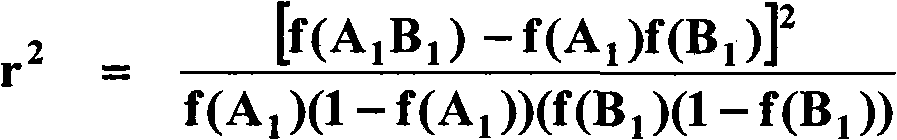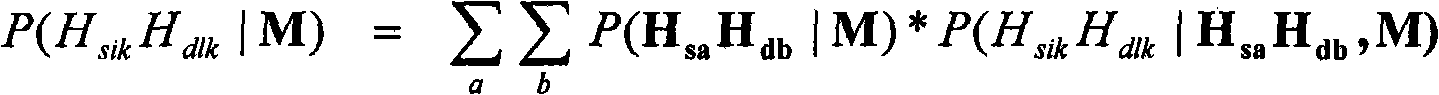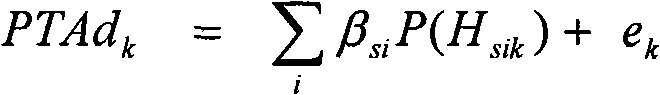Methods of using genetic markers and related epistatic interactions
A marker, allelic technology for the application of genes and genetic markers in the field of genetic markers used to improve fitness and/or productivity traits in dairy cows
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] Example 1: Determine the association between genetic markers and phenotypic traits
[0089] The simultaneous discovery and fine mapping of genetic-based quantitative traits (quantitative trait locus: QTL) based on the genome-wide range requires genetic markers that densely cover the entire genome. As described in this example, from microsatellite (microsatellite) markers and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers with previously estimated positions in the bovine genome, as well as from human sequences based on the bovine genome The homology and the SNP markers of the inferred positions of the human / bovine comparative map construct a marker map with dense coverage of the whole genome. A new linkage mapping software package was developed as an extension of the CRIMAP software (Green et al., Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, 1990) to enable more effective, densely distributed markers on the genome range of well-defined pedigree livestock (Liu and Gro...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2: Analysis of interaction effects between multiple genetic markers
[0112] SNP clustering from candidate genes : Mainly due to the smaller effective population size and stronger selection, alleles from closely connected SNPs are usually related in animal populations (for example, Farnir et al., 2000; Du et al., 2007). Obviously, if two SNPs are in a perfect LD, their association with the trait of interest and their interaction with other SNPs on the trait of interest will be similar, which will not provide much additional statistical evidence. Therefore, it is useful to cluster SNPs from the same candidate gene when genotyping multiple SNPs at a single gene.
[0113] Trait phenotypic preconditioning : This research focuses on traditional milk production traits, including milk production ("MILK") (lbs), fat production ("FAT") (lbs), fat percentage ("FATPCT") (%), production life ("PL") ) (Month), somatic cell score ("SCS") (Log), offspring pregnancy rate ("DPR") ...
Embodiment 3
[0125] Example 3: Use single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) to improve offspring traits
[0126] In order to improve the average genetic value of the population for the selected trait, two or more markers that are significantly related to the trait can be used when selecting breeding animals. In the case of each found locus, the use of animals possessing marker alleles (or haplotypes of multiple marker alleles) in the population range LD with favorable QTL alleles will increase the number of breeding The breeding value of the animal increases the frequency of the QTL allele in the population over time and thereby increases the population’s average genetic value for the trait. This increased genetic value can be spread to commercial populations to fully realize the value.
[0127] For example, progeny testing protocols can greatly improve the rate of genetic progress or the success rate of graduation by using markers to screen juvenile bulls. Usually, the offspring testing program ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com