Compound containing cyclic group having disulfide structure and preparation method and application of compound
A technology of cyclic groups and compounds, which is applied to compounds with cyclic groups containing disulfide structures and their preparation and application fields, can solve the problems of low grafting efficiency, uneven grafting, and failure to achieve chemical grafting. In order to achieve the effect of expanding the dynamic volume, increasing the viscosity and improving the salt resistance and hydrophilic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
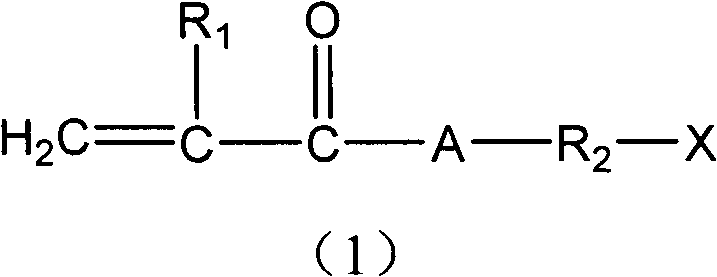
[0032] According to the present invention, the preparation method of the compound having a cyclic group containing a disulfide structure comprises: in the presence of a solvent and a polymerization inhibitor and under condensation reaction conditions, contacting the first reactant with the second reactant; The first reactant is a compound shown in general formula (4), and the second reactant is a compound shown in general formula (5):
[0033]
[0034] In general formula (4), R 2 and X are as defined above in the present invention, and Y can be -OH or -NH 2 ;
[0035] In general formula (5), R 1 As defined above in the present invention, Z can be -Cl or -OH;
[0036] And when Y is -OH, Z is -Cl, when Y is -NH 2 , Z is -OH.
[0037] According to a specific embodiment of the present invention, Y in the first reactant is -OH, and Z in the second reactant is -Cl. When Y in the first reactant is -OH, and Z in the second reactant is -Cl, as long as the molar ratio of the fi...
Embodiment 1
[0051] This example is used to illustrate the compound with a cyclic group containing a disulfide structure provided by the present invention and its preparation method.
[0052] In a three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer, a stirrer, and a reflux condenser, add 1 part of thioctylamine (scientific name: 6,8-dithioctylamine), 10 parts of solvent toluene and 0.01 part of polymerization inhibitor agent hydroquinone, heated to 60°C to dissolve it completely, and then added 2 parts of methacrylic acid and 0.1 part of concentrated sulfuric acid (98% by mass concentration) in sequence. First heat and reflux for about 3 hours, and then install a water separator for azeotropic dehydration. After separating 0.7 parts of water, the temperature in the three-necked flask was maintained at 120°C. When it was observed that the desorption amount was equivalent to the theoretical value (1 part of water), the reaction was stopped, the temperature was lowered to room temperature, and un...
Embodiment 2
[0056] This example is used to illustrate the compound with a cyclic group containing a disulfide structure provided by the present invention and its preparation method.
[0057] In a three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer, a stirrer, and a reflux condenser, based on the amount of the substance, after adding 0.01 part of the polymerization inhibitor hydroquinone, add 1 part of thioctyl alcohol (scientific name: 6,8-dithioctyl alcohol) in sequence. Octanol), 1.2 parts of triethylamine, 10 parts of toluene solvent, warming up to 50 ° C, then adding 2 parts of methacryloyl chloride (the molar ratio of the three is 1:1.2:2) in the dropping funnel, drop 1 After the dropwise addition is completed, the temperature is kept at 50° C. for 8 hours. After the reaction, filter the salt generated by the reaction, distill under reduced pressure, remove the solvent and excess acid chloride, then pour the product into a beaker, wash off hydroquinone and a small amount of acrylic acid w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com