Porous carbon-containing compounds as water carriers and cell size controlling agents for polymeric foams
A technology of porous carbon and compounds, applied in the field of extruded foam products, can solve the problems of increasing production costs and increasing downtime, and achieve the effect of increasing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] Composed of 75 wt% polystyrene (NOVA1600 from NOVA Chemical, PA) and 25 wt% powdered activated carbon (DARCO KB-G from Norit Americas, Texas) was prepared by extrusion process using an LMP twin extruder from Leistitz. Microporous compound (PS / PAC25).
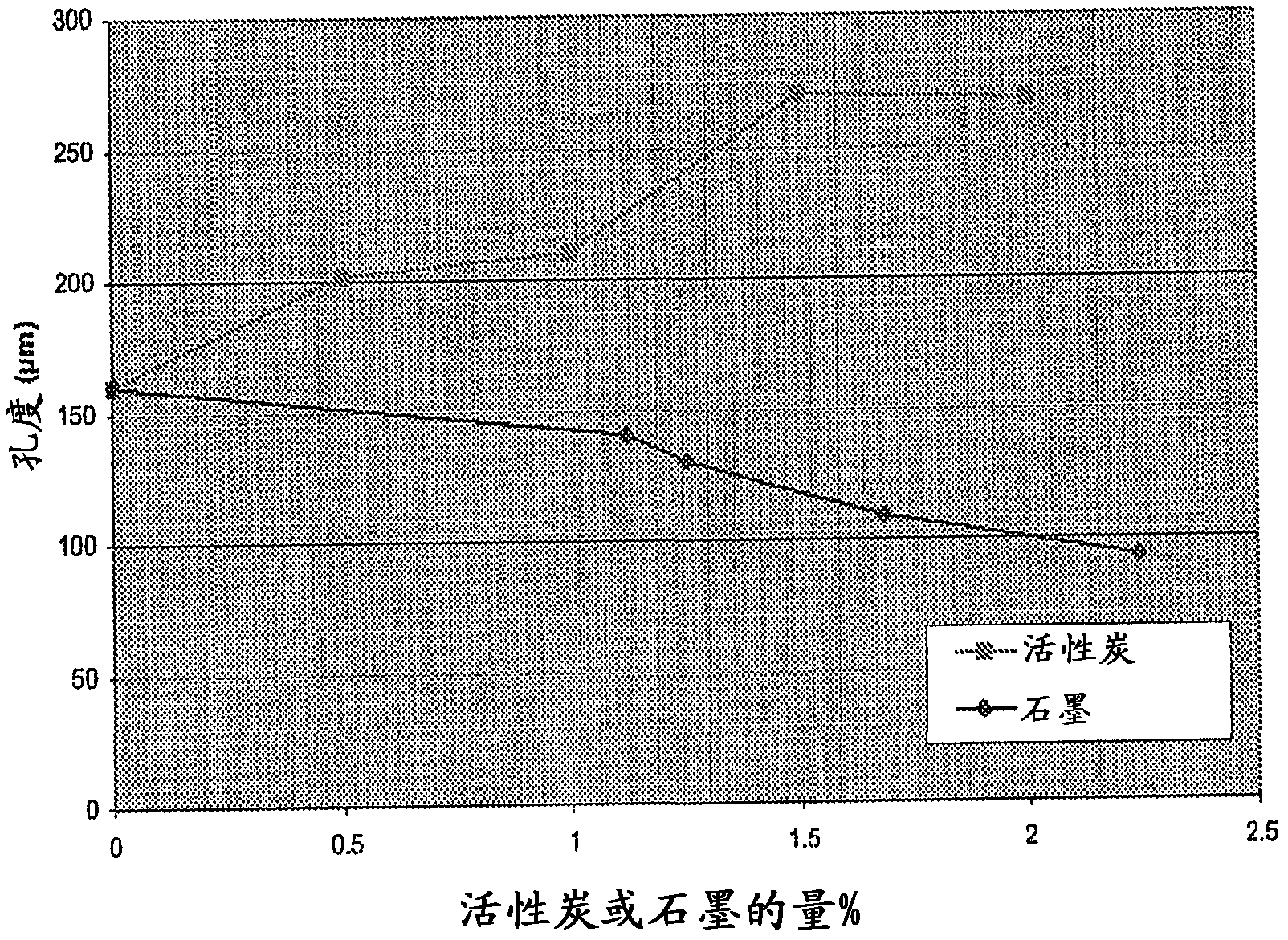
[0087] The porosity, pore size and density of the formed microporous compound PS / PAC25 were measured by mercury intrusion analysis. The results are listed in Table 1.
[0088] Table 1 Porosity analysis of microporous PS / PAC25 compounds
[0089] project
[0090] The microporous compound was further processed by (1) temperature and humidity conditioning and (2) steam impregnation. For temperature and humidity conditioning tests, the microporous compounds were placed in a conditioning chamber for 24 to 72 hours, where the temperature was controlled between 20°C and 30°C and the relative humidity was maintained between 50 and 98%. The PS / PAC25 compound particles have a size of about 2-3 mm. Table 2 summarizes t...
Embodiment 2
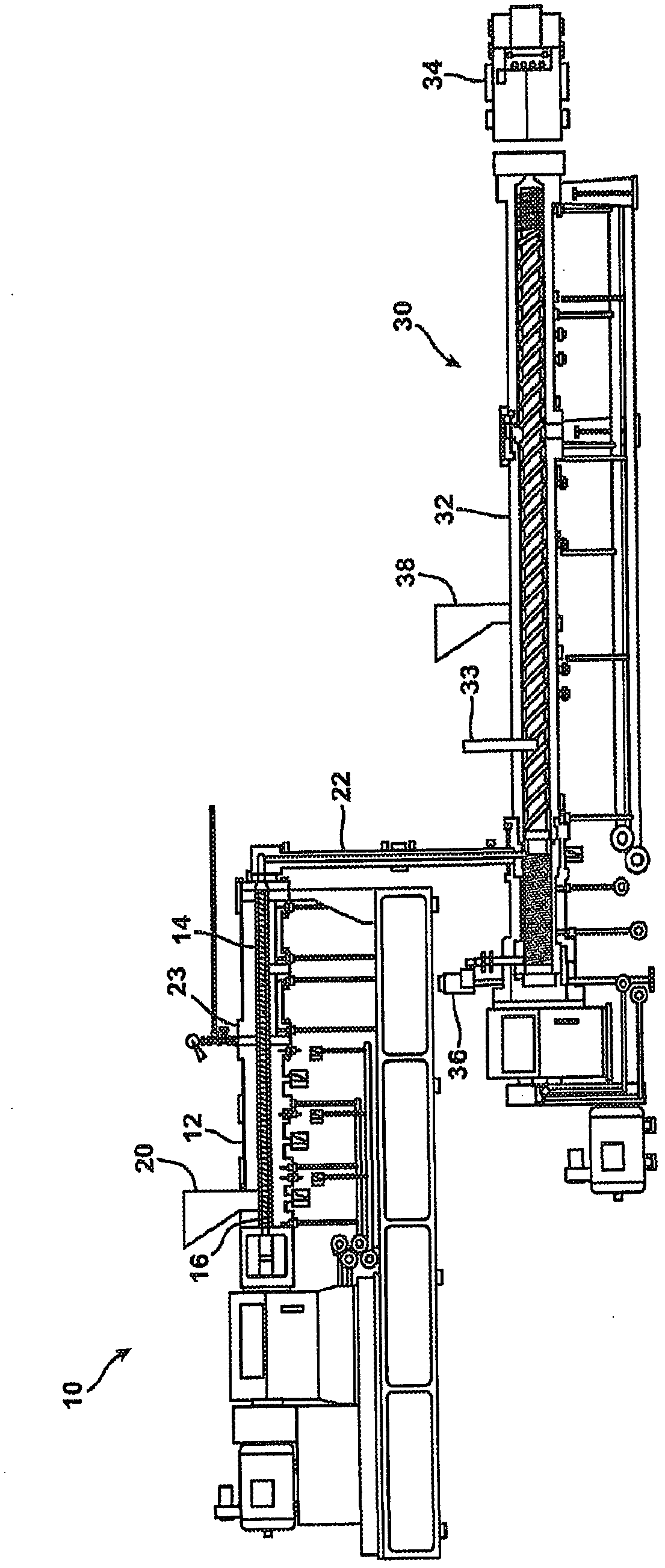
[0100] In the following samples and comparative samples, rigid polystyrene foam boards were produced by a twin-screw LMP extruder. Table 4 shows the processing operating conditions for the samples in the twin-screw extruder used to make foam boards with a width of 16 inches and a thickness of one inch.
[0101] Table 4
[0102] The processing conditions of the samples
[0103] wt% of HFC-134a
4
CO 2 wt%
2
Injection pressure, Kpa(psi)
13000-17000(1950-2400)
Mold melting temperature (℃)
110-130
Die pressure, Kpa(psi)
6900-8280(1000-1200)
Linear speed, m / min (feet / min)
5-10(16-35)
Output, kg / h
150-200
Die gap, mm
0.8-1.5
Vacuum KPa(inch Hg)
0-3.4(0-16)
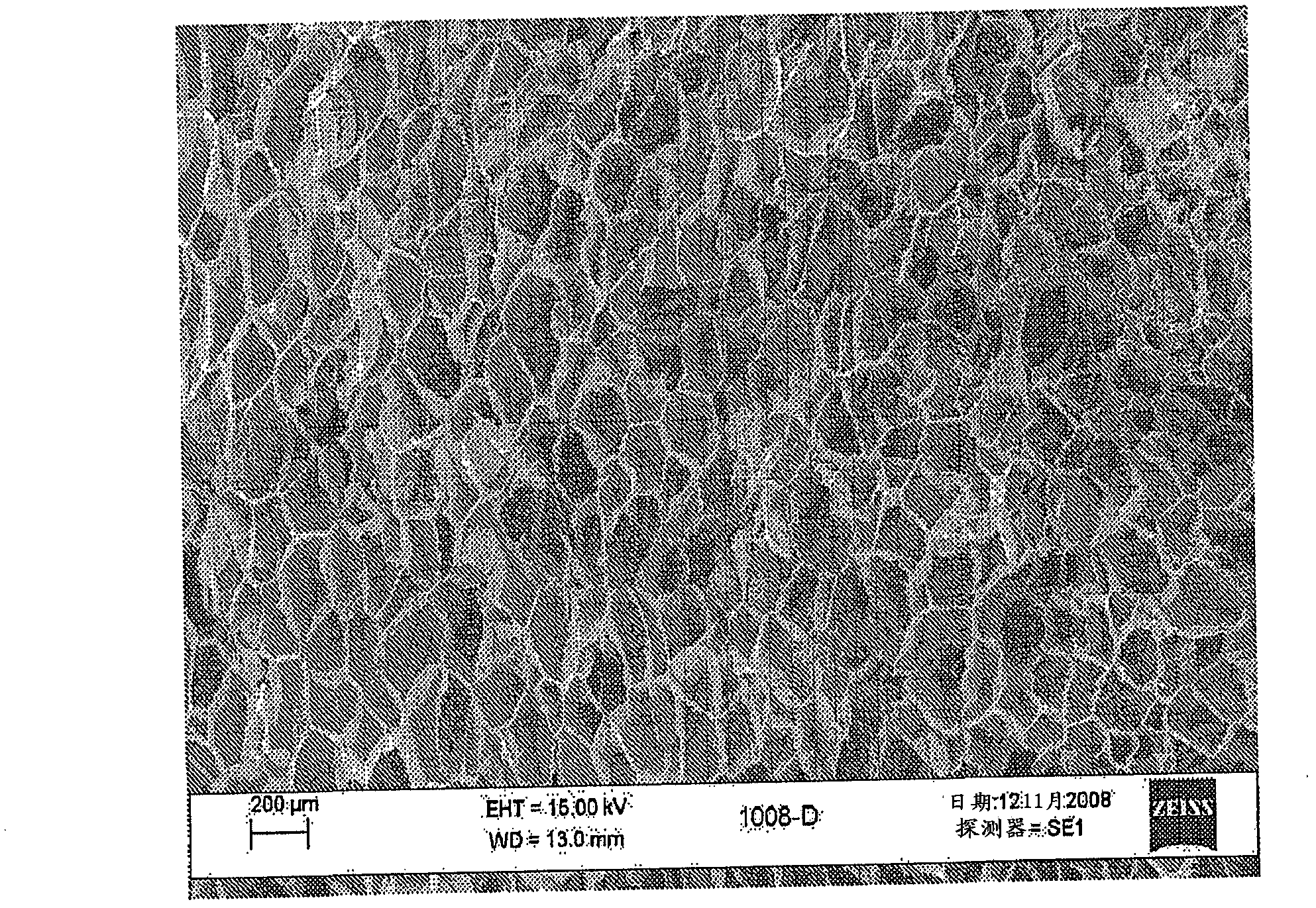
[0104] The results of Example 2 are summarized in Tables 5 and 6. Pore size was determined by Nikon Optiphot-2 light microscope and Clemex Vision image analysis software. Foam density was measured a...
Embodiment 3
[0112] The polystyrene resin used in this example was polystyrene (NOVA 1600 from NOVA Chemical Company, PA) with a melt index of approximately 5.2 and a molecular weight of 250,000. The microporous compound PS from Example 1 was mixed before feeding the microporous compound / polystyrene mixture into a co-rotating twin extruder (Leistritz ZSE-27 with D 27 mm and L / D 40) / PAC25 with the polystyrene.
[0113] Blowing agent carbon dioxide (from Praxair) was injected into the extruder at L / D 16 position (melting and mixing zone) via a model ISCO 1000D syringe pump. During the entire extrusion process, the temperature and pressure are maintained above the supercritical point, that is, the carbon dioxide remains in the supercritical stage before foaming at the end of the die.
[0114] Water was injected through a separate ISCO 1000D syringe pump at the L / D 26 location (transfer zone) close to the die. During the extrusion process prior to foaming, water remains in liquid phase acco...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com