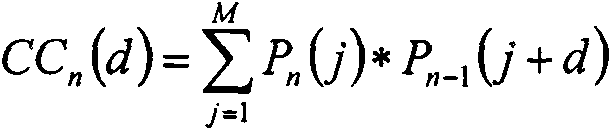Cardiac Axial Movement Correction Method for Myocardial Spectrum Perfusion Imaging
A technology of axial movement and correction method, which is applied in image data processing, equipment for radiological diagnosis, medical science, etc., can solve problems such as misdiagnosis, false positive, myocardial blood perfusion image defects, etc., to broaden the scope of application, The effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
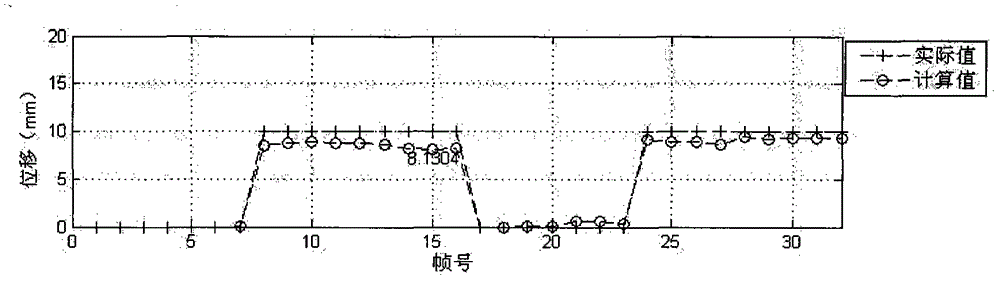
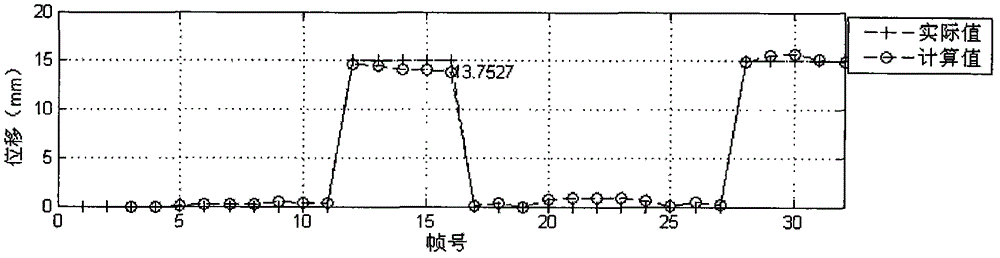
[0027] Correction for a single move
[0028] This embodiment is used to simulate the situation that all projections after a certain frame have the same displacement during the acquisition process.
[0029] Collection of projections:
[0030] Imaging instrument SPECT, injected in myocardial model 99 Tc m Myocardial perfusion imaging was performed 30 minutes after injection at 1 mCi. The probe was rotated from right anterior oblique 45° to left posterior oblique 45°. The angular interval between frames was 6°. Each probe had 16 frames, and a total of 32 frames were collected. A low-energy high-resolution collimator was selected, the acquisition matrix was 64×64, the magnification factor was 1.46, and each frame was collected for 20s.
[0031] During data acquisition, the phantom was manually moved, and the actual size of the movement was determined by a ruler fixed on the examination table.
[0032] data processing:
[0033] (1) After the projection data collection is compl...
Embodiment 2
[0055] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that steps (1) and (2) are implemented by manually moving to correct the displacement of the projection.
Embodiment 3
[0057] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that step (8) uses other criteria to stop the iterative process, such as comparing the difference between the corrected projection and the reprojection, such as the mean square error of each pixel, and uses the established difference criteria to stop the iteration.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com