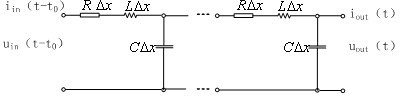
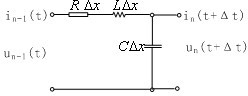
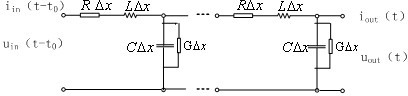
Longitudinal differential protection method of power transmission line
A transmission line, longitudinal differential protection technology, applied in emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components and other directions, can solve the problem of not fully equivalent distributed parameter circuits, not suitable for the quick-action requirements of longitudinal differential protection, unsuitable for high-voltage long-distance transmission lines, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0161] Experimental example 1: Detection of normal working conditions inside and outside the transmission line
[0162]In the normal working state inside and outside the transmission line, the A-phase current value is collected and calculated, and a total of 40 points are sampled in each cycle, and the collected value and calculation of the first 10 points of the A-phase line current are taken The values are compared in Table 1 below:
[0163] Table 1 The normal situation of the structure inside and outside the line area
[0164]
[0165]
[0166] It can be seen from Table 1 that when both the inside and outside of the transmission line are working normally, as the value of the unit number j increases, the calculated current value is closer to the collected value of the current, that is, the absolute error is getting smaller and smaller; When j=4, the relative error is lower than 1%, and the accuracy is sufficient. Therefore, if the number of units is j=4, the accurac...
experiment example 2
[0167] Experimental example 2 Detection of the state of normal operation inside the transmission line and external short circuit
[0168] When the structure in the line area is normal and the A phase outside the area is short-circuited to ground, the current value of the A phase is collected and calculated, and a total of 40 points are sampled in each cycle, and the acquisition of the first 10 points of the A phase line current is taken The values and calculated values are compared in Table 2 below:
[0169] Table 2 The structure of the line in the area is normal, and the ground short circuit of phase A outside the area
[0170]
[0171] It can be seen from Table 2 that in the case of a normal structure in the line area and a ground short circuit of phase A outside the area, as the value of the number of units j increases, the calculated current value is still closer to the collected value of the current , that is, the absolute error is getting smaller and smaller; whe...
experiment example 3
[0172] Experimental example 3 Detection of the internal A-phase metal grounding short circuit of the transmission line
[0173] In the case of a metal-to-ground short circuit of the internal phase A of the transmission line, the current value of the phase A is collected and calculated, and a total of 40 points are sampled in each cycle, and the collected value and calculated value of the phase A line current of the first 10 points are taken Compare the table 3 below:
[0174] Table 3 Metal grounding conditions of phase A in the line area
[0175]
[0176] It can be seen from Table 3 that in the case of a metal-to-ground short circuit of the internal phase A of the transmission line, at this time, a major change occurs in the structure of the line area, and no matter what the number of units j is, the calculated current value is significantly higher or lower than Due to the collected value of the current, the absolute error is very large, and the relative error changes sign...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com