Laser reflector
A technology of laser reflection and laser, which is applied in the field of laser reflectors to achieve the effect of reducing spherical aberration and preventing damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
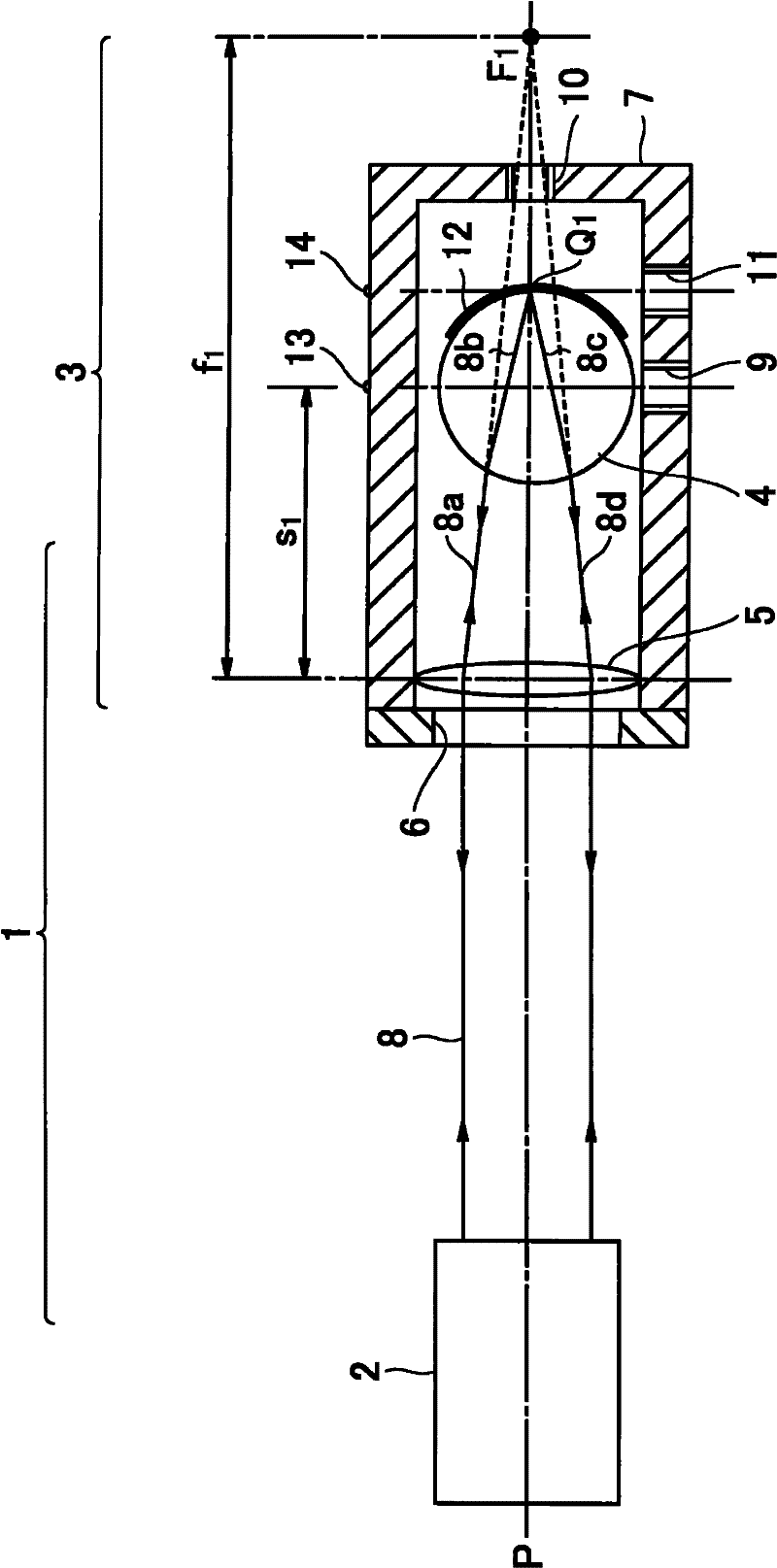
[0043] The structure of the laser interferometer
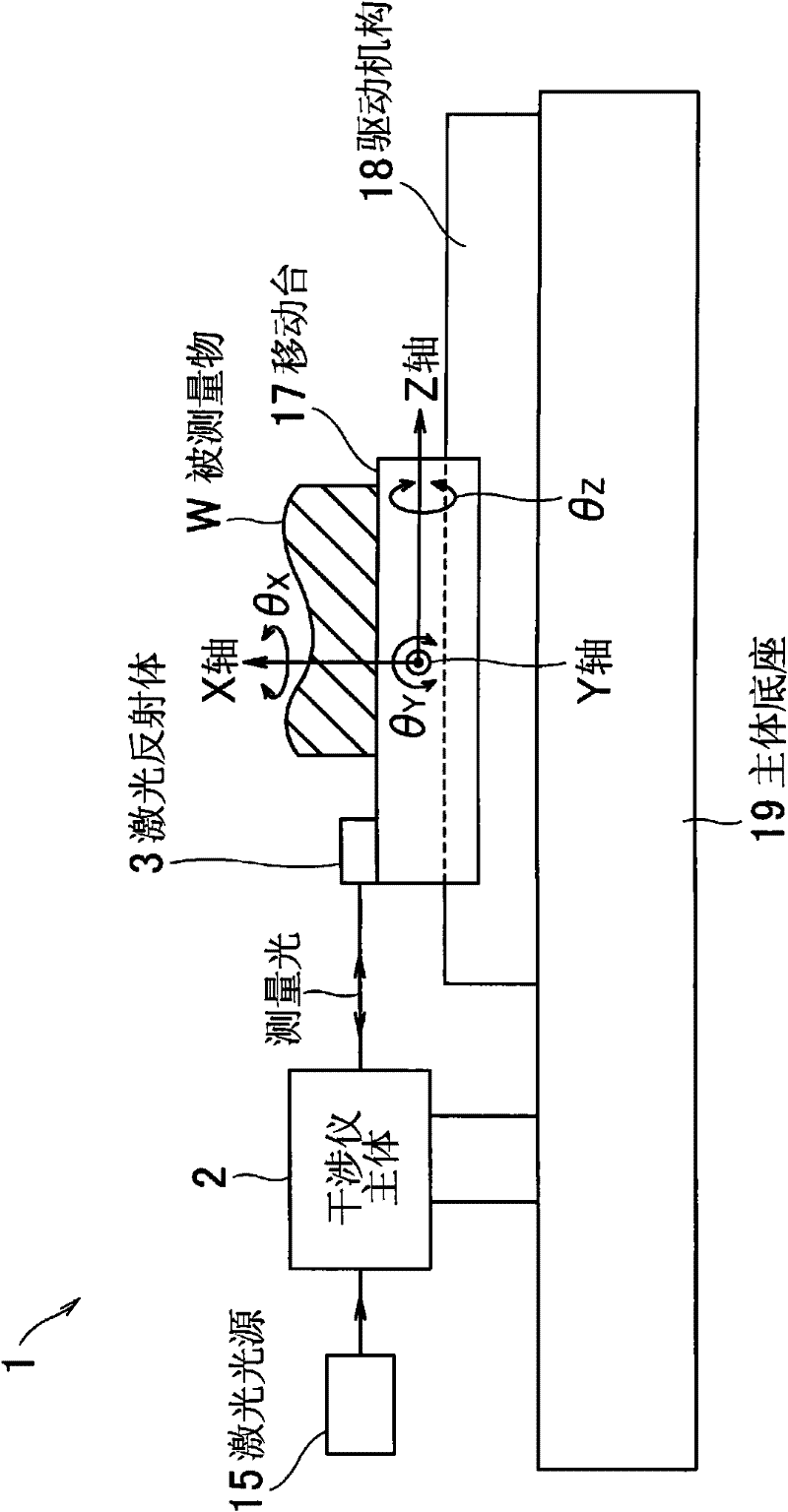
[0044] figure 1 It is a schematic configuration diagram showing the laser interferometric length measuring instrument according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0045] The laser interferometric length measuring instrument 1 of this embodiment has a main body base 19, a laser light source 15, an interferometer main body 2, a moving table 17 for placing the object W to be measured, a driving mechanism 18 of the moving table 17, and a Laser reflector 3 on top. In addition, the interferometer main body 2 functions as the irradiation means of the present invention.
[0046] The laser light source 15 is provided independently of the interferometer main body 2 , and supplies laser light of a predetermined wavelength (λ) to the interferometer main body 2 .
[0047] Interferometer main body 2 is fixed on the main body base 19, and Figure 11 Similarly, the conventional interferometers described in hereinafter h...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
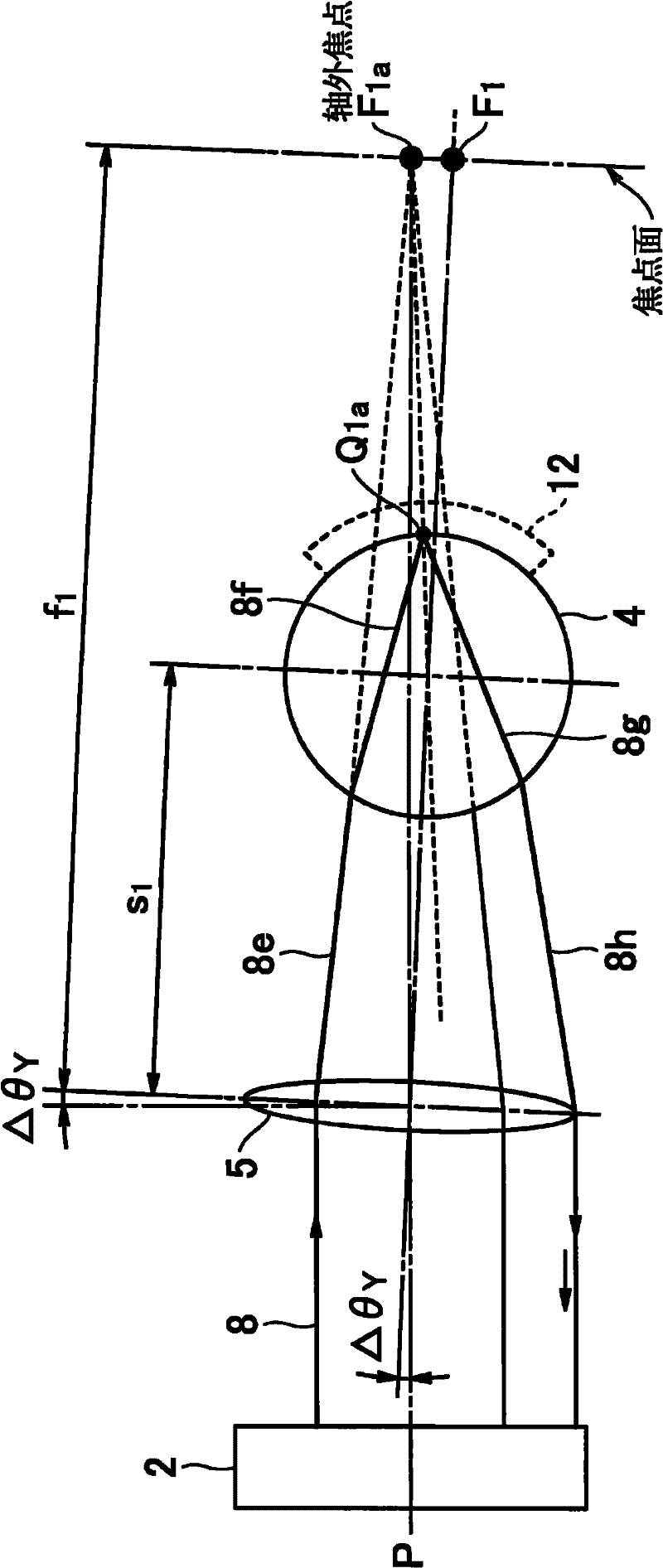
[0079] Image 6 It is a cross-sectional view showing a laser reflector according to a second embodiment of the present invention. The laser interferometer 101 has substantially the same structure as above, but the structure of the laser reflector is different. Here, a description will be given using reference numerals obtained by adding 100 to the reference numerals of members different from the above. The laser reflector 103 includes a focal length f 2 A lens 105, a sphere 104 with a refractive index n2, and a housing 107. Set the center distance S between the lens 105 and the sphere 104 2 Or the focal length f of the lens 105 2 , so that the focal length f 2 Distance from center S 2 unanimous. The cladding body 12 covering a part of the surface of the sphere 104 is in the region of the hemispherical surface of the sphere 104 farther away from the lens 105 (away from the lens 105), at the intersection point (A) of the hemispherical surface and the optical axis (P axis)...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0090] Figure 9 It is a cross-sectional view showing a laser reflector according to a third embodiment of the present invention. The laser interferometer 201 has substantially the same structure as above, but the structure of the laser reflector is different. Here, a description will be given using reference numerals obtained by adding 200 to the reference numerals of members different from the above.
[0091] The laser reflector 203 includes a spherical body 204 having a refractive index n3 and a case 207 holding the spherical body 204 . A circular window 6 is formed on the casing 207 in the same manner as described above. In addition, a part of the surface of the spherical body 204 is covered with the covering body 12 in the same manner as above.
[0092] The sphere 204 is made of a special material with a refractive index n3 approximately 2 (n3≈2). Therefore, when the laser light 8 is incident on the sphere 204, it converges on a point on the surface of the sphere oppo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com