffer was added, and the process was repeated once. The PTAA binds fibril insulin and settles to the bottom of the tube under centrifugation. Samples were then measured using a fluorescent microplate reader. Reference samples of PTAA-native insulin and PTAA-fibril insulin without centrifugation were also measured. display the results in Figure 12 middle.
[0115] The PTAA-fibril aggregates settled to the bottom of the tube and they could be e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com