Method, device and transmission system for transmitting and receiving data block
A data block and sender technology, applied in network traffic/resource management, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems that cannot meet the needs of a large number of terminal access
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
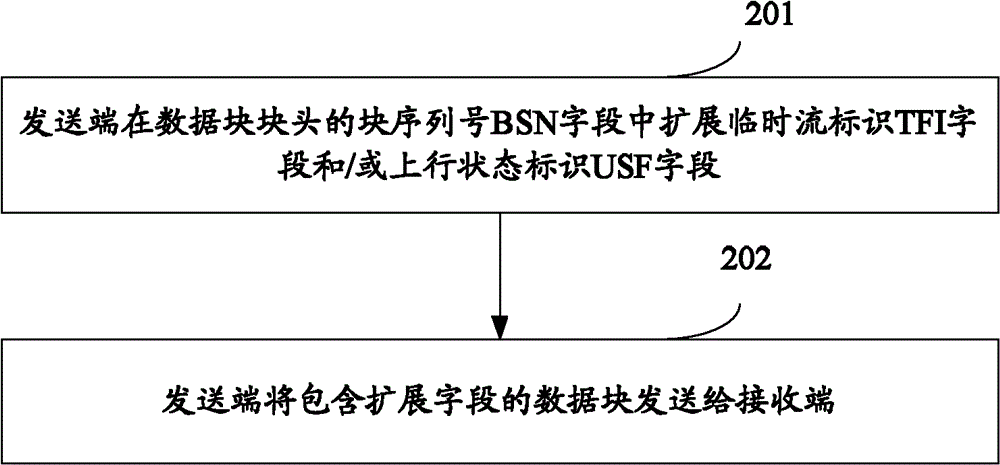
[0037] see figure 2 , which is a flowchart of an embodiment of a method for sending a data block in the present invention, including the following steps:
[0038] Step 201: The sending end extends the temporary flow identifier TFI field and / or the uplink state identifier USF field in the block sequence number BSN field of the data block header;
[0039] Wherein, the sending end expands the TFI field and / or the uplink status identifier USF field in the BSN field of the data block header includes: the sending end extends the temporary flow identifier TFI field in the block sequence number BSN field of the uplink data block header; the sending end Extend the TFI field and / or the uplink status identifier USF field in the BSN field of the block header of the downlink data block.
[0040] Step 202: the sending end sends the data block including the extension field to the receiving end.
[0041] It can be seen from the above embodiments that at the sending end, one or several bits...
Embodiment 2
[0043] see image 3 , which is a flow chart of another embodiment of a method for sending a data block in the present invention. In this embodiment, the terminal acts as a sending end to extend the TFI field in the BSN field of the block header of the uplink data block. The method includes the following steps:
[0044] Step 301: The terminal extends the temporary flow identifier TFI field in the block sequence number BSN field of the uplink data block header;
[0045] For example, if there is only one BSN1 field in the uplink RLC / MAC data block header, one or more bits can be used in the BSN1 field to extend the TFI field, see Pic 4-1 , Pic 4-1 It is a schematic structural diagram of extending the TFI field in a BSN field of the uplink RLC / MAC data block header in the present invention,
[0046] For another example, there are two BSN fields BSN1 and BSN2 in the RLC / MAC data block header, and one or more bits can be used in the BSN1 and BSN2 fields to extend the TFI field, ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] see Figure 5 , which is a flow chart of another embodiment of a method for sending a data block in the present invention. In this embodiment, the base station, as the sending end, extends the TFI field and / or the uplink state identifier USF in the BSN field of the block header of the downlink data block field, the method includes the following steps:
[0053] Step 501: the base station extends the TFI field and / or the uplink state identifier USF field in the BSN field of the downlink data block header;
[0054] Since the field to be extended in the downlink data block header may be the TFI field or the USF field, or the TFI field and the USF field may be extended simultaneously, therefore, the TFI field and / or the USF field may be extended in the BSN field.
[0055] Among them, in addition to the following Pic 4-1 and 4-2 In addition to the extended TFI field of the structure, you can also follow the Figure 6-1 In the manner shown, one or more extended USF fields...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com