Systems, devices, and methods for measuring whole blood hematocrit based on initial fill velocity
A technology of hematocrit and initial filling, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, biological tests, and electrochemical variables of materials, and can solve problems such as wrong determination of results, time-consuming, negative impact on accuracy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
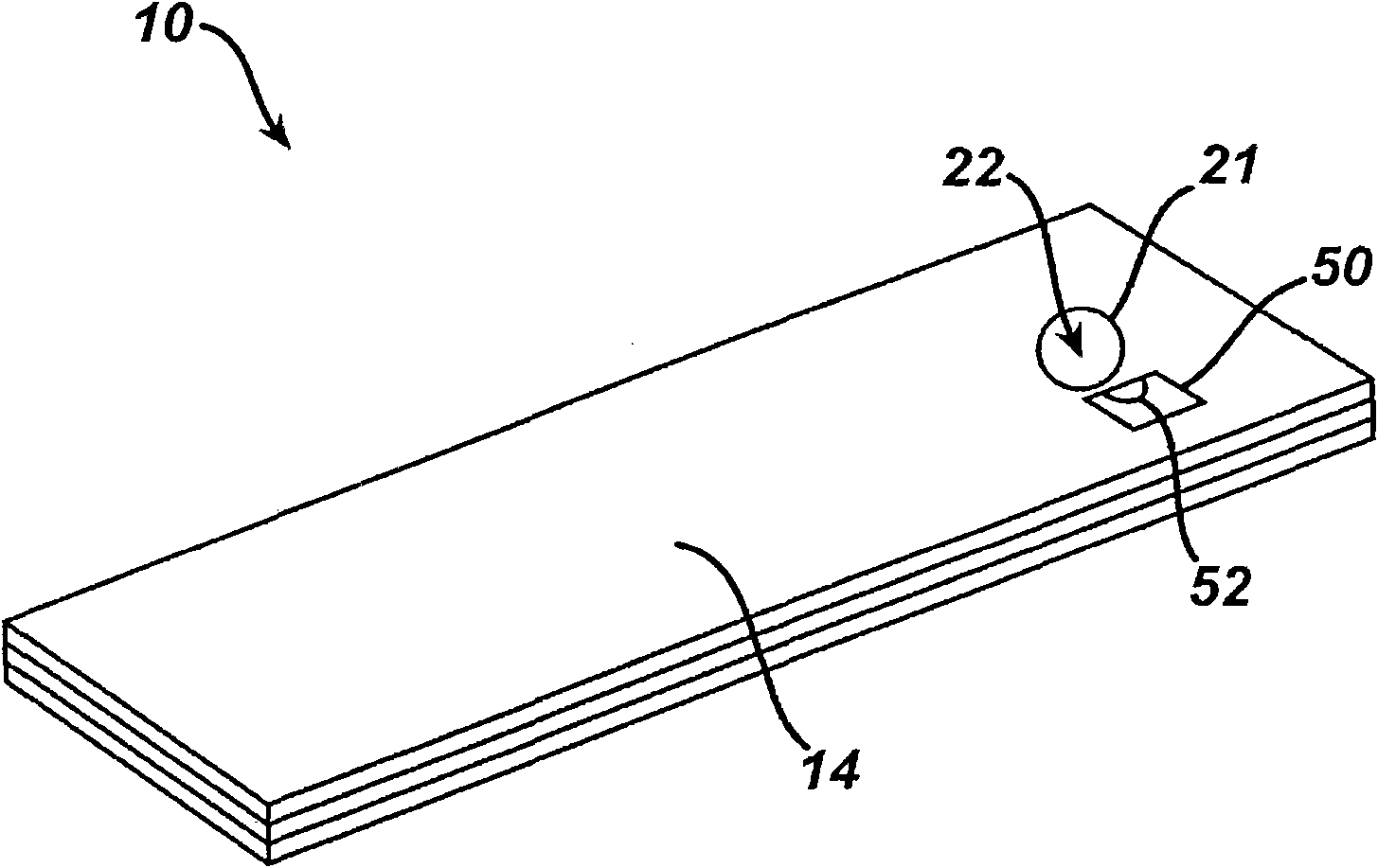
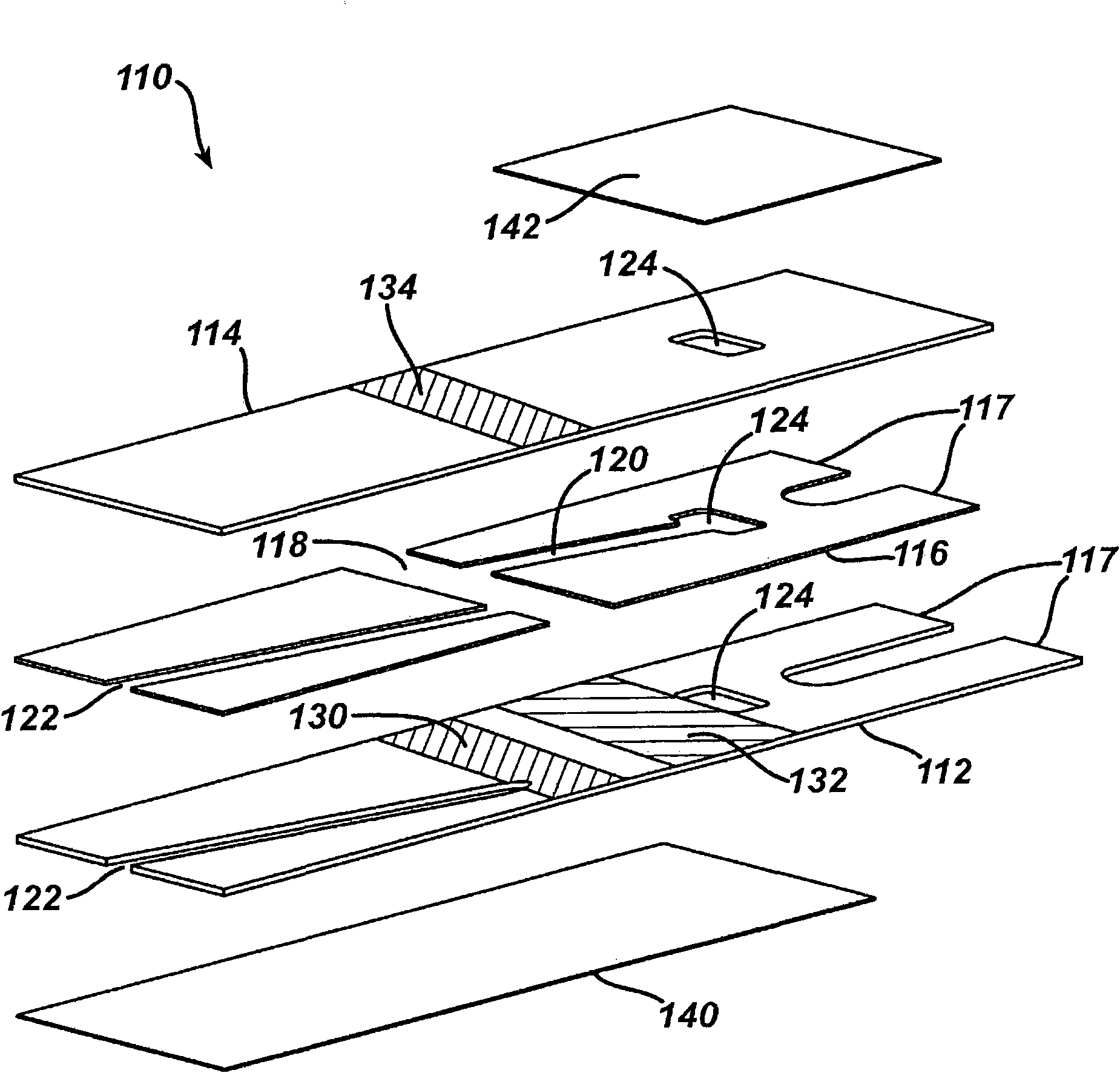
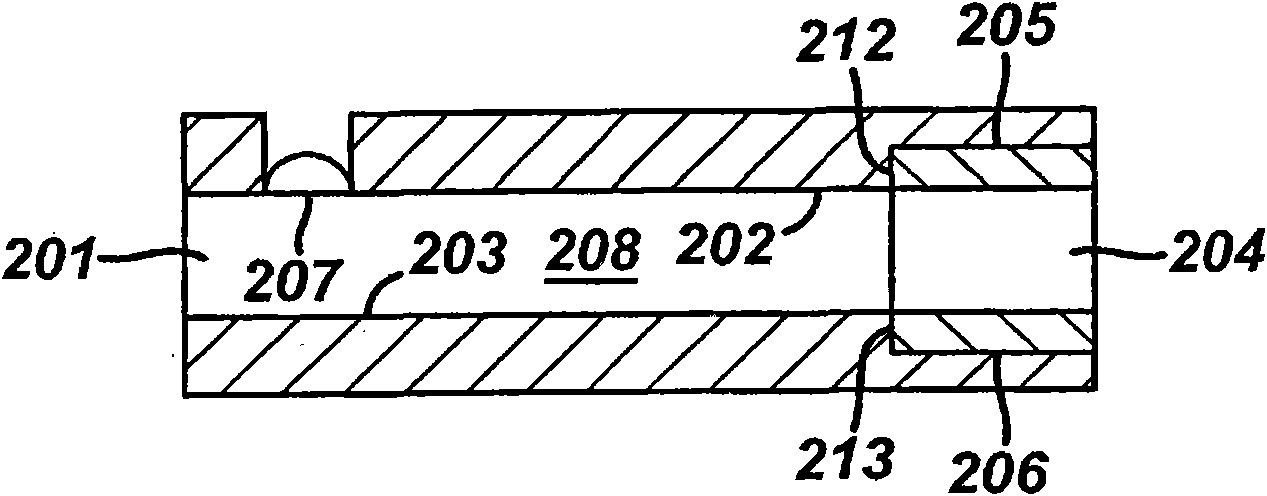
[0087] The use of the electrochemical system for measuring the initial fill rate based on the measurement of the current is illustrated by the following example. In the following examples, the system includes a sample analysis device, specifically, a figure 2 The immunosensor 110, the gauge configured for applying a potential and the control unit configured for determining the initial filling rate. Specifically, a potential is applied to the electrodes of the immunosensor 110, the hematocrit level is determined, and then the potential is reversed. The analyte concentration is then determined based on the determined hematocrit level. The hematocrit level is determined from the calculated initial fill rate.
[0088] Various samples were provided for analysis to test the performance of the systems, devices and methods disclosed herein. The sample is a blood sample containing C-reactive protein, so the concentration of the analyte determined is that of C-reactive protein. The...
example 2
[0101] The application of an electrochemical system to measure the initial fill rate based on the measurement of the current is further illustrated by another example. The sample analysis device used in this example was also figure 2 The immunosensor 110, the gauge configured to apply a potential and the control unit configured to determine the initial filling rate. Specifically, a potential is applied to the electrodes of the immunosensor 110, the hematocrit level is determined, and then the potential is reversed. Analyte concentrations are then calculated from the determined hematocrit levels. Similar to the previous examples, multiple samples with different hematocrit levels were used with the system to illustrate the performance of the system. Known levels of hematocrit concentration are about 33.5%, about 41%, about 47.5%, and about 56.5%.
[0102] The sample is introduced into the unheated immunosensor by capillary action. The sample enters the fill chamber and move...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com