Random storage
A random access memory and storage unit technology, applied in the field of storage processing, can solve problems such as shortening refresh time, increasing leakage, complex logic circuits, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing complexity and improving integration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
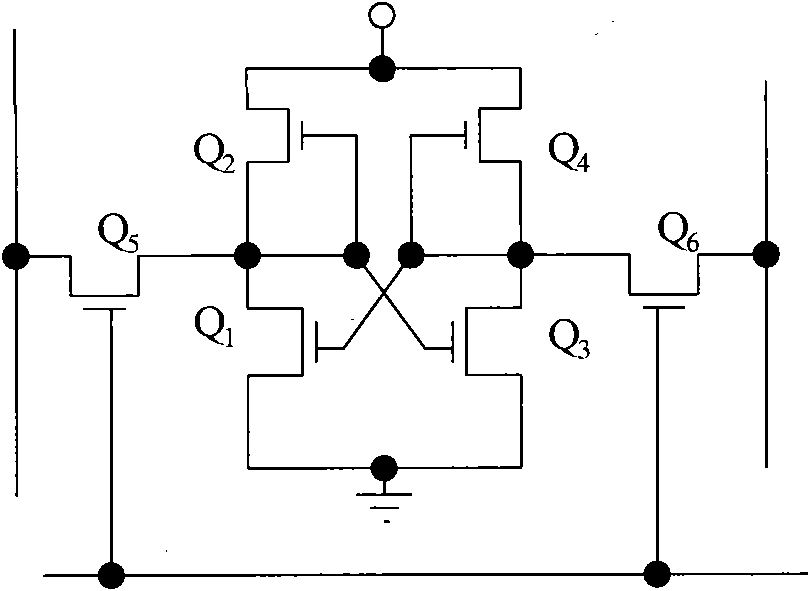
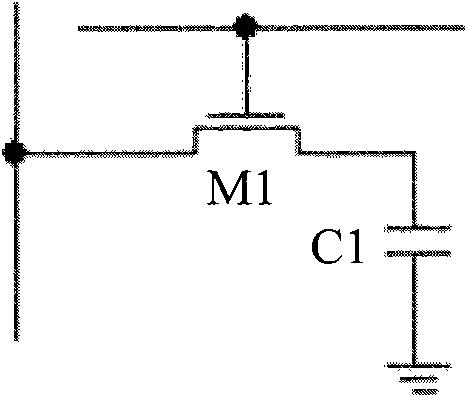
[0042]In view of the above problems, the inventor found through research that, on the one hand, both DRAM and SRAM have reset noise when reading and writing. On the other hand, the existing SRAM occupies a large area, while the DRAM process is much more complicated, and the access speed is slow, and the amount of stored charge decreases with time and temperature, so it must be refreshed regularly. Conductive interconnection between C1 and MOS transistor M1, so there is a contact hole for conductive interconnection, the contact hole needs to be in contact with the silicon surface when interconnecting with the MOS transistor, so that the contact hole and silicon There will be an interface state at the contact interface, and the electrons in the interface state are relatively active (plasma etching is required when making a contact hole, which will cause damage to the chip surface, and at the same time, there will be an interface state in the contact of the two interfaces, due to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com