Asparagus-pawpaw functional drink and its production method
A technology of functional drinks and asparagus leftovers, applied in the field of food processing, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory consumers, and achieve the effect of high quality, refreshing taste and refreshing taste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
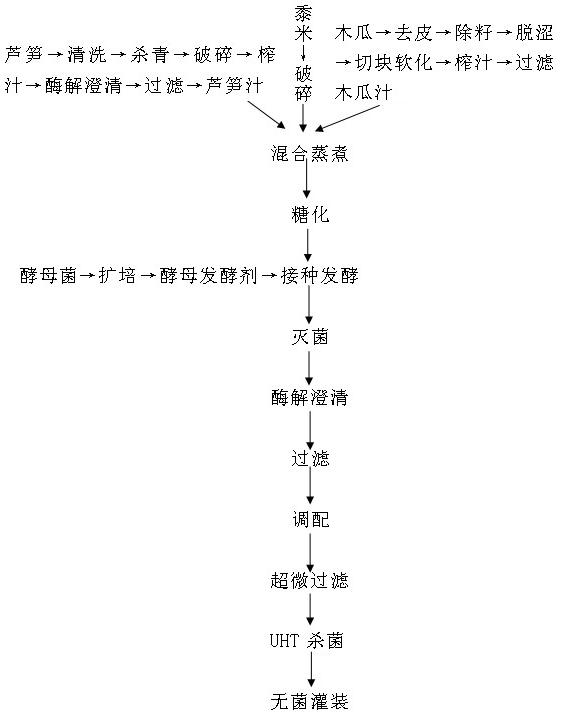
[0040] 1. Preparation of asparagus juice
[0041] (1) Raw material pretreatment:
[0042] Cleaning: Choose non-rotten asparagus outside the grade, canned asparagus, and leftovers from quick-frozen asparagus production as raw materials, and strictly wash the raw materials to remove microorganisms, sand, dead leaves and some pesticides attached to the surface of the raw materials to ensure the quality of the product. Quality stability.
[0043] Add 0.2‰ of multi-surfactant, 0.8~1‰ of vitamin C and 0.3‰ of citric acid to the cleaning solution to improve the cleaning effect and remove copper and other heavy metals in the fungicide.
[0044] Finishing: The cleaned raw materials should be cleaned with citric acid water at 95°C and 0.3‰ for three minutes. This cleaning process can maintain the color of the raw juice and the activity of inactivated enzymes to prevent browning and microbial corruption in subsequent processing procedures. , while removing part of the bitterness.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com