Distribution method of PCIs (Physical Cell Identities) in long-term evolution network
A technology of physical cell identification and long-term evolution network, which is applied in network planning, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., and can solve the problems of not giving division and allocation of PCI, PCI may not be enough, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
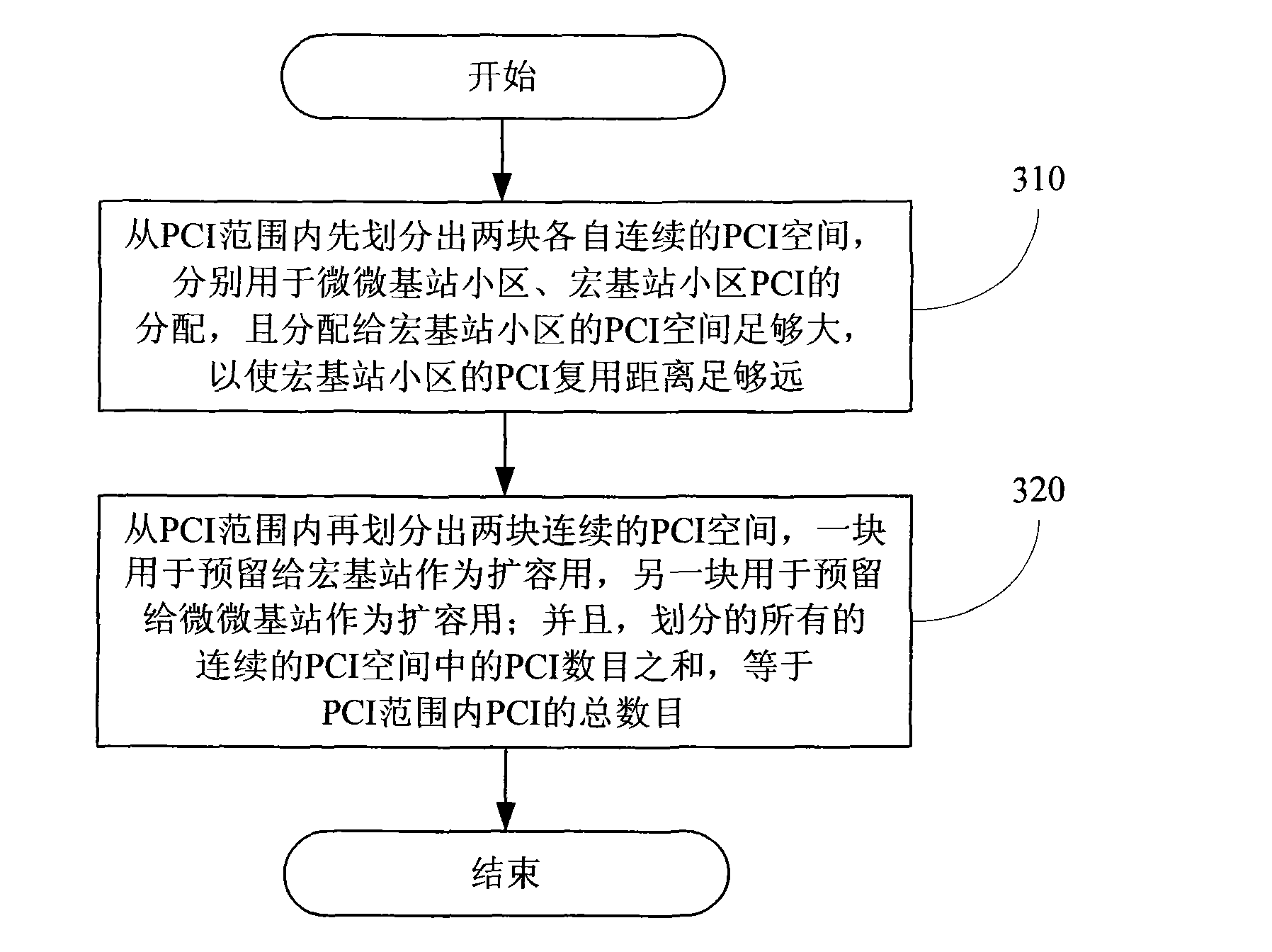
[0040] For general urban coverage scenarios, that is, there are certain buildings but the density is not particularly high, the PCI space allocation method is as follows:
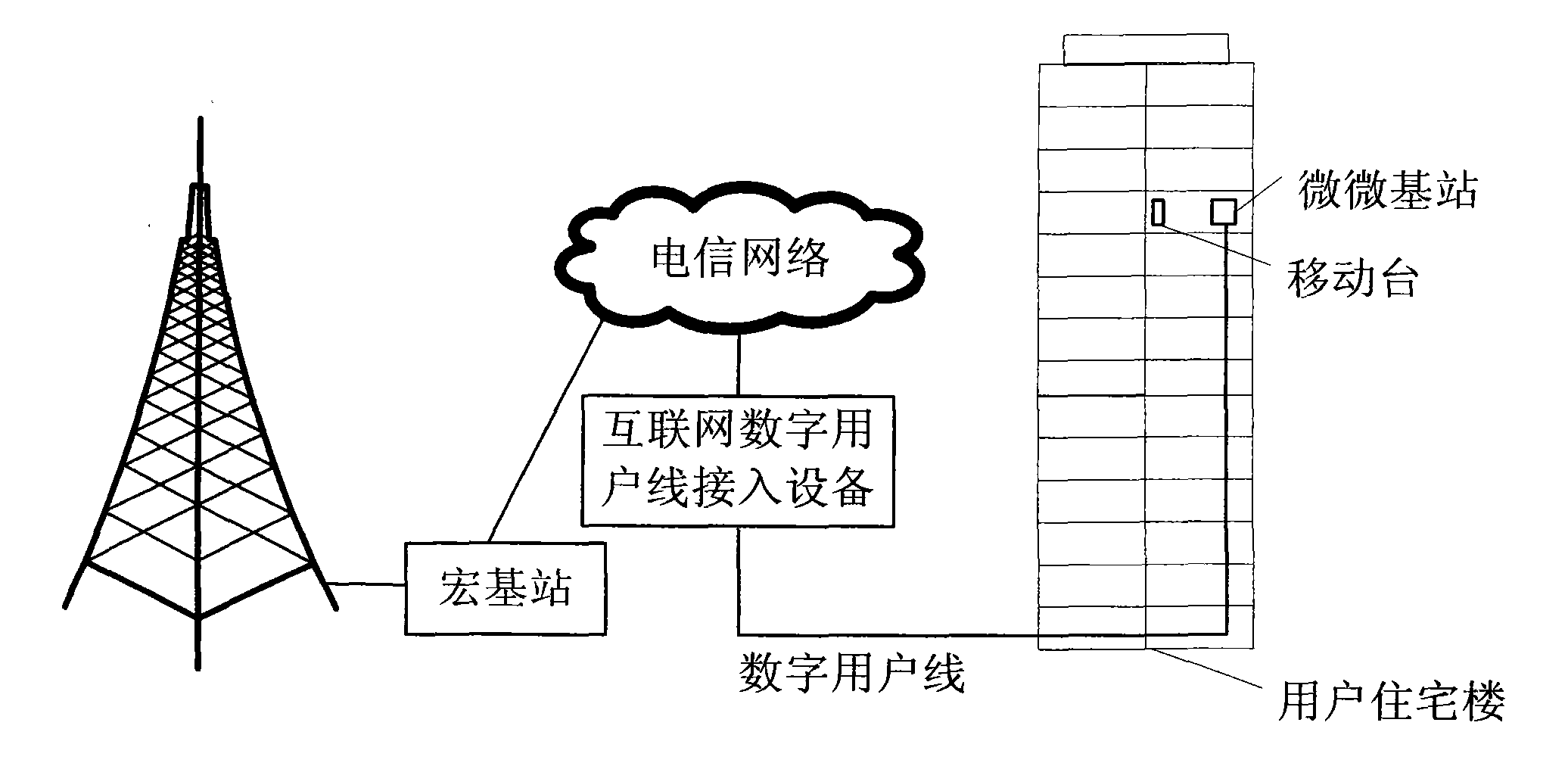
[0041] Step 1: Allocate a continuous piece of PCI space for the pico base station cell, ranging from 1 to 50, of which there are 50 PCI values;
[0042] In this way, the requirement that the PCI collision probability is very low in the picocell coverage area can be met, and further indicators such as the call drop rate of the mobile station in the network can be optimized.
[0043] Step 2: Allocate a large enough continuous PCI space for the macro cell cluster base station cell, ranging from 51 to 321, where the number of PCIs is 271;
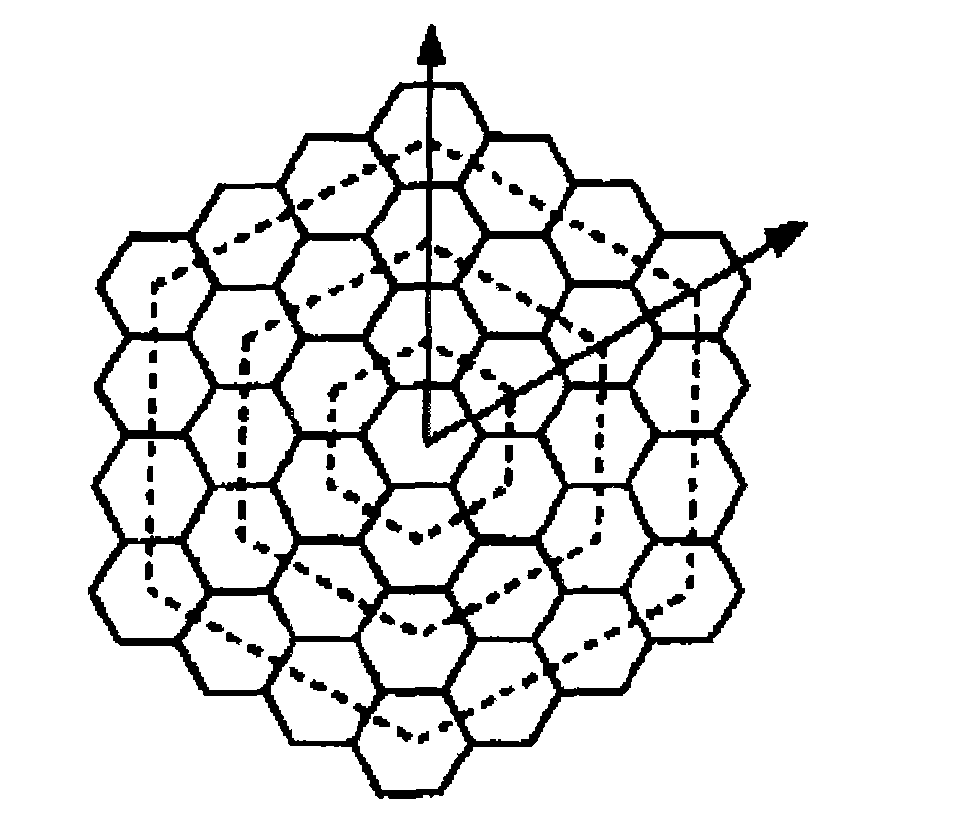
[0044] Take the radius of 500 meters in the urban area as a typical value, and the radius of 2000 meters in the suburban area as a typical value, and set n=10. After taking this step, the typical multiplexing distance of PCI in urban areas is about 10×500×2=10,000 meters, w...
Embodiment 2
[0049] For suburban and rural coverage scenarios, i.e. low building density, PCI space is allocated as follows:
[0050] Step 1: Allocate a continuous PCI space for the pico base station, ranging from 1 to 30, of which there are 30 PCI values;
[0051] Of course, from the perspective of Embodiments 1 and 2, for general urban or suburban and rural coverage scenarios, the PCI values assigned to pico base stations are all possible within the range of (50±m), where m=0-20, according to Specific building densities are adjusted.
[0052] Step 2: Allocate a large enough continuous PCI space for the macro cell cluster base station, the range is 31-301, and the number of PCIs is 271;
[0053] This can ensure that the multiplexing distance of the PCI of the macro cell is far enough.
[0054] Step 3: Reserve a continuous PCI space for the macro cell cluster base station, ranging from 302 to 447, and the number of PCIs in it is 146, which can be used to expand and join the macro cell;...
Embodiment 3
[0058] For a dense urban scene, that is, an area with a high density of buildings and a high density of pico base stations, the PCI space allocation method is as follows:
[0059] Step 1: Allocate a continuous PCI space for the picocell, ranging from 1 to 100, of which there are 100 values;
[0060] Of course, for high-density building coverage scenarios, the PCI values are all possible in the range of [(50±m)×2], where m=0-20, and adjusted according to the density of specific buildings.
[0061] Step 2: Allocate a large enough continuous PCI space for the macro cell cluster base station, for example, the range is 101-371, and the number of PCIs in it is 271;
[0062] Step 3: Reserve a continuous PCI space for the macro cell cluster base station, ranging from 372 to 447, and the number of PCIs in it is 76, which is used to expand and join the macro cell;
[0063] Considering that in dense urban areas, the density of macro base stations is already high, and large-scale expan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com