Resistance-change non-volatile memory device
A non-volatile storage, resistance change technology, applied in information storage, static storage, digital storage information, etc., can solve the problems of inability to read the same performance, hindering low voltage, and increasing the complexity of the chip area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0107] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
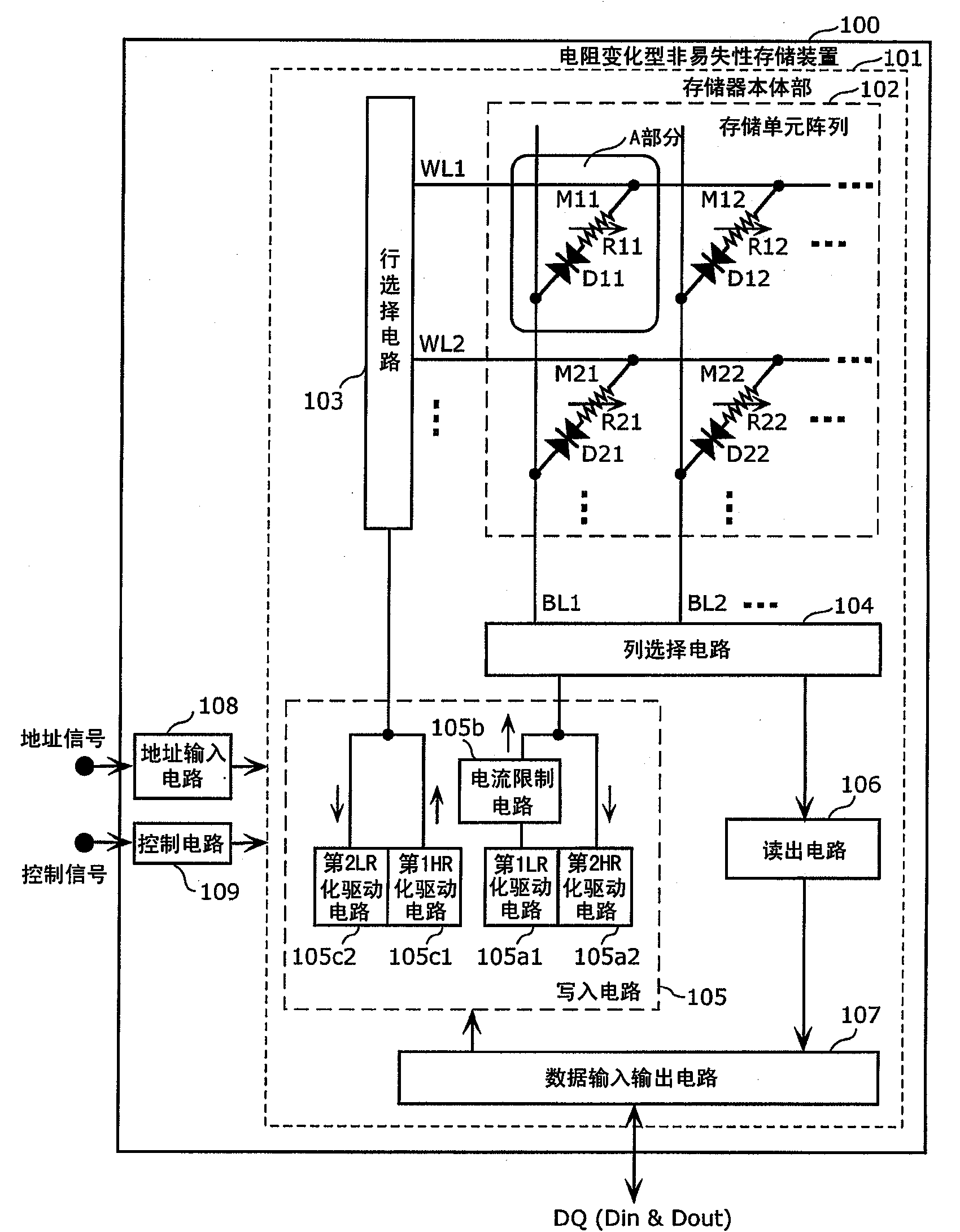
[0108] The variable resistance nonvolatile memory device according to the embodiment of the present invention is a cross-point nonvolatile memory device using a plurality of 1D1R type memory cells connected in series to a variable resistance element and a current steering element. The pattern of the resistance variable characteristic of the resistance variable element, and the structure of the driving circuit is optimized according to the fixed pattern.
[0109] [Basic data of the present invention]
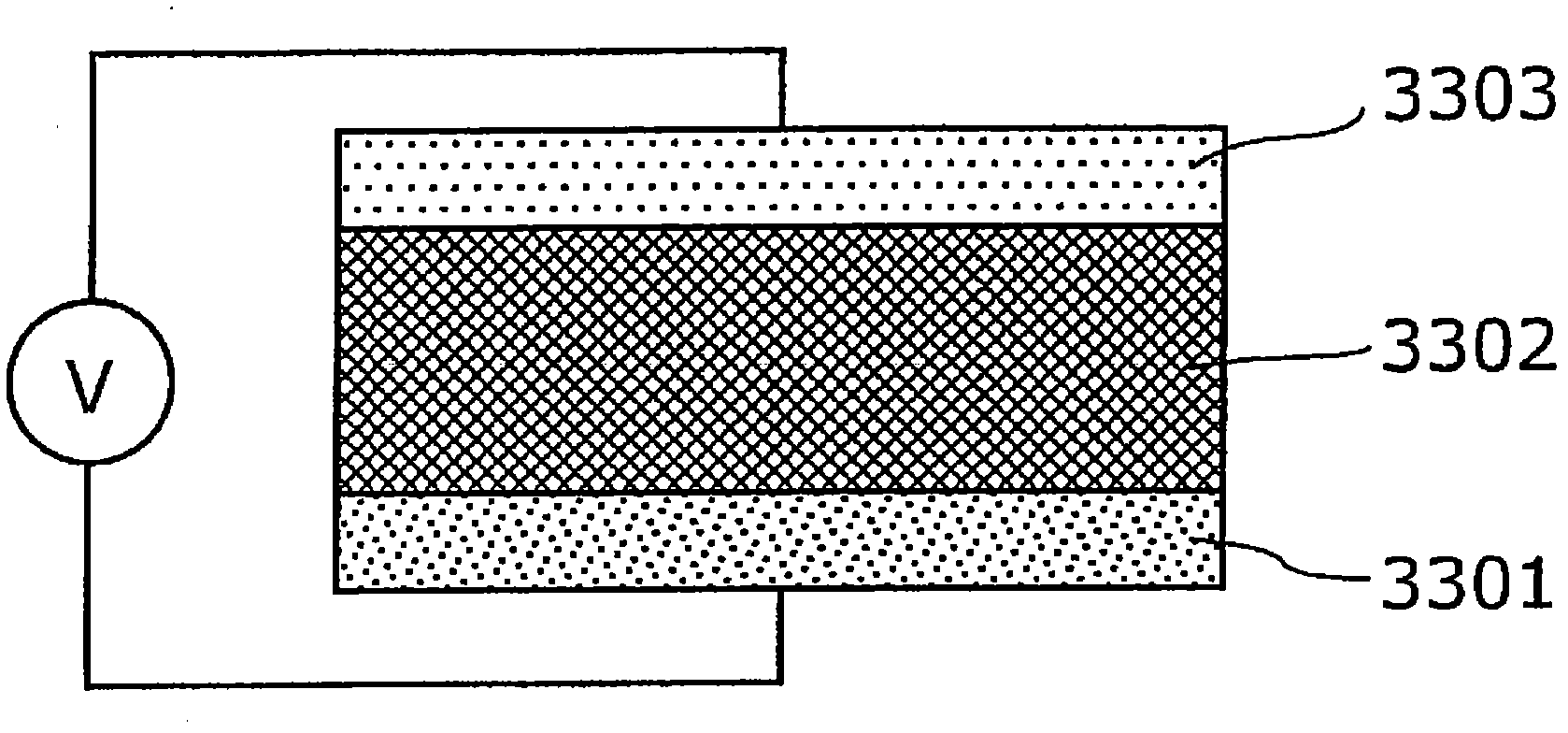
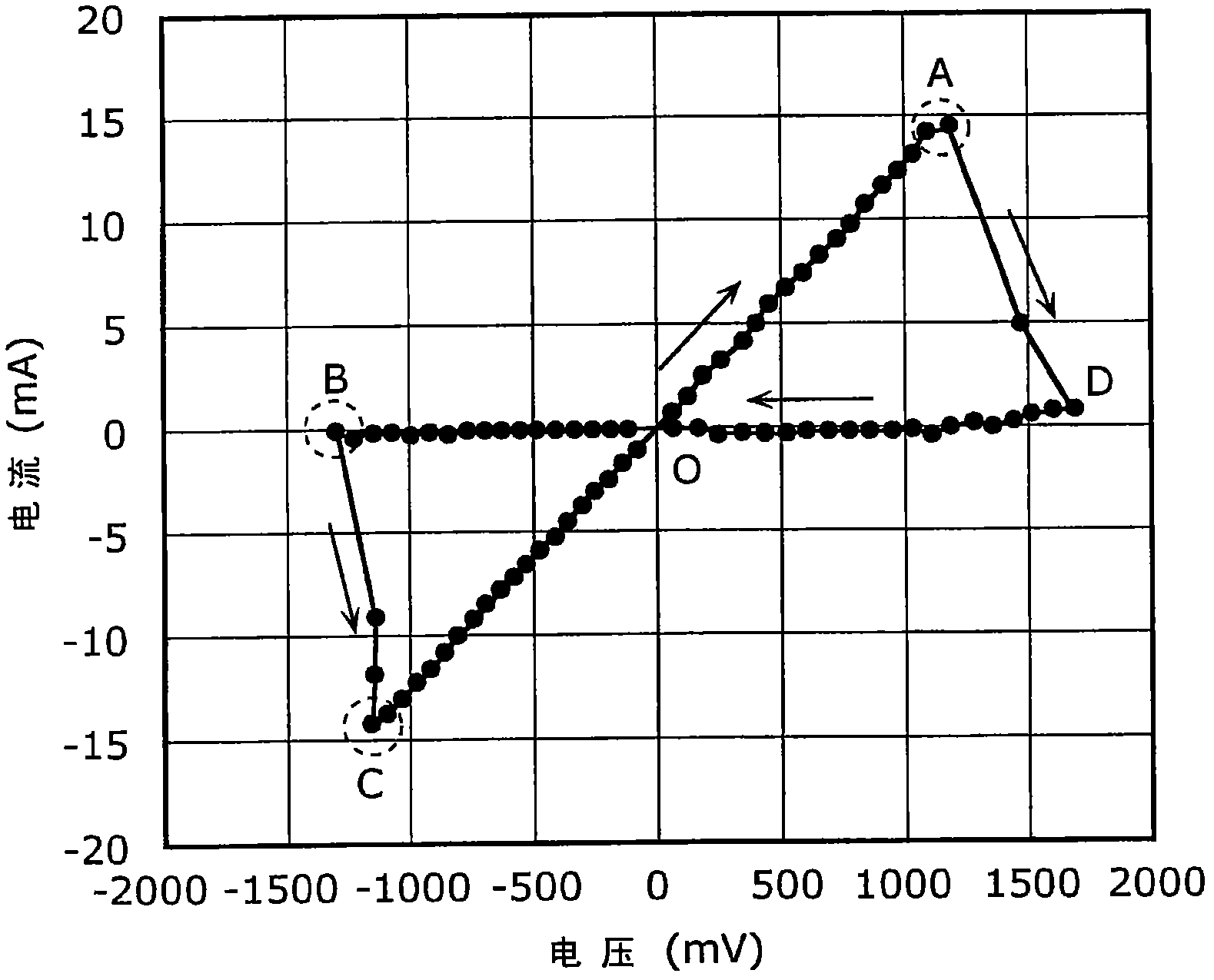
[0110] As a preparation, basic data related to two types of variable resistance materials used in the variable resistance element of the variable resistance nonvolatile memory device of the present invention will be described.
[0111] These variable resistance elements are composed of upper and lower electrodes made of different materials, respectively sandwich...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com