Speed sensor-less method for estimating rotor angle and revolving speed of permanent-magnet synchronous motor
A technology of permanent magnet synchronous motor and speed sensorless, which is applied in the field of speed estimation and rotor angle of permanent magnet synchronous motor, and can solve problems such as large amount of calculation, complex principle, and unstable system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
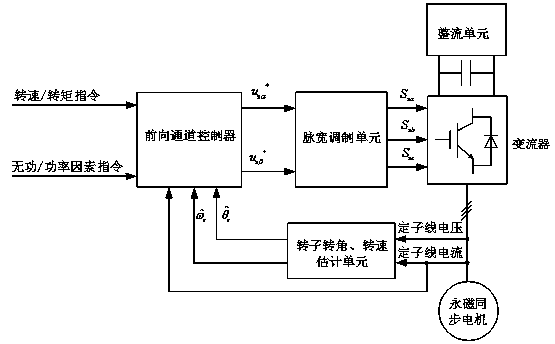
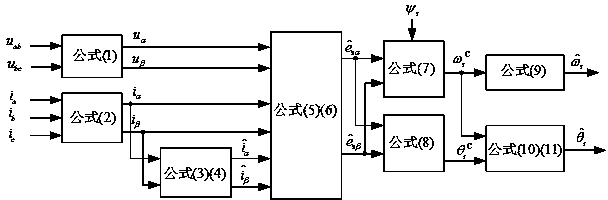
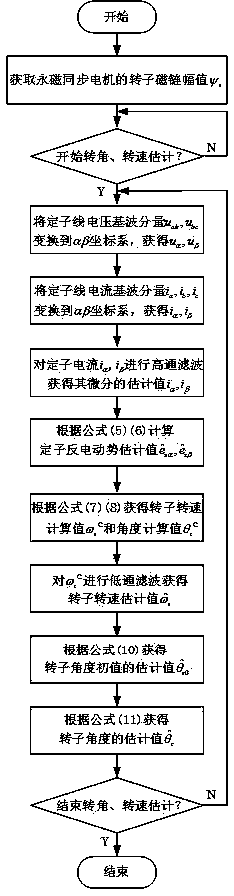
[0059] figure 1 It is a typical system block diagram of an existing speed sensor-based permanent magnet synchronous motor. The controlled object is a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and the actuator is a converter. The rectification unit rectifies the grid voltage and maintains the DC bus voltage of the converter constant, thereby ensuring the normal operation of the converter. The control system mainly includes three parts, the forward channel controller, the pulse width modulation unit and the rotor angle and speed estimation unit. The forward channel controller receives the given speed / torque command and reactive power / power factor command, and controls the component u of the stator voltage in the αβ coordinate system according to the stator current feedback and the estimated rotor angle and speed feedback. sα * , u sβ * . PWM unit for u sα * , u sβ * Modulate to generate the switching signal S required by the converter sa ,S sb ,S sc , and then drive the p...
Embodiment 2
[0096] In this embodiment, the method for estimating the rotor angle and rotational speed of the permanent magnet synchronous motor provided by the present invention is applied to a direct-drive wind power generation system based on a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The main parameters of the direct drive permanent magnet synchronous wind power generation system are as follows:
[0097] parameters
value
Permanent magnet synchronous generator rated capacity S N (MW)
1.5
690
Rated frequency f N (Hz)
11.5
Stator phase resistance ( mΩ )
3.0
Direct axis inductance L d ( mH )
2.9
Quadrature axis inductance L q ( mH )
2.9
Stator voltage pulse width modulation frequency f PWM (kHz)
2
[0098] Firstly, the rotor flux amplitude ψ of the permanent magnet synchronous motor r It can be calculated from the rated parameters: Then, follow f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com