Operation of organic light emitting diodes by means of pulse width modulation
A technology of pulse width modulation and light-emitting diodes, applied in the direction of electroluminescence light source, light source, electric light source, etc., can solve the problems affecting OLED capacitance, etc., and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and precise detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
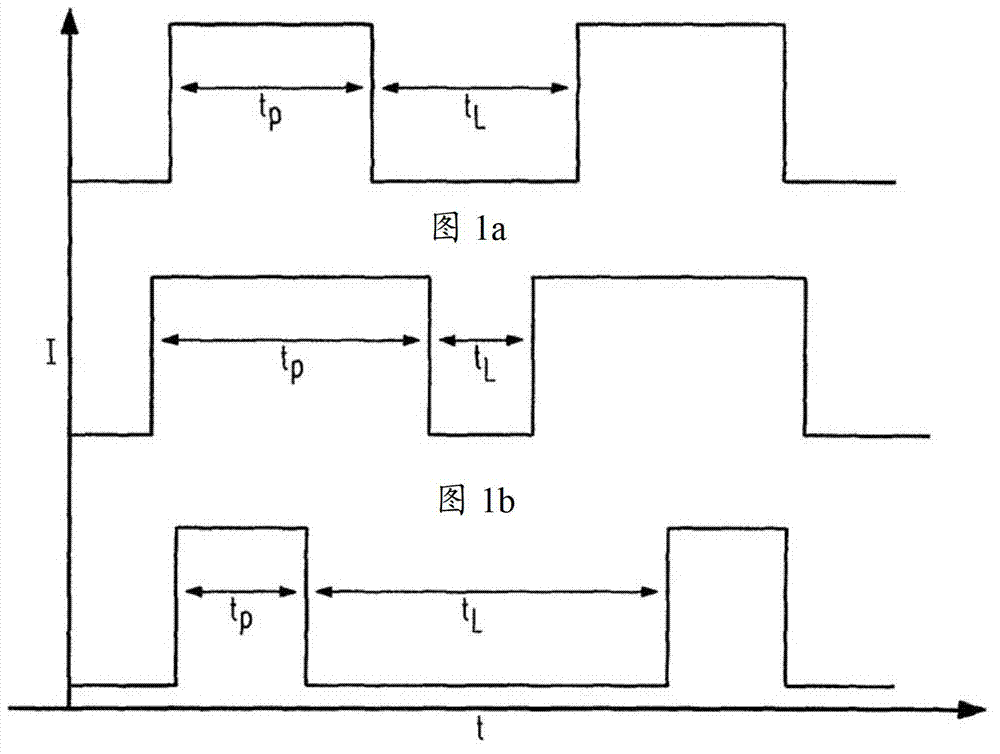
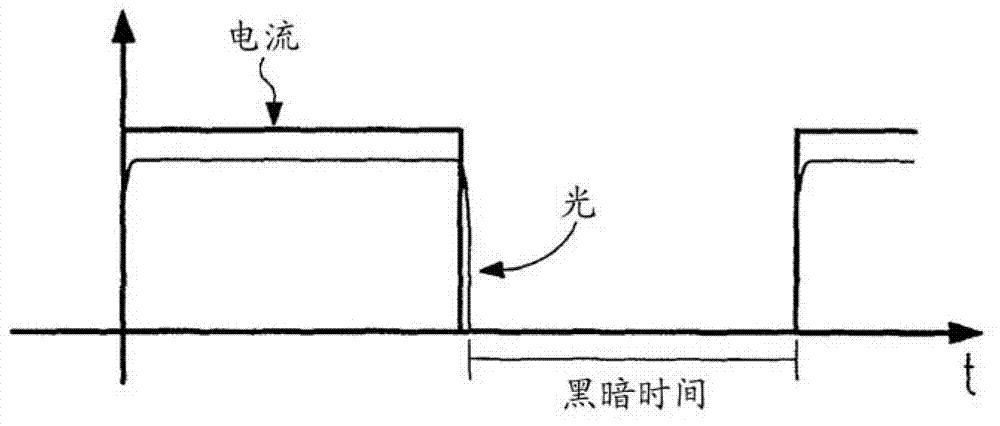
[0063] Figure 5 A driver circuit 1 according to the invention is shown, which can implement the driver method according to the invention. In this case, the driver circuit 1 is connected to the OLED 2 . Here, the drive circuit 1 includes a drive unit 3 that supplies current to the OLED. The power supply to OLED 2 takes place by means of pulse width modulation (PWM). The drive unit 3 is controlled by a control unit 4 . The control unit 4 controls the drive unit 3 in such a way that it adjusts the PWM current pulses, in particular their amplitude and pulse width t P , and to adjust the PWM vacancy, especially its width t L . Furthermore, the control unit 4 is suitable, for example, as Figure 4 As shown, the falling edge at the end of the PWM current pulse of the OLED 2 is shortened using circuit technology, for example by short-circuiting. This avoids afterglow of OLED 2 in PWM vacancy. To this end, for example, a low-impedance jumper conductor is connected in parallel ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com