Dynamic matrix control (DMC) engineering method based on model simplification and prediction error correction
A technology of error correction and model simplification, which is applied in the direction of instruments, adaptive control, control/adjustment systems, etc., can solve the problems of system accuracy and robustness degradation, difficulty in realizing bottom-level control, and inability to apply DMC, etc., and achieve control law simplification , online calculation and memory usage are reduced, and the effect of timely correction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
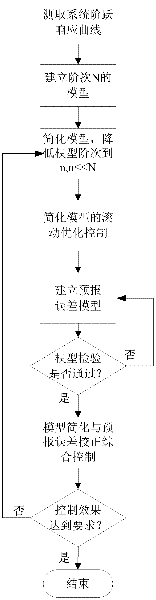
[0021] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this implementation mode, the concrete steps that this implementation mode comprises are as follows:
[0022] Step 1. Measure the step response curve of the system; establish a model with an order of N, divide the whole step process into N equal parts according to time, N is a natural number, and the selection of N includes all dynamic processes;
[0023] Step 2. Simplify the model obtained in step 1 to obtain a simplified model. The specific process is: reduce the order of the model to n, n<<N; take the first n segments of the step curve after equalization to establish a simplified model;
[0024] Step 3, the rolling optimization control of the simplified model; obtain the simplified model and the actual system error sequence {e(k)};
[0025] Step 4, establishing a forecast error model; establishing an AR model through the error sequence {e(k)};
[0026] Step 5. Judging whether the AR model established in st...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific implementation mode two: the specific process of step one in the implementation mode one is:
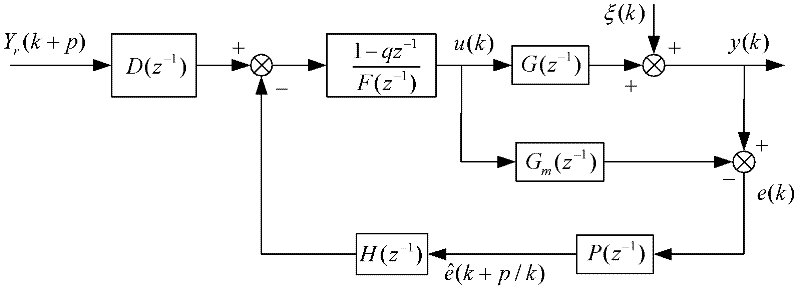
[0029] The predictive control of DMC is based on the step response sequence a 1 , a 2 ,...a N , related to the sampling period,
[0030] DMC consists of expressions (1) to (3): Y m (k+1)=AΔU(k)+A 0 U(k-1) (1)
[0031] A,A 0 matrix by a 1 , a 2 ,...,a N constitute;
[0032] Y p (k+1)=AΔU(k)+A 0 U(k-1)+he(k) (2)
[0033] e(k) is the error between the actual output and the model output,
[0034] ΔU ( k + i - 1 ) = D i T [ Y r ( k + 1 ) - A 0 U ( k - 1 ) ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0038] Specific implementation mode three: the process of establishing a simplified model in step two in the first implementation mode is aimed at A in the model 0 U(k-1) performs simplified dimensionality reduction, the specific process is:
[0039] The system model uses G(z -1 ) = g 1 z -1 +g 2 z -2 …+g n z -n …+g N z -N (4)
[0040] expression, where g 1 =a 1 , g i =a i -a i-1 , i=2, 3,...N;
[0041] For the over-damped self-balancing object, that is, g in formula (4) n z -n The subsequent items can be processed according to exponential decay, so formula (4) is approximated as formula (5) G ( z - 1 ) = g 1 z - 1 + g 2 z - 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com