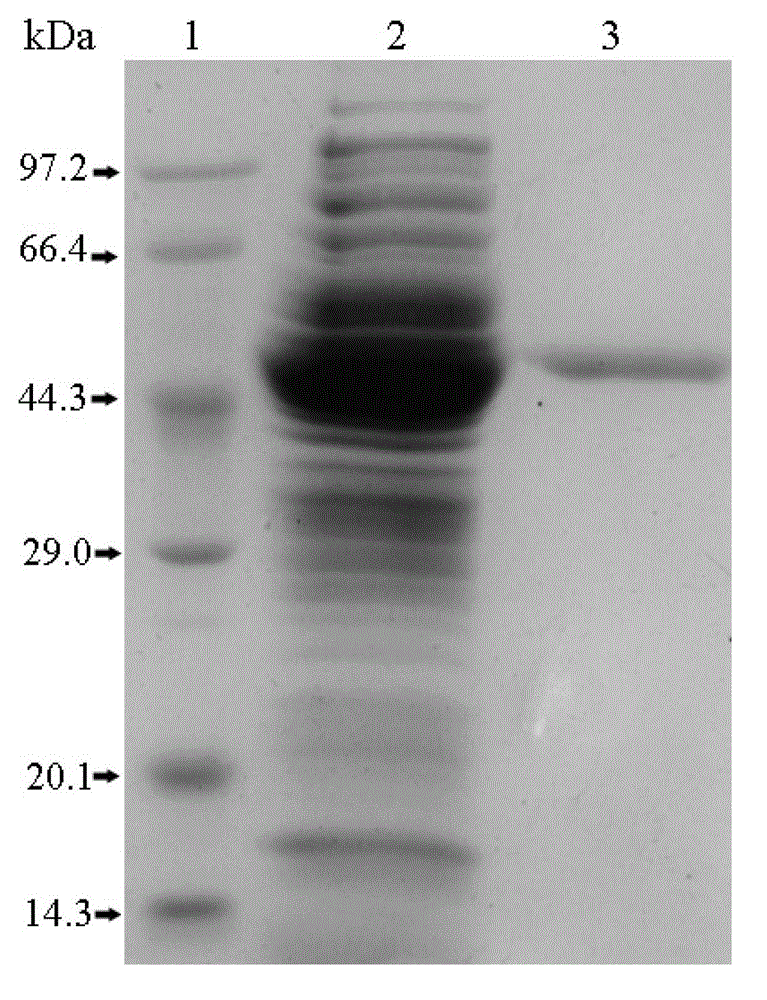
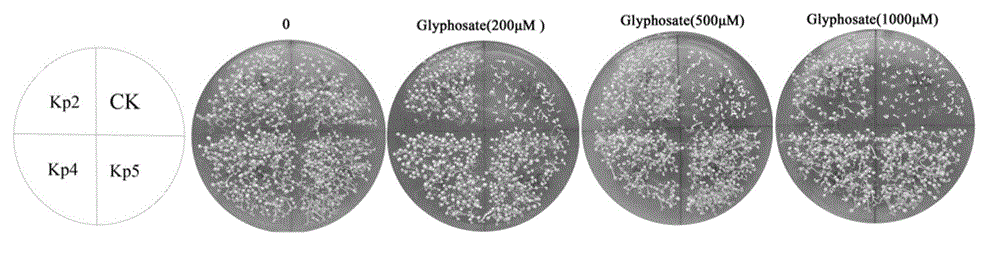
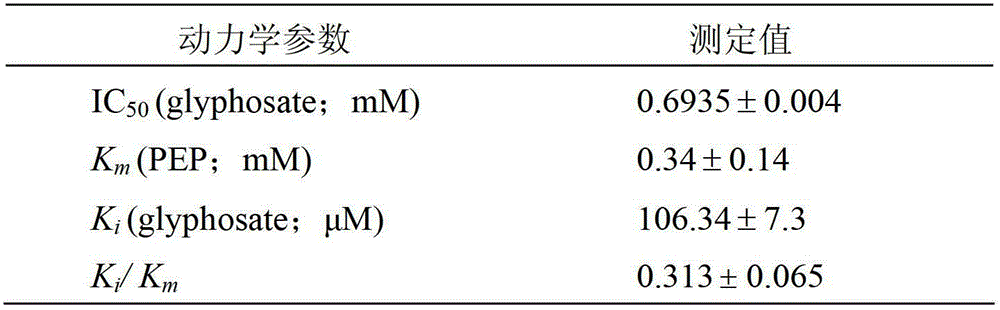
EPSP synthase gene from Klebsiella pneumoniae 342 and application of EPSP synthase gene
A technology of Klebsiella and EPSP synthase, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 DNA fragment cloning of high tolerance to glyphosate
[0029] 1. Collection of soil samples in paddy fields where glyphosate is frequently used
[0030] Soil samples were collected from orchards that had been used at least four times a year and had been used continuously for more than ten years.
[0031] 2. Screening of glyphosate-resistant strains
[0032] Weigh 1g of the orchard soil sample frequently used by glyphosate, add 1ml of 0.9% (w / v) sodium chloride solution, shake and mix at 5000 rpm, centrifuge gently at 3000 rpm, pour off the supernatant, and then add 0.9% (w / v) 1ml of sodium chloride solution, shake and mix at 5000 rpm, let it stand on ice for 10 minutes, draw 150 μl of the solution, spread it and culture it in LB solid medium containing 60mM glyphosate for 24 hours. Inoculate the grown single colony into a test tube added with 1.6ml LB liquid medium, cultivate at 28°C for 48h, then draw 150μl of the culture solution and spread it again and cu...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 Sequence analysis of DNA fragments highly tolerant to glyphosate
[0042] The highly tolerant glyphosate plasmid pAroA obtained by screening in Example 1 by step-by-step sequencing method k.pneumonia Full sequence DNA sequencing. Analysis results show that the fragment is 2100bp in size, which contains a reading frame of 1284, its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO 1, and it encodes 428 amino acids, and its sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO 2. .
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Artificial synthesis and screening of EPSP synthase gene highly tolerant to glyphosate
[0044] Cloning the above plasmid containing pAroA by gene synthesis [Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32, e98] k.pneumonia 26 primers were designed, and the EPSP synthase gene of the present invention was synthesized and screened. The designed primers are as follows:
[0045] 1. KP-1:Tm=54,60mer
[0046] GGA, TCC, ATG, GAA, TCC, CTG, ACG, TTA, CAA, CCC, ATC, GCA, CGC, GTA, GAG, GGC, ACC, GTG, AAC, CTG
[0047] 2. KP-2:Tm=54,60mer
[0048] GAG,CGG,CCA,GCA,GCA,GCG,CGC,GGT,TGG,AGA,CGC,TTT,TCG,AAC,CTG,GCA,GGT,TCA,CGG,TGC
[0049] 3. KP-3:Tm=54,60mer
[0050] TGG, CCC, GCG, GCA, CGA, CGG, TGC, TGA, CCA, ACC, TGC, TGG, ACA, GCG, ACG, ATG, TGC, GCC, ATA, TGC
[0051] 4. KP-4:Tm=54,60mer
[0052] GAT, AGG, GTA, TAT, TGA, ACC, CCC, AGC, GCA, CTC, AGG, GCA, TTC, AGC, ATA, TGG, CGC, ACA, TCG, TCG
[0053] 5. KP-5:Tm=54,60mer
[0054] TGC, CGA, CCG, CAC, CCG, CTG, CGA, AGT, GAC,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com