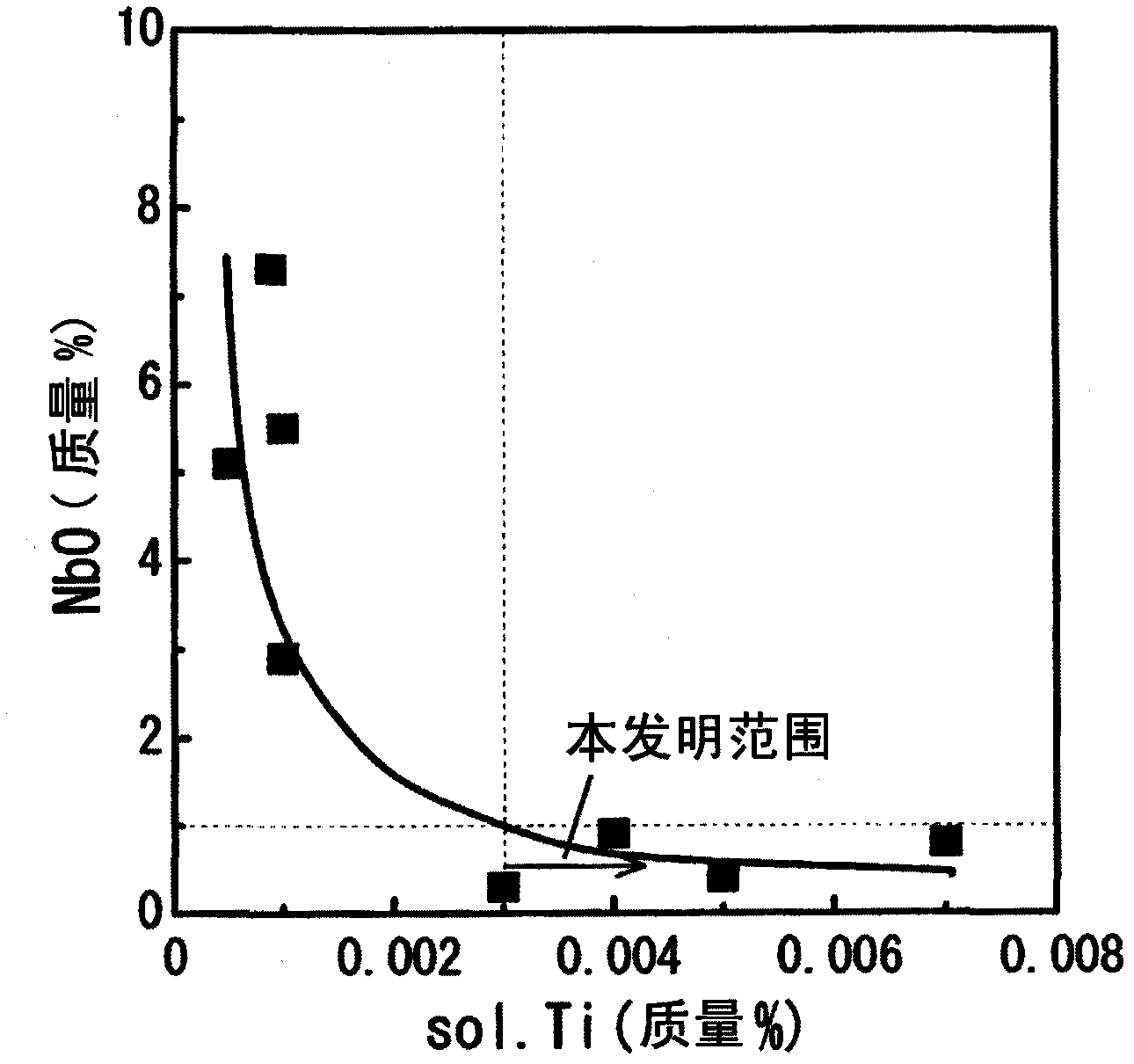
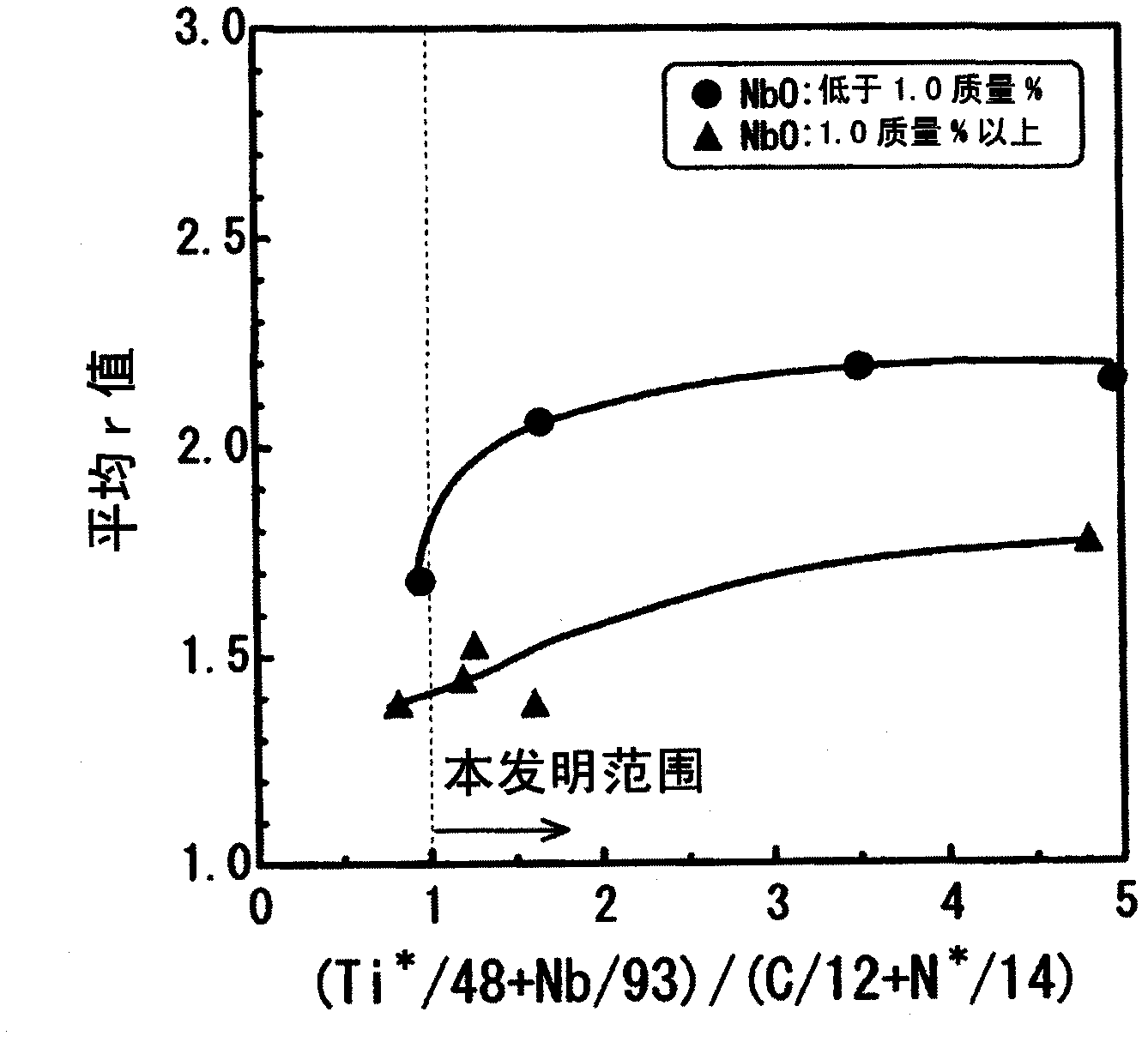
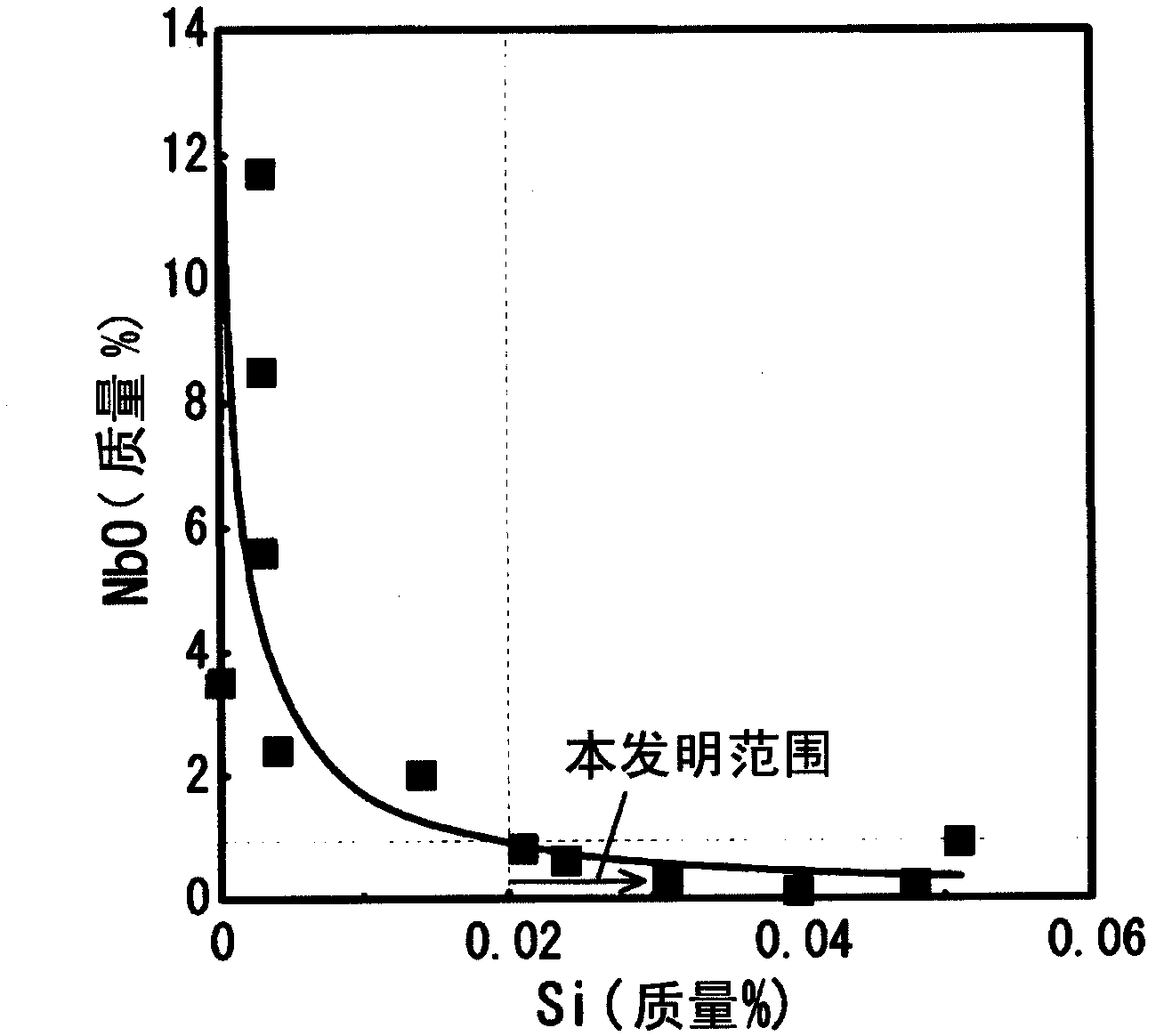
Steel sheet, hot-dip zinc-coated steel sheet and processes for production of same
A manufacturing method, a technology of hot-dip galvanizing, applied in the field of hot-dip galvanized steel sheets, capable of solving problems such as rising recrystallization temperature and impairing productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0177] Steels having the chemical compositions shown in Table 1 were melted and cast using a vacuum melting furnace for experiments. These steel ingots were hot-forged into steel sheets with a thickness of 20 mm, heated to 1250° C. in an electric heating furnace, and kept for 30 minutes. After the steel sheet was taken out from the furnace, it was hot-rolled in a temperature range of 910° C. or higher using a hot rolling mill for experiments to obtain a hot-rolled steel sheet with a thickness of 4 mm. After hot rolling, immediately cool to 650°C by water spray cooling, take this temperature as the coiling temperature, and put it into an electric heating furnace maintained at this temperature for 30 minutes, and then proceed to the furnace at a cooling rate of 20°C / h. Cooling is a slow cooling process after coiling. The obtained steel sheet was pickled and used as a cold-rolled base material, and cold-rolled at a rolling reduction of 82.5%, to obtain a cold-rolled steel sheet ...
Embodiment 2
[0188] 290 tons of molten steel were decarburized and refined in a converter, and the ladle containing the undeoxidized molten steel was transferred to the RH device, where vacuum decarburization was performed by the RH device. After the vacuum decarburization is completed, it is also used as the pre-deoxidation of the undeoxidized molten steel and the heating operation of the molten steel and the addition of Al. Add Al to the molten steel in the vacuum tank with 38Nm 3 Oxygen is supplied per minute, and the oxidation reaction is properly used to heat molten steel. Then, various alloys other than Ti were added and adjusted in consideration of the oxygen concentration contained in the molten steel, and finally Ti was added and adjusted to the chemical composition shown in Table 3. In Al-killed steels (steels T, U), this process is carried out to a state containing 0.04% or more of Al, and then Ti is added to adjust the chemical composition.
[0189] [table 3]
[0190]
[...
Embodiment 3
[0205] Using a vacuum melting furnace for experiments, steels having chemical compositions shown in Table 6 were melted and cast. Hereinafter, the same manufacturing method as in Example 1 was carried out to obtain an alloyed hot-dip galvanized steel sheet.
[0206] The same evaluation as in Example 1 was performed on the obtained alloyed hot-dip galvanized steel sheet.
[0207] [Table 6]
[0208]
[0209] Table 7 shows the composition analysis and performance evaluation results of oxide-based inclusions. In the test results (test numbers 101, 102, 105, 108, and 110) of the steel sheets within the range specified by the present invention, the surface properties were all good, and the average r value was 1.90 or more, showing good deep drawability.
[0210] [Table 7]
[0211]
[0212] Test results of steel plates manufactured using steels (steels AC, AD, AF, AG, AI, AK) whose steel composition or oxide-based inclusion composition is out of the range specified in the pr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com