LED (Light-Emitting Diode) illumination dimming device
A technology for LED lighting and dimming devices, applied in lighting devices, light sources, electric light sources, etc., can solve the problems of large power supply and difficult layout and wiring of LED lamp beads, and achieve mature application technology, improve power supply utilization, and circuit work. Stable and reliable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
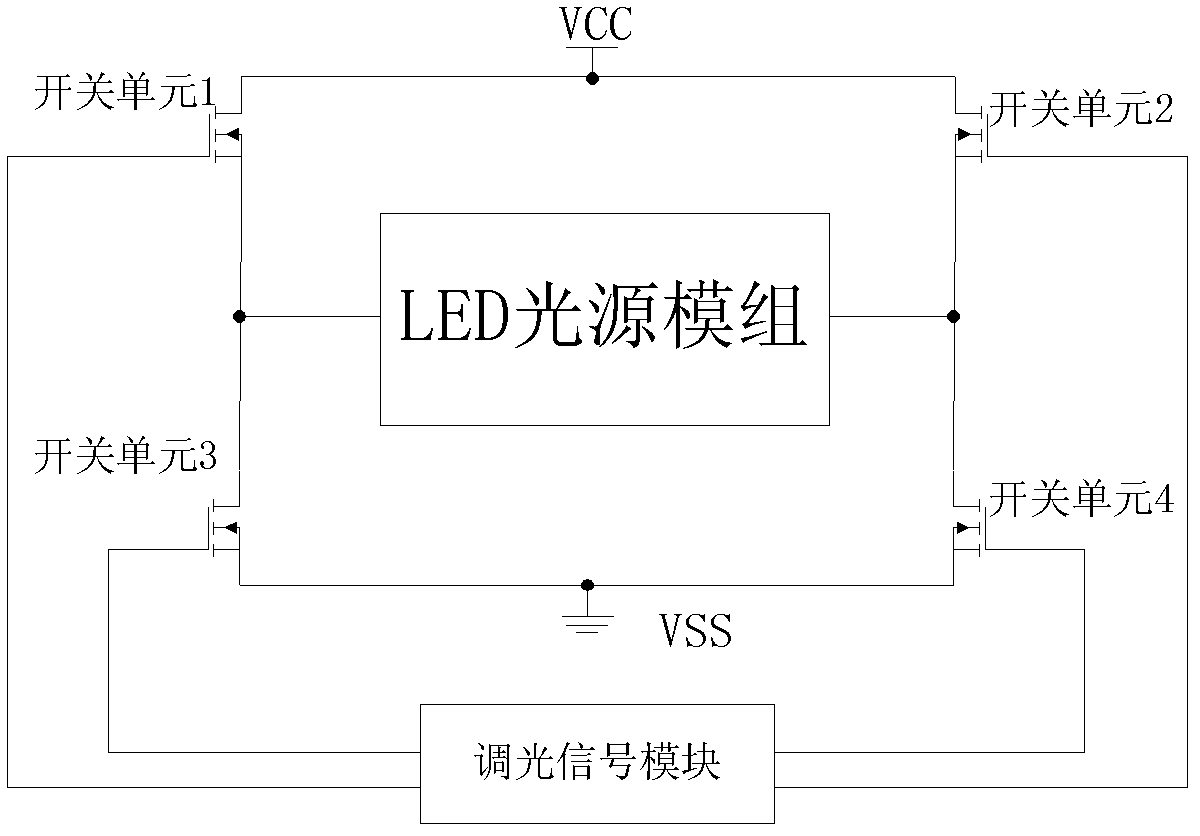
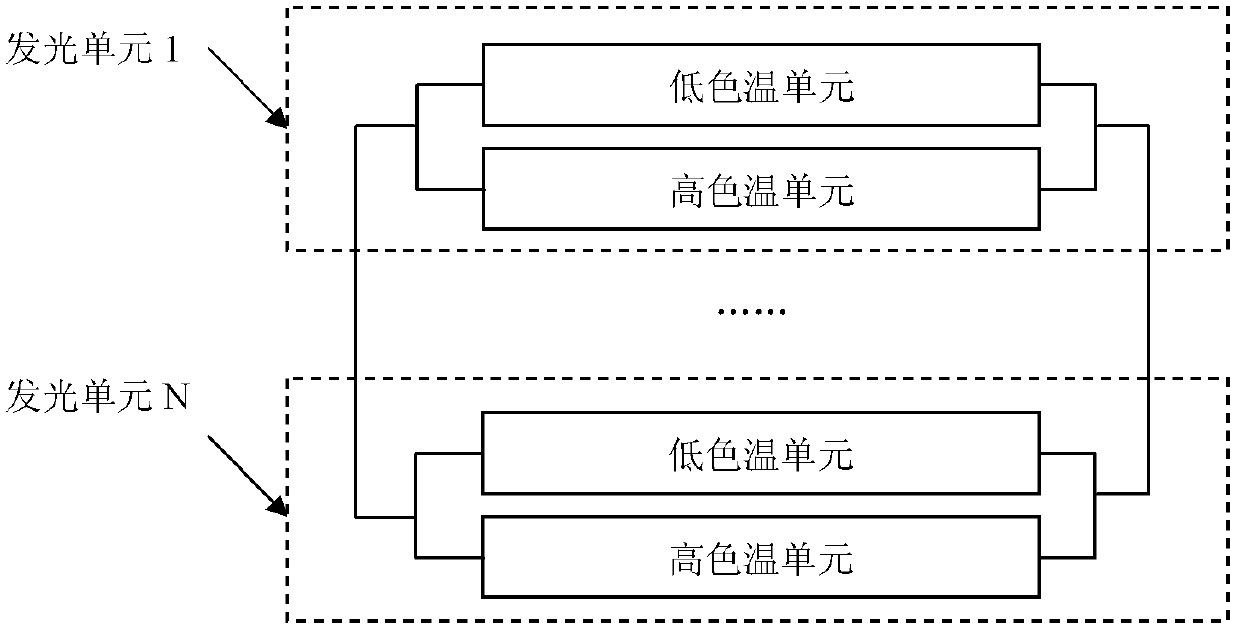
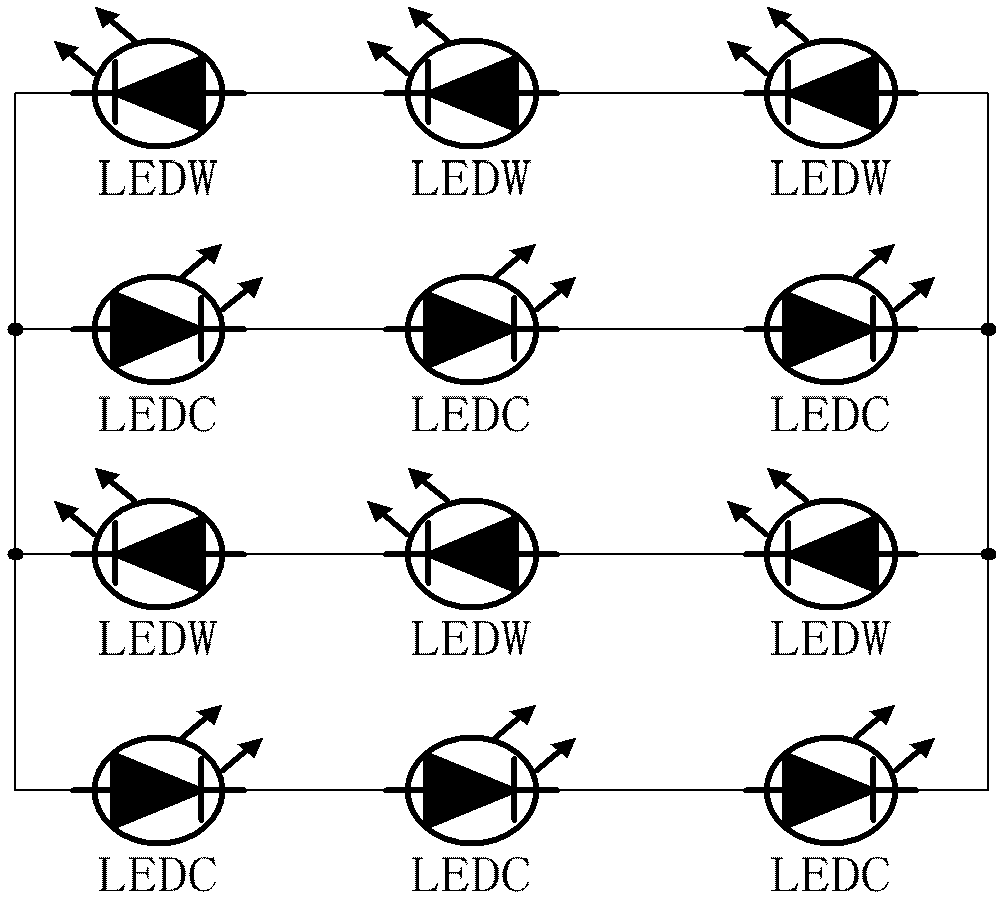
[0043] see Figure 6 , is the schematic diagram of the basic application circuit of the present invention. The control signals PWM1 and PWM2 are output by the control system. When the control signal PWM1 is at a high level, the control signal PWM2 is at a low level, and the control signal PWM1 controls the conduction of the MOS transistor Q1 and the MOS transistor Q4. , the high color temperature LEDC emits light; when the control signal PWM2 is at a high level, the control signal PWM1 is at a low level, and the control signal PWM2 turns on the MOS transistor Q2 and the MOS transistor Q3, and the low color temperature LEDW emits light. When the frequency of PWM1 and PWM2 is high enough, the light with high color temperature and low color temperature emitted by the LED will be mixed into a color temperature between high color temperature and low color temperature. By changing the high level time of PWM1 and PWM2, the color temperature can be achieved. adjustment.
Embodiment 2
[0045] see Figure 7 , is a preferred application circuit schematic diagram of the present invention, the control signals PWM1 and PWM2 are output by the control system, when the control signal PWM1 is at a high level, the control signal PWM2 is at a low level, and the control signal PWM1 controls the conduction of the MOS transistor Q1 to control The signal PWM1 reverses through the reverse gate B1 to turn off the MOS transistor Q3, the control signal PWM2 controls the MOS transistor Q2 to turn off, the control signal PWM2 passes through the reverse gate to turn on the MOS transistor Q4, the current flows through the MOS transistor Q1, and flows through the high The color temperature LEDC returns to the VSS terminal through the MOS tube Q4, and the high color temperature LEDW emits light; when the control signal PWM2 is at a high level, the control signal PWM1 is at a low level, and the control signal PWM2 controls the conduction of the MOS tube Q2, and the control signal PWM2...
Embodiment 3
[0047] see Figure 8 , is another preferred application circuit schematic diagram of the present invention, the control signal PWM is output by the control system, when the control signal PWM is at a high level, the MOS transistor Q1 is turned on, and the control signal turns off the MOS transistor Q3 through the reverse gate B1, The control signal passes through the reverse gate B3 to turn off the MOS tube Q2, the control signal passes through the reverse gate B3 and then through the reverse gate B2 to turn on the MOS tube Q4, the current flows through the MOS tube Q1, flows through the high color temperature LEDC, and passes through the MOS tube Q4, back to the VSS terminal, the high color temperature LEDC emits light; when the control signal PWM is low, the MOS transistor Q1 is turned off, the control signal passes through the reverse gate B1 to turn on the MOS transistor Q3, and the control signal passes through the reverse gate B3 to make the MOS transistor Q4 turn on. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com