Method for realizing average clock synchronization of wireless sensor network through cluster averaging
A wireless sensor and clock synchronization technology, applied in the direction of synchronization devices, network topology, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the life of network nodes, limiting network scalability, and high network traffic overhead, so as to improve scalability and reduce transmission The effect of the number of times and the stable synchronization state
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
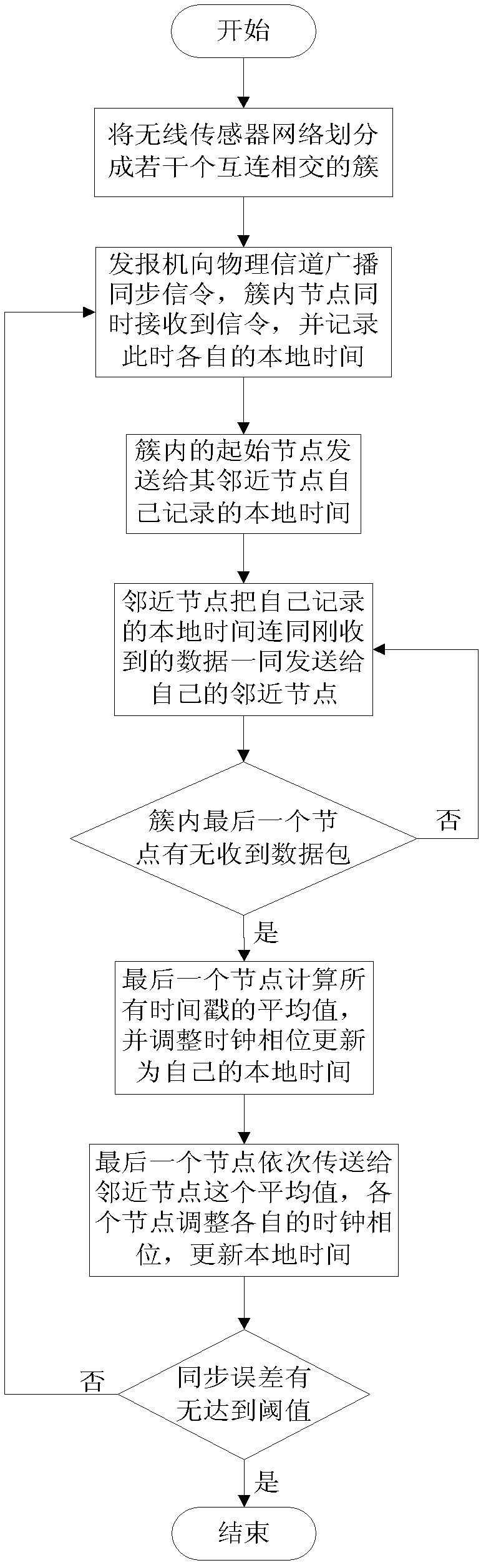
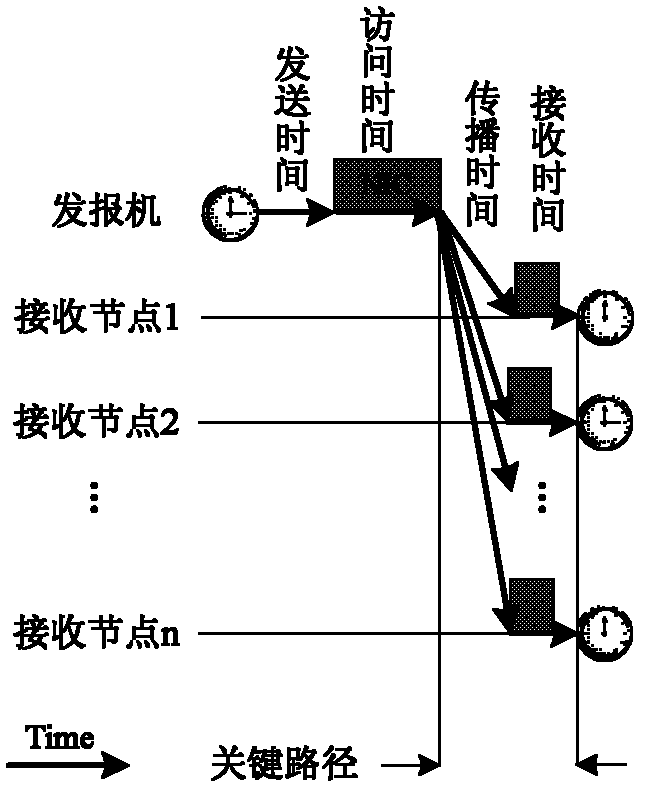
[0029] refer to figure 1 , the present invention mainly includes three parts: one is to divide the wireless sensor network into several clusters, the other is to perform local clock synchronization of the nodes in the cluster, and the third is to realize the global clock synchronization of the entire network. The specific steps are described as follows:
[0030] Step 1. Divide the wireless sensor network into several clusters.
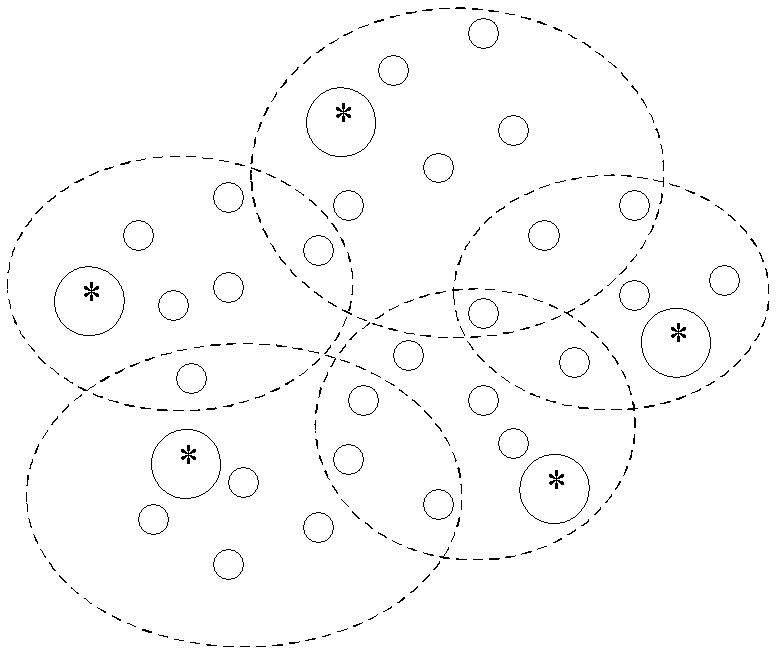
[0031] According to the communication relationship between sensor nodes in the network, the wireless sensor network is divided into several interconnected clusters, and each cluster has a transmitter, such as figure 2 As shown, among them, a cluster refers to a complete communication network composed of nodes that can directly communicate in pairs. Assuming that the wireless sensor network has N sensor nodes, it can be divided into M clusters according to the communication relationship between sensor nodes in the network.
[0032] Step 2. Perform loc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com