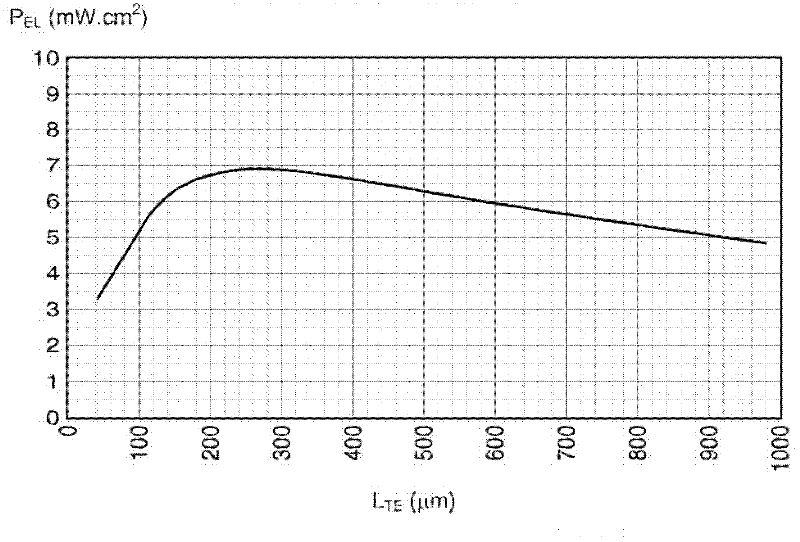
Deposition of thermoelectric materials by stamping
A technology of thermoelectric materials and polymer materials, which is applied in the directions of thermoelectric device junction lead-out materials, printing, and post-processing of printing, etc., which can solve the problems of heavy implementation and difficult large-scale application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] It is proposed herein that the internal stresses are limited due to the removal of solvent and polymer material by spray depositing the ink. The spraying conditions are chosen such that a part of the solvent evaporates when the deposition takes place. A porous layer is then obtained which will allow stress relaxation when the final removal of the additive takes place.
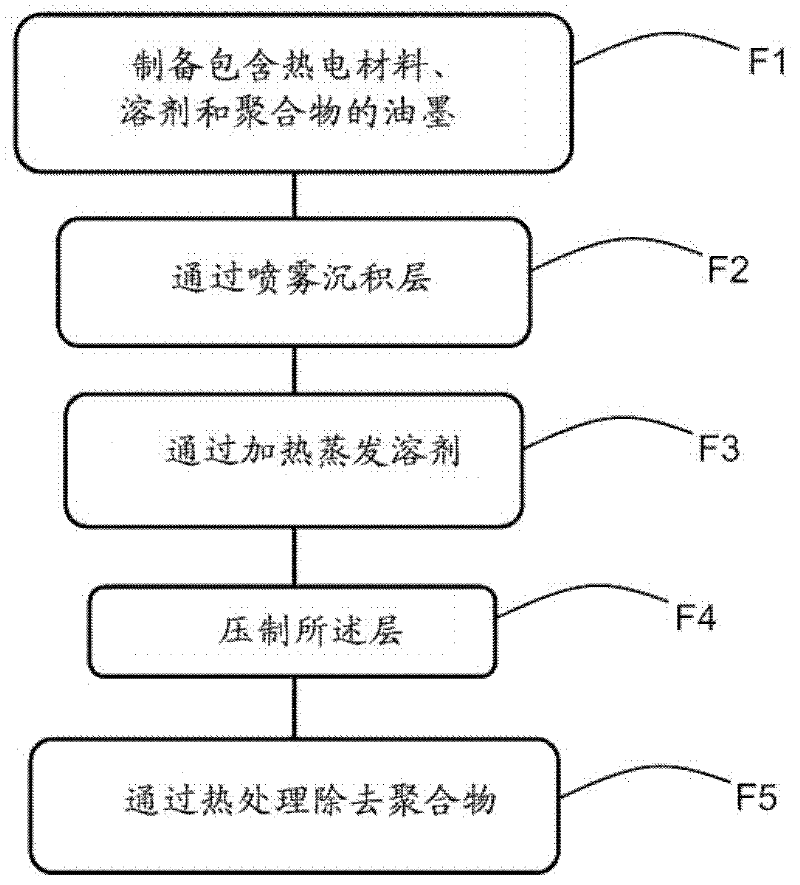
[0023] figure 2 The steps of a method of producing a layer of thermoelectric material with relaxed stress are shown in flow chart form.
[0024] In step F1, an ink compatible with spray printing techniques is prepared. The ink contains a thermoelectric material designed to form a thermocouple, a polymeric material and a solvent.
[0025] The thermoelectric material is preferably in the form of semi-metallic or semiconductor particles having a diameter comprised between 10 nm and 10 μm dispersed in a solvent. Thermoelectric materials can be selected from alloys of bismuth and tellurium, such as Bi fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com