Mixed addressing method for heaven and earth networks based on geographical position information
A hybrid technology of geographic location information and network, applied in the field of hybrid addressing of sky-earth networks, can solve problems such as inability to complete routing, unsuitable for processing mobile nodes, etc., and achieve the effect of improving routing efficiency and improving robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Each node in the network has two addresses: absolute address (SD) and relative address (RD). The absolute address is the permanent identification of the node, which will not change with the passage of time and the change of the node location. When communicating between any nodes, at least the absolute address of the other party must be known to communicate. The relative address is the current identification of the node, which will change with the position of the node and the change of the covering satellite.
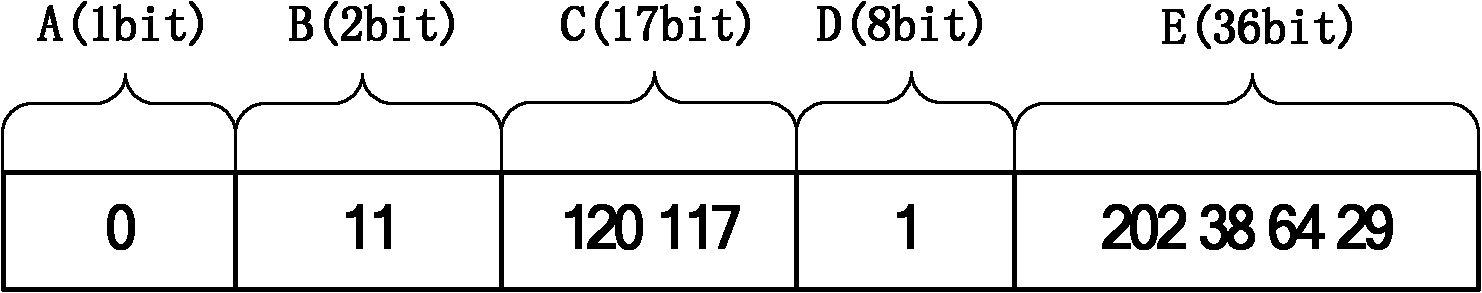
[0041] For example, for a mobile node i located in Hefei City (31.51° north latitude, 117.17° east longitude), the address in the IP network is 202.38.64.29, and the absolute address (SD i ) and relative addresses (RD i ), assuming that the node is within the coverage of No. 1 satellite at this time. figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the absolute address of the node, and the generation of each field in the absolute address is as follows:
[0042] Address t...
Embodiment 2
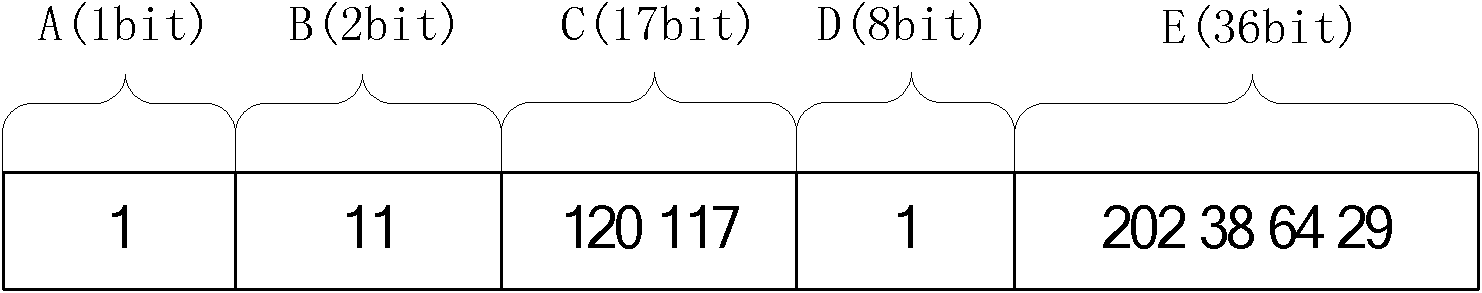
[0050] The equatorial coordinate system with the center of the earth as the center and synchronous rotation with the earth is adopted, and fixed nodes such as ground stations are fixed in this coordinate system. For such nodes, the relative address remains unchanged. At this time, the relative address is not very useful. It is just to be unified with the mobile node. The addressing can be routed directly through the geographic location information in the absolute address; for satellite nodes, extract The satellite ID contained in the unique identification field in the absolute address can carry out normal communication. Therefore, for these two nodes, the node address has been determined not to change, and no further management and update of the address is required. For a mobile node, it needs a relative address for communication, and the relative address will change as the node moves. In this case, it is necessary to provide an update and management mechanism of the mobile no...
Embodiment 3
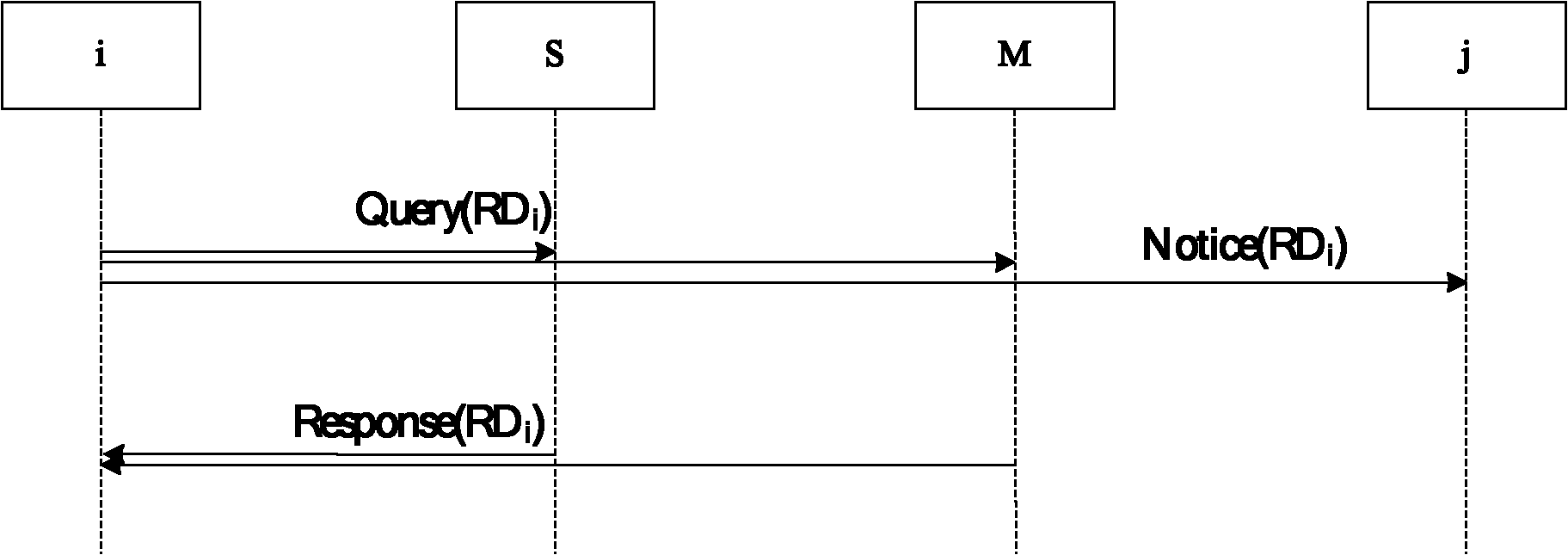
[0067] When a node moves from one area to another, its geographic location changes, and its relative address also needs to be changed accordingly. For example, the mobile node i whose initial location is in Hefei City is currently moved to Beijing (39.92° north latitude, 116.46° east longitude). At this time, certain processing needs to be performed to ensure that the relative address of the node is updated in time. Let the initial registration satellite of mobile node i be S, and the initial registration base station be M.
[0068] image 3 The relative address update process for mobile node i is given, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0069] a) Mobile node i updates the geographic location domain in the relative address to [128 116], indicating that the address is 39° north latitude and 116° east longitude, and obtains a new relative address RD with the new geographic location area as the geographic location field content i , that is, the relative address is update...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com