Method for detecting abnormal events of wireless sensor network in distributed way
A wireless sensor and network anomaly technology, applied in the field of distributed detection, can solve the problems of unable to suppress data transmission loss, unscientific, monitoring, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
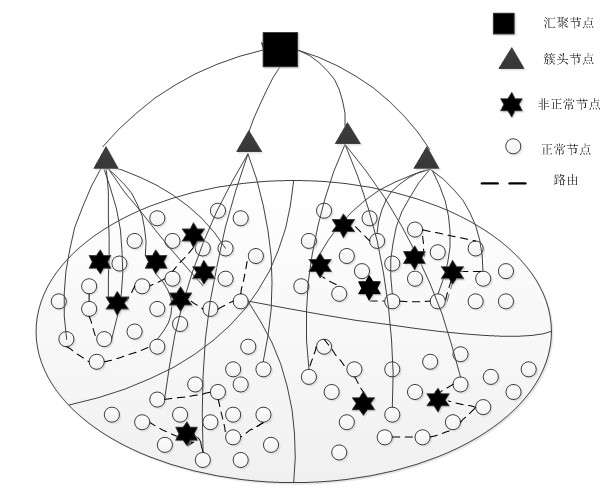
[0057] figure 1 Shown is the network model of clustering compressed sensing for the wireless sensor network in the present invention. Assume that the wireless sensor network of the present invention includes N sensor nodes, where N≥1. According to the size of the wireless sensor network, the value of N can be between tens and tens of thousands. The numbers of each sensor node can be set to 1, 2, 3...N respectively, and the numbers of each node are different from each other. Among them, the probability that the initial data of K sensor nodes is 1 is greater than or equal to 0.5 and is a fixed value. The K nodes The probabilities of initial data of 1 are different from each other; the initial data of other sensor nodes are always 0. The initial data is 1, which means that the node has an event, and the initial data is 0, which means that the node has no event. Referring to the actual wireless sensor network, the probability of occurrence of events on different nodes is relate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com