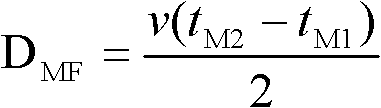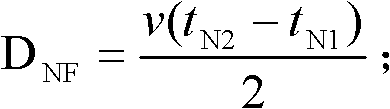Fault distance measuring method for combined travelling wave of power transmission line
A technology of transmission lines and ranging methods, applied in radio wave measurement systems, fault locations, measuring devices, etc., can solve the reliability and accuracy of given line length errors, influences, and unreliable ranging results of the double-ended principle, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of improving reliability and accuracy, broad application prospects, and improving power supply reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
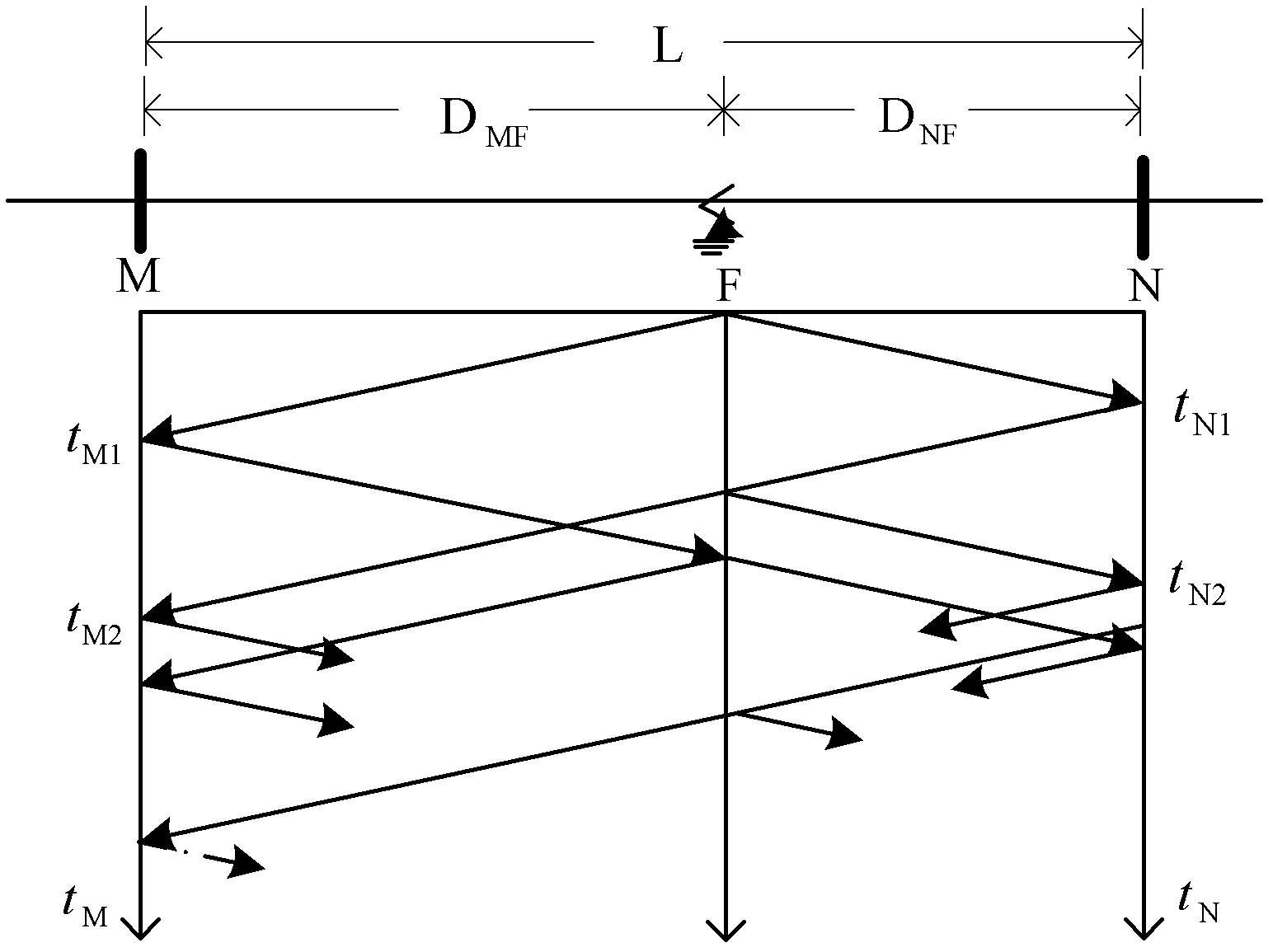
[0015] Embodiment 1: The voltage level is 220kV, M and N are the busbars at both ends of the transmission line, and the length of the transmission line is L=100km, t M1 , t M2 is the time when the fault traveling wave arrives at the M-terminal bus for the first time and the second time after the line fault, t N1 , t N2 is the time when the fault traveling wave arrives at the N-terminal bus for the first time and the second time. The fault point F is 25km away from the M-side busbar, and the wave velocity of the traveling wave in the transmission line is v=295.0813km / ms. A fault occurs at time t=0.
[0016] Step 1. Preliminary test: after the line fault, measure the time t when the fault traveling wave arrives at the M-terminal bus for the first time and the second time M1 = 86μs, t M2 =256μs, the time t for the first and second arrival at the N-terminal bus N1 = 256μs, t N2 = 425 μs. Using the single-ended traveling wave principle to calculate the distance between two ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Embodiment 2: the voltage level is 220kV, M and N are the busbars at both ends of the transmission line, and the length of the transmission line is L=100km, t M1 , t M2 is the time when the fault traveling wave arrives at the M-terminal bus for the first time and the second time after the line fault, t N1 , t N2 is the time when the fault traveling wave arrives at the N-terminal bus for the first time and the second time. The fault point F is 35km away from the N-terminal bus, and the wave speed of the traveling wave in the transmission line is v=295.0813km / ms. A fault occurs at time t=0.
[0024] Step 1. Preliminary test: after the line fault, measure the time t when the fault traveling wave arrives at the M-terminal bus for the first time and the second time M1 = 222μs, t M2 =458μs, the time t for the first and second arrival at the N-terminal bus N1 = 120μs, t N2 = 357 μs. Using the single-ended traveling wave principle to calculate the distance between two p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com