Secondary-battery temperature-raising apparatus and vehicle having same
A secondary battery and heating device technology, applied in secondary batteries, secondary battery repair/maintenance, battery/fuel cell control devices, etc., can solve problems such as performance degradation, reduced battery capacity, and reduced charge and discharge characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
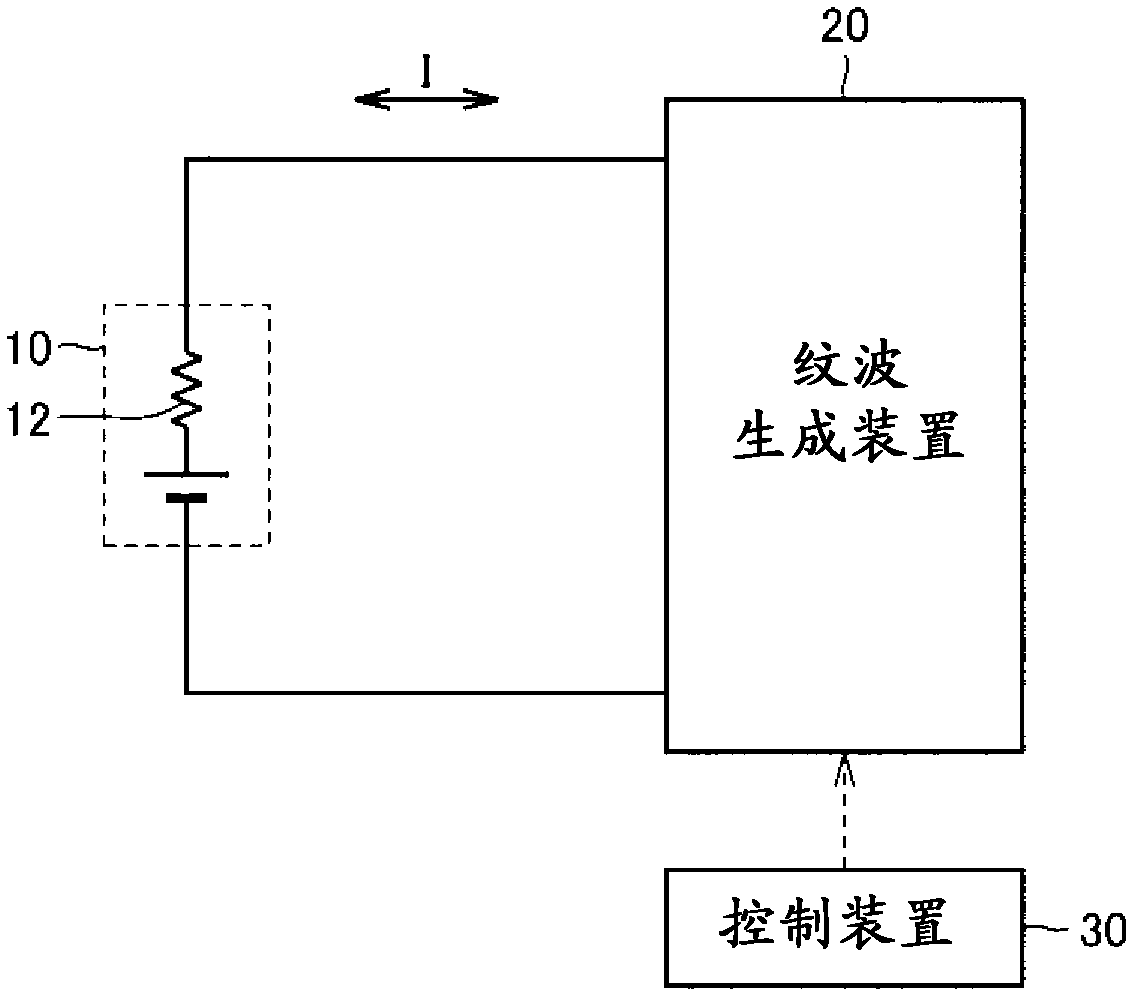
[0055] figure 1 It is an overall configuration diagram of a temperature rising device for a secondary battery according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Reference figure 1 , The heating device includes: a ripple generating device 20 and a control device 30. The ripple generating device 20 is connected to the secondary battery 10.
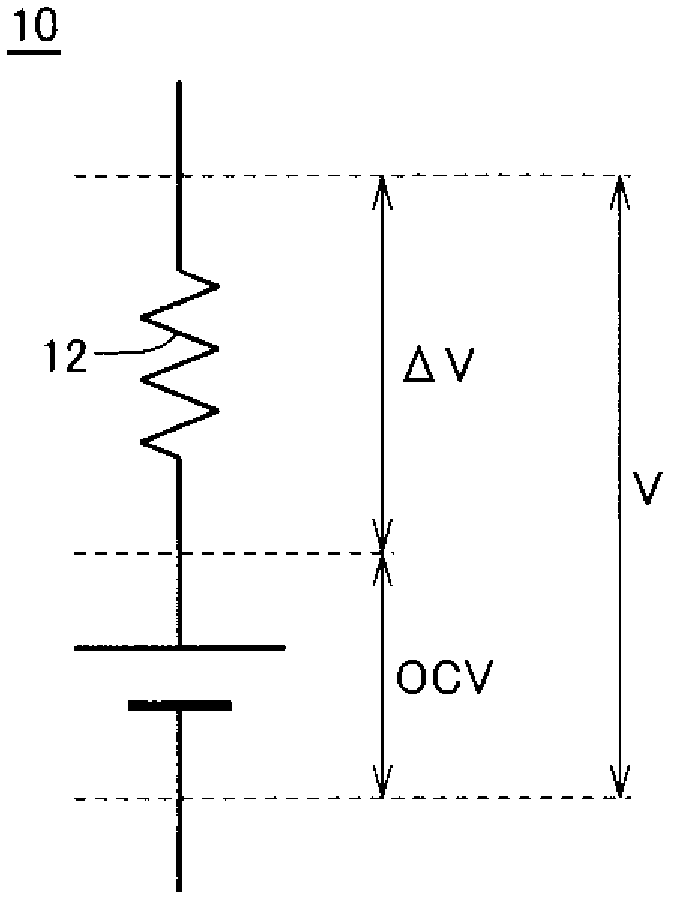
[0056] The secondary battery 10 is a rechargeable battery represented by a lithium ion battery or a nickel-hydrogen battery. The secondary battery 10 includes an internal resistance 12. As described later, this internal resistance 12 is temperature-dependent, and at the same time, it varies greatly depending on the frequency of the current flowing through the battery.
[0057] The ripple generation device 20 is controlled by the control device 30 to cause the secondary battery 10 to actively generate a ripple current I of a predetermined frequency. For example, the power semiconductor switching element constituting the ripple generati...
Embodiment approach 2
[0099] In the second embodiment, the secondary battery 10 is a lithium ion battery, and when the precipitation of lithium (Li) in the negative electrode is a problem due to the ripple current in the charging direction, the ripple frequency is set to avoid the generation of Li precipitation. Hereinafter, the way to consider the ripple frequency in this second embodiment will be described.
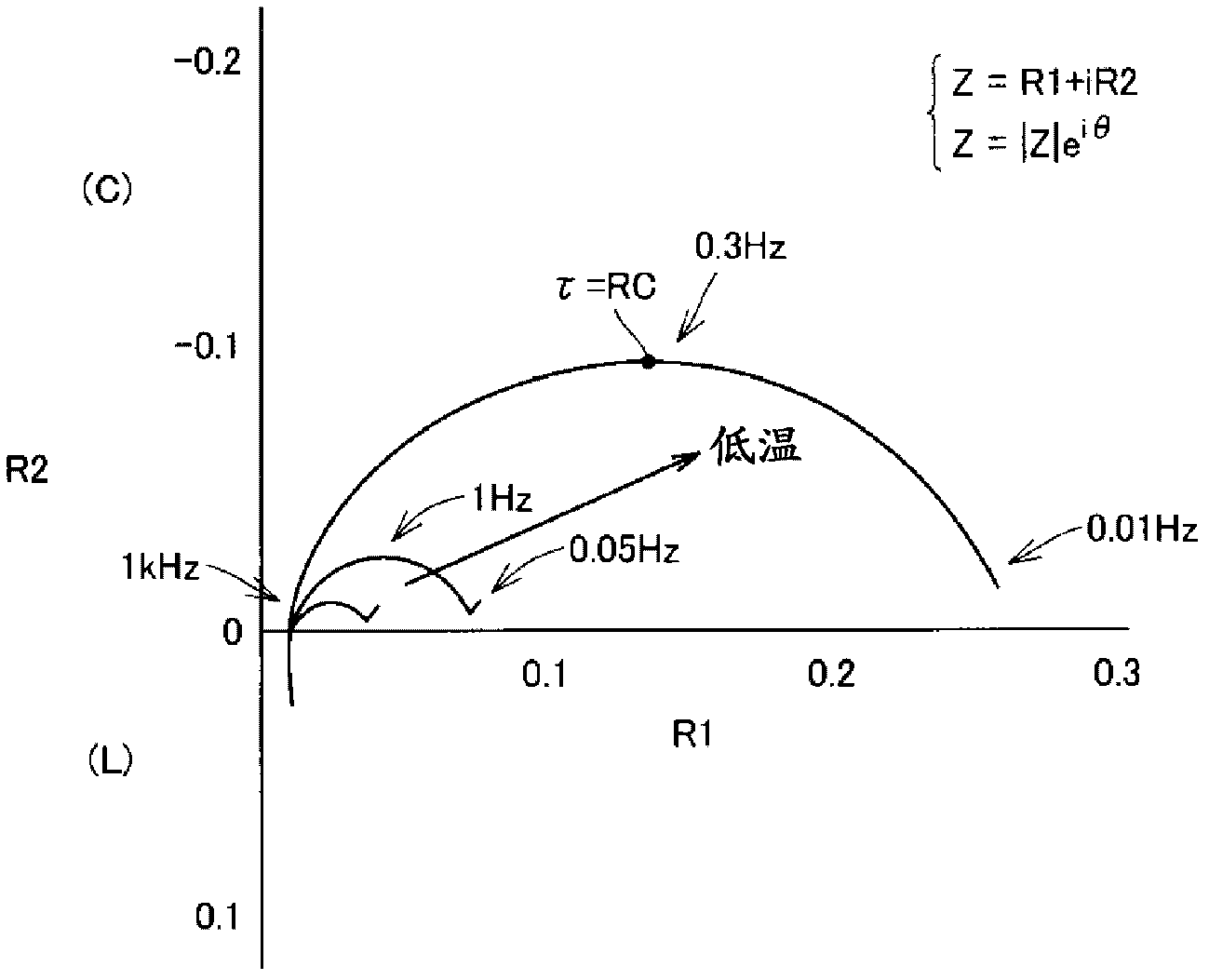
[0100] Picture 12 It is an equivalent circuit diagram of the electrode / electrolyte interface of the secondary battery 10. Reference Picture 12 The internal resistance of the secondary battery 10 mainly includes: negative electrode precipitation resistance R1-, negative electrode reaction resistance R2-, negative electrode electric double layer capacitor C-, positive electrode reaction resistance R+, positive electrode electric double layer capacitor C+, and electrolyte resistance Rsol.
[0101] The negative electrode precipitation resistance R1- is the charge transfer resistance of the negative...
Embodiment approach 3
[0107] In the third embodiment, the secondary battery 10 is a lithium ion battery, and when the precipitation of lithium (Li) in the negative electrode becomes a problem due to the ripple current in the charging direction, a ripple current is generated so that the average value of the ripple current is The discharge side is biased.
[0108] As a specific method, refer to Figure 9~Figure 11 , For example, by Picture 9 When the illustrated circuit implements the ripple generating device 20, the duty ratio command value d when the ripple rises may be set to a value smaller than 0.5. Or through Picture 9 In the case where the illustrated circuit implements the ripple generating device 20, the necessary energy source for raising the ripple is only the secondary battery 10. Here, even if the duty ratio command value d when the ripple temperature rises is set to 0.5, the ripple current biases the loss in the ripple generation device 20 to the discharge side, so this can be used.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com