Nanoemulsions
A nanoemulsion, droplet size technology, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanostructure manufacturing, etc., can solve problems such as high pumping pressure and reduced drilling efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
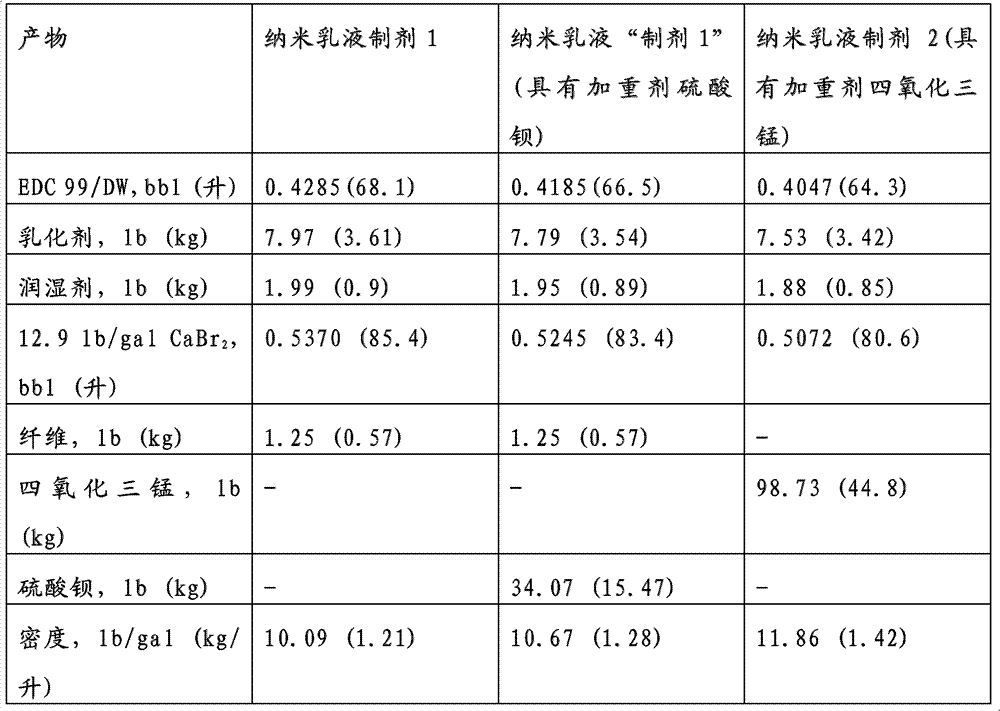
[0116] The previous two embodiments (those represented as similar to Examples 1 and 2) can sometimes be "intensified", wherein the addition of step (2) continues with mixing until the composition of (2) is at 25°C at 500 / The viscosity measured at a shear rate of s reaches at least about 275 cP; and the mixing of (3) is continued until the viscosity of the composition of (3) drops below about 20 cP at 25° C. at a shear rate of 500 / s .
[0117] Other nanoemulsion compositions corresponding to each method of preparation of a nanoemulsion composition given and disclosed herein (including all variations and combinations) can be defined by means of a method to define a product. It is worth noting here that nanoemulsion compositions may be formulation route dependent; ie different compositions may result when the same components are combined in different ways.
[0118]The use of nanoemulsion compositions in various processes related to the oil and gas industry is also contemplated....
Embodiment 1
[0124] Example 1: Nanoemulsion without solid weighting agent
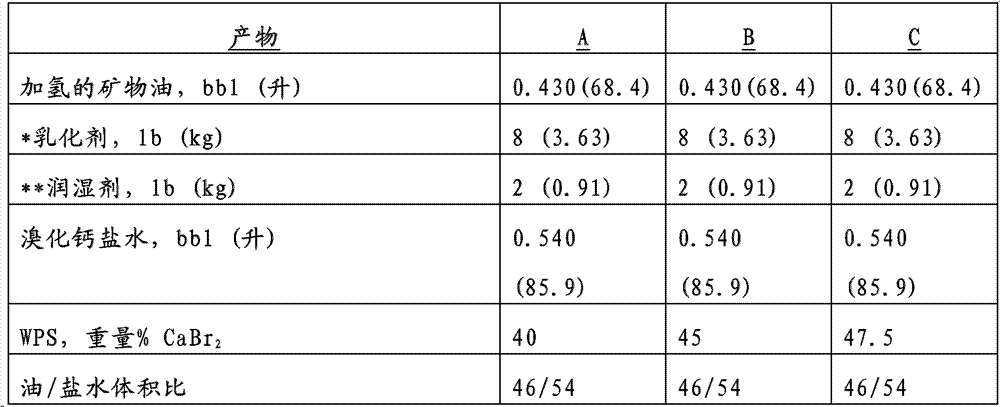
[0125] Various oil external phase emulsion formulations were prepared using various water phase salinities (WPS) to verify the formation of nanoemulsions. Calcium bromide brine was used as the internal phase of the emulsion, while hydrogenated mineral oil (EDC 99 / DW; source: Total) was used as the external phase. An emulsifier (imidazoline with about 3% by weight methanol) and a wetting agent (succinamide) were added to properly stabilize the emulsion.
[0126] The formulations were prepared to demonstrate the formation of saline-in-oil emulsions as well as saline-in-oil nanoemulsions. The formulation of each fluid is shown in Table 1 below.
[0127] Table 1
Embodiment 1
[0128] Fluid formulation of Example 1 (SI or metric equivalents are given in parentheses)
[0129]
[0130] *Emulsifier is surfactant
[0131] ** Wetting agent is a co-surfactant
[0132] Described emulsion adopts following procedure to prepare:
[0133] 1. Measure an appropriate amount of oil, emulsifier, wetting agent and calcium bromide brine of appropriate salinity, and prepare 1 laboratory barrel for each mixture to be prepared.
[0134] 2. Using a multi-mixer and a stainless steel conical mixing chamber, begin mixing the oils. The emulsifying and wetting agents were added using a syringe.
[0135] 3. Allow the oil / emulsifier / wetting agent mixture to mix for 1 minute.
[0136] 4. Begin slowly adding the brine. Once about half of the brine has been added, the viscosity of the mixture will increase to the point where the vortexing ends. Continue mixing for two minutes to reduce viscosity, then add the remaining brine by hand.
[0137] 5. Stabilize the emulsion by ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com