Land use change modeling method and system implemented in combination with spatial filtering
A technology of spatial filtering and modeling methods, applied in the field of geographic information science, can solve problems such as model accuracy and sensitivity decline, algorithm rule setting cannot be comprehensive, and land category evaluation result deviations, etc., to improve the overall fitting accuracy and eliminate Spatial autocorrelation, full-featured effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
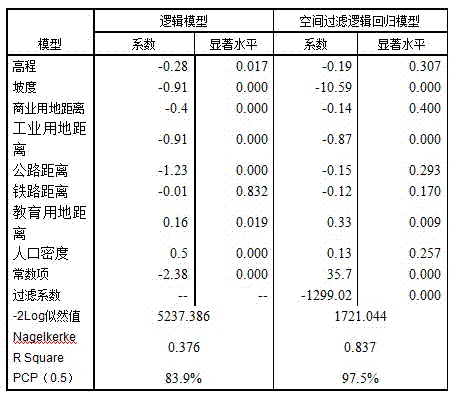
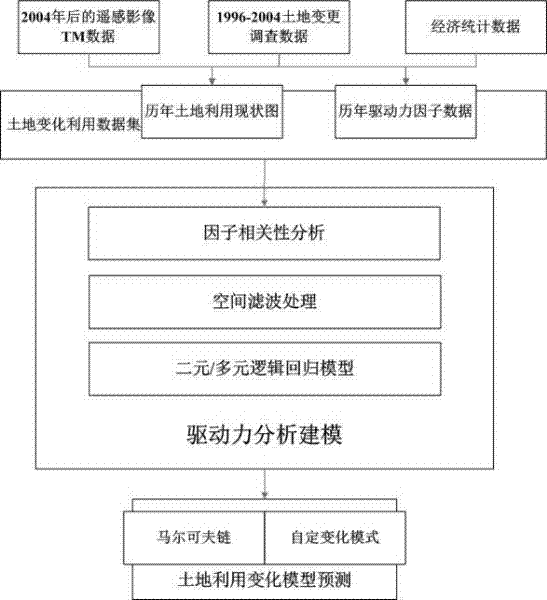
[0018] The specific implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and implementation drawings. The data in the embodiment of the present invention is the modeling process of land use change in Shenzhen City from 1996 to 2008, and this data does not limit the scope of the present invention. This embodiment includes three main components, namely, preprocessing of geographic data and construction of data sets, construction of logistic regression model combined with spatial filtering, and prediction using land use change model.
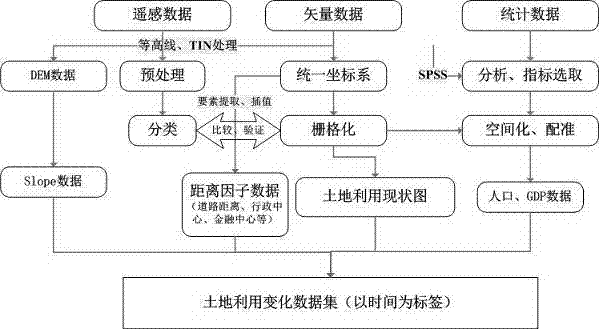
[0019] Step 1: The process of preprocessing geographic data and building datasets is as follows: figure 2 As shown, follow the following requirements:
[0020] First of all, it is necessary to adopt the same land use classification system, the purpose of which is to ensure the convenience of model analysis and the connection between data. For example, the present ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com