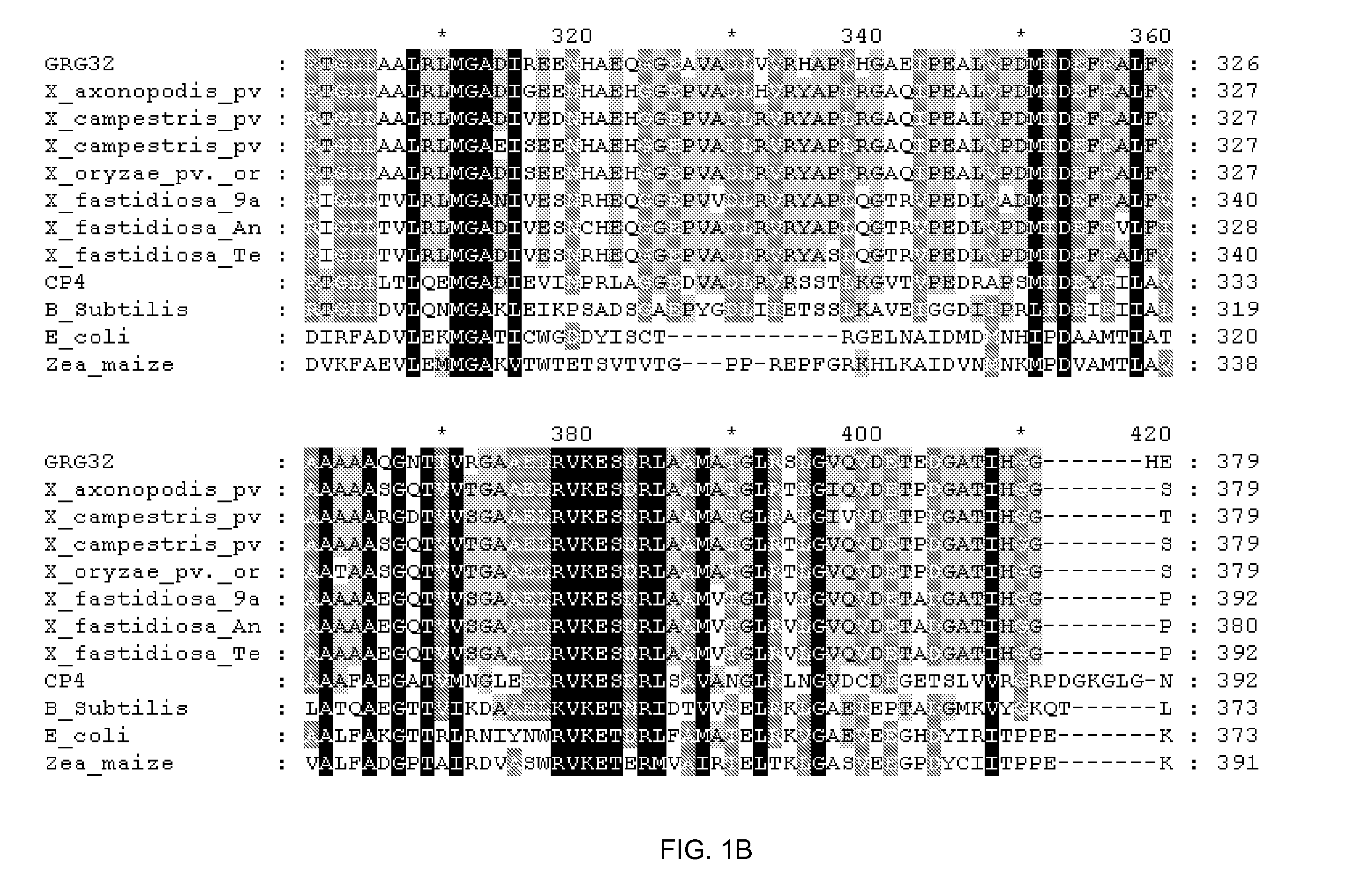
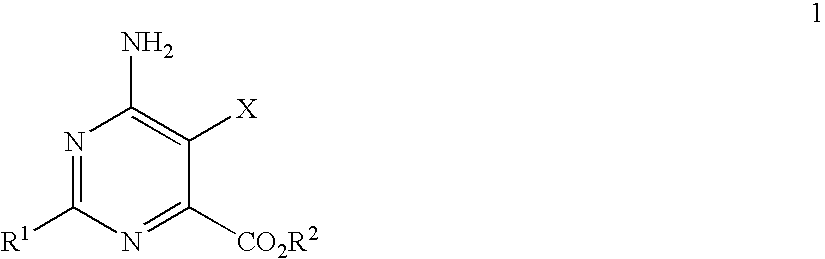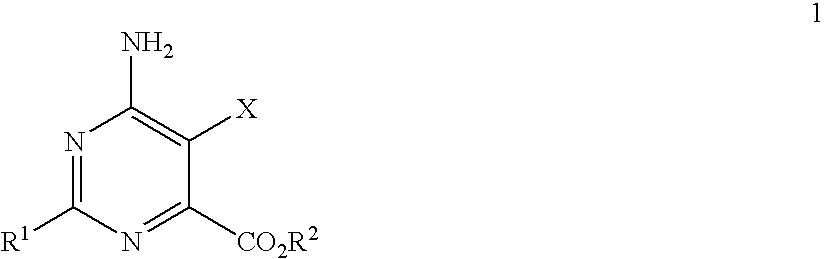Patents
Literature
65 results about "EPSP synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
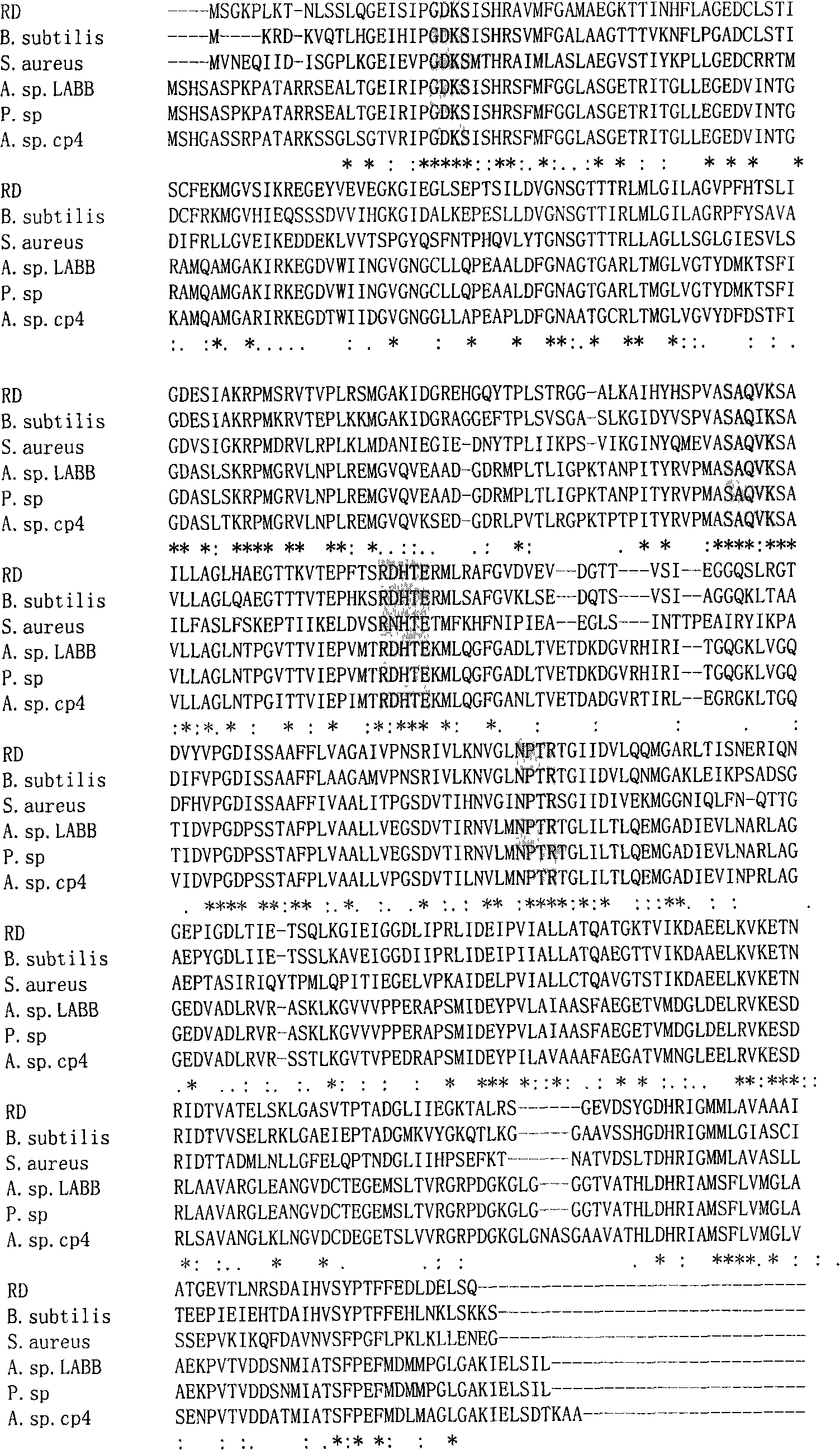
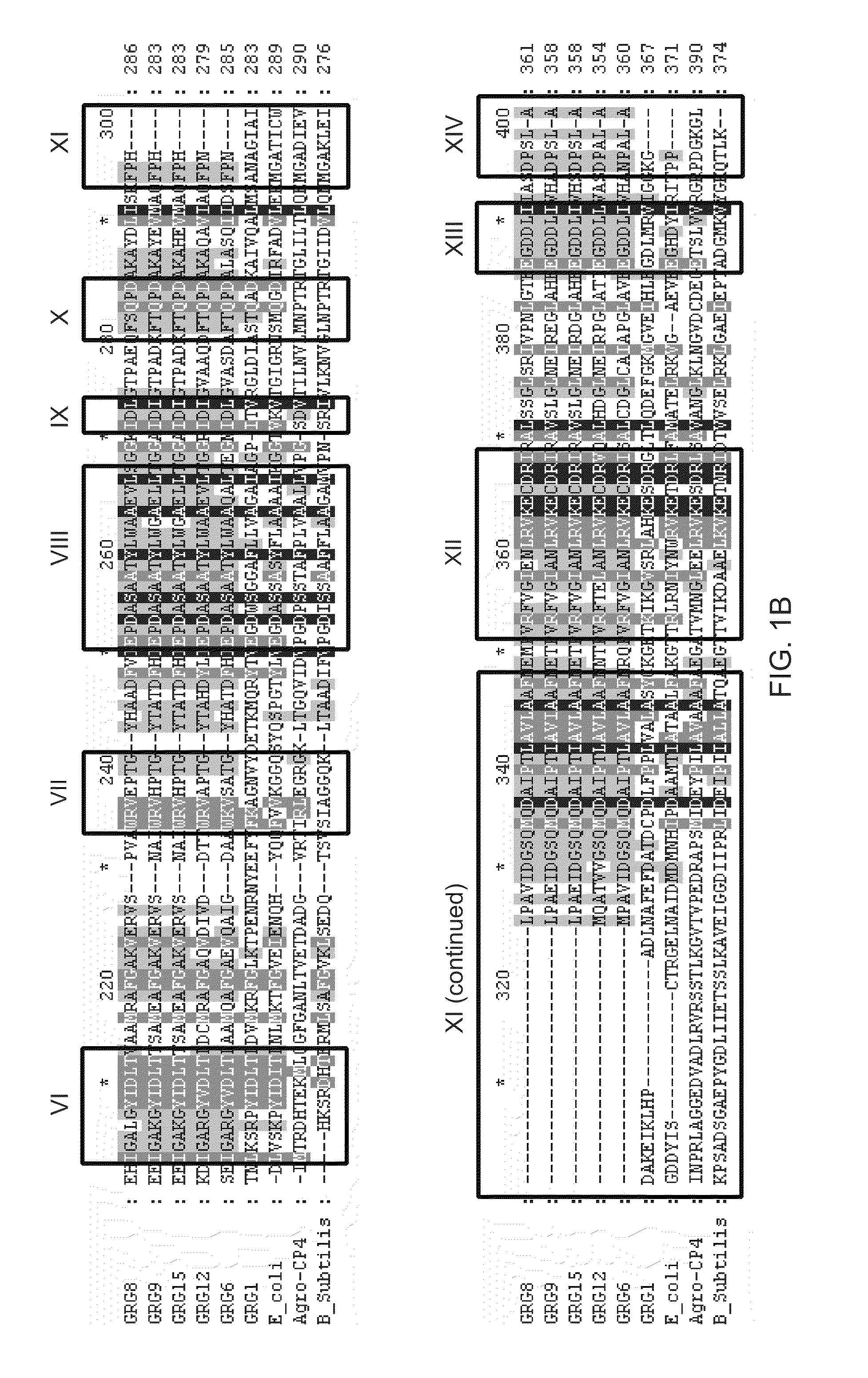
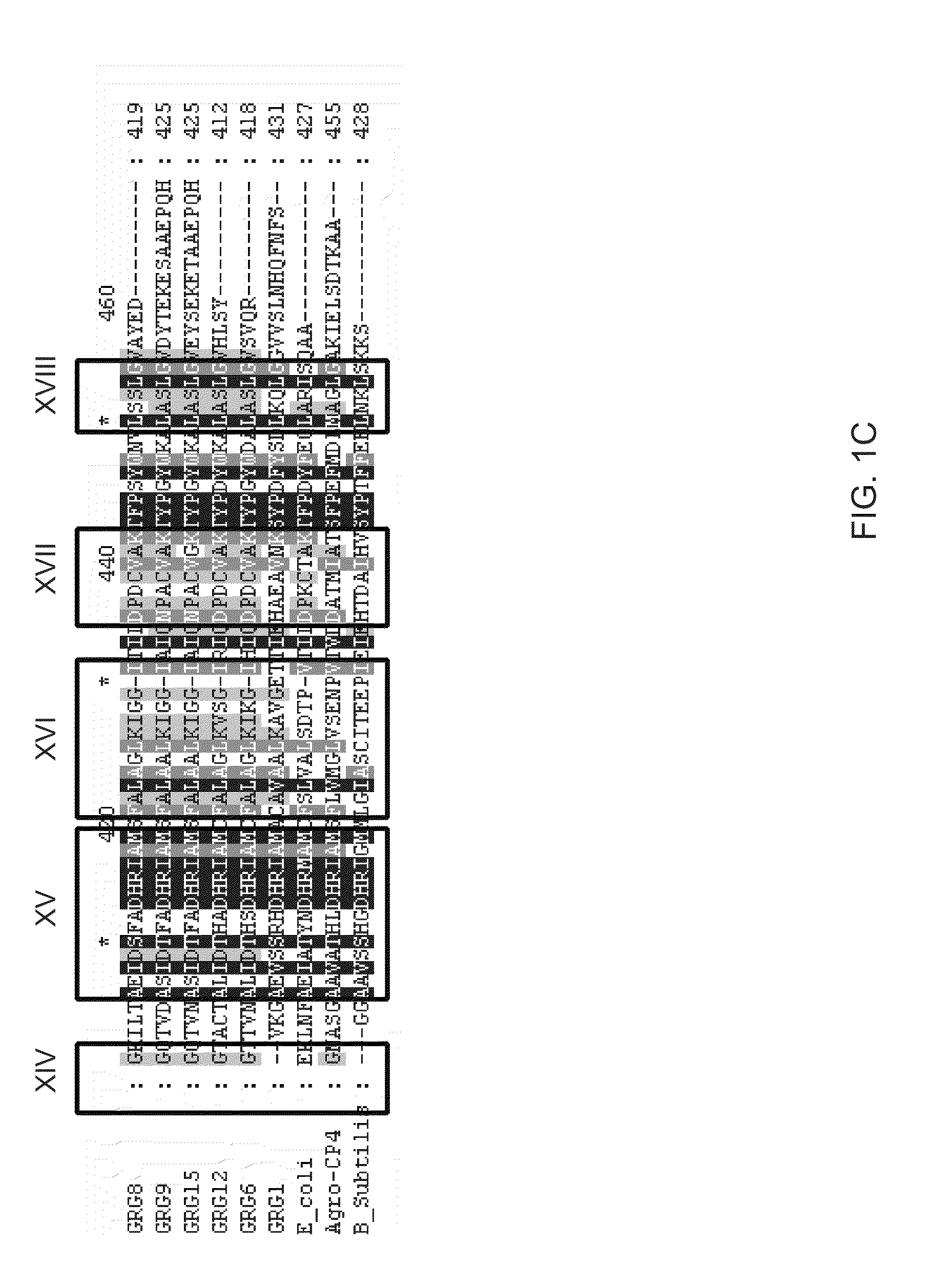
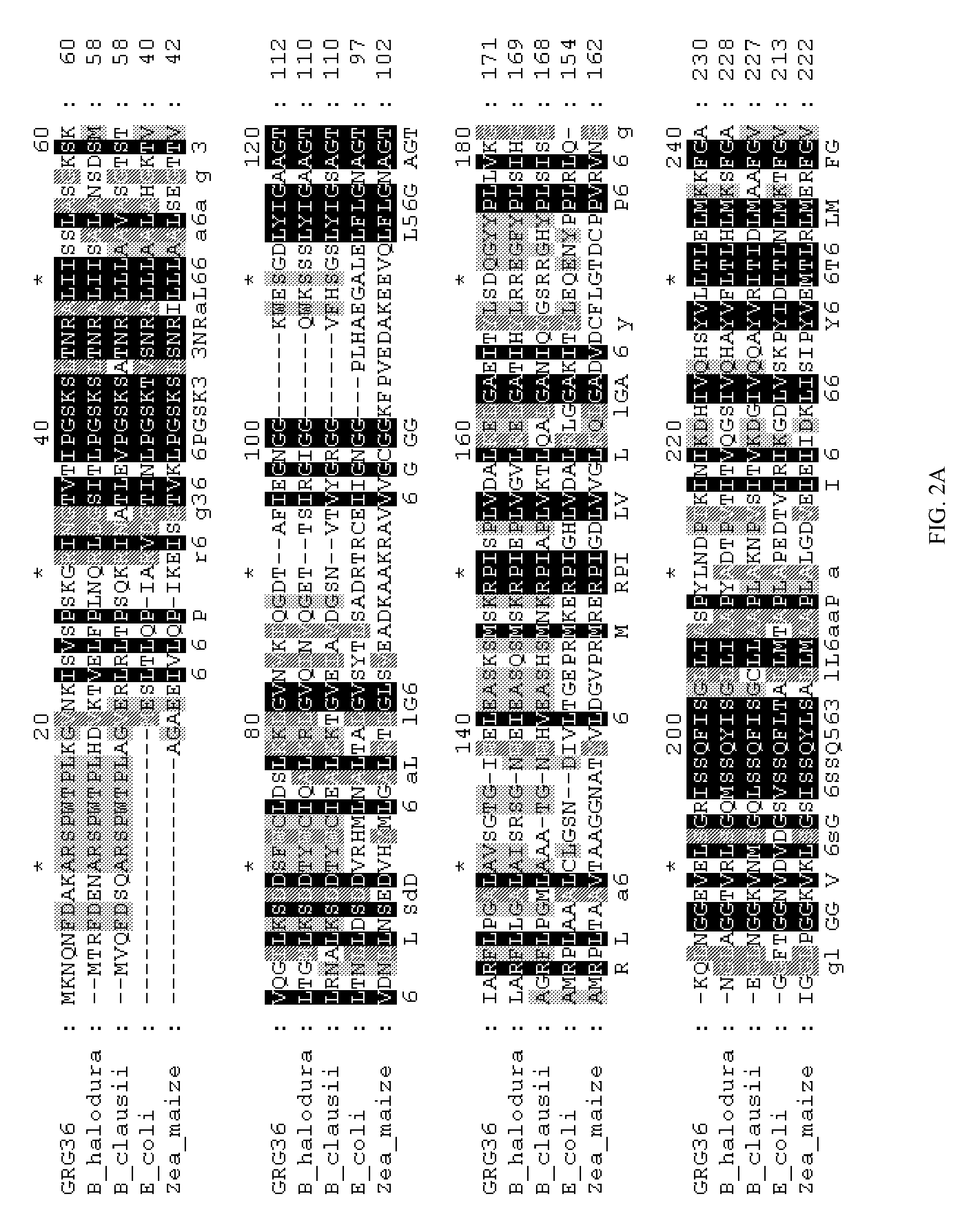
5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase is an enzyme produced by plants and microorganisms. Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and 3-phospho-shikimate, whereas its two products are phosphate and 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate.
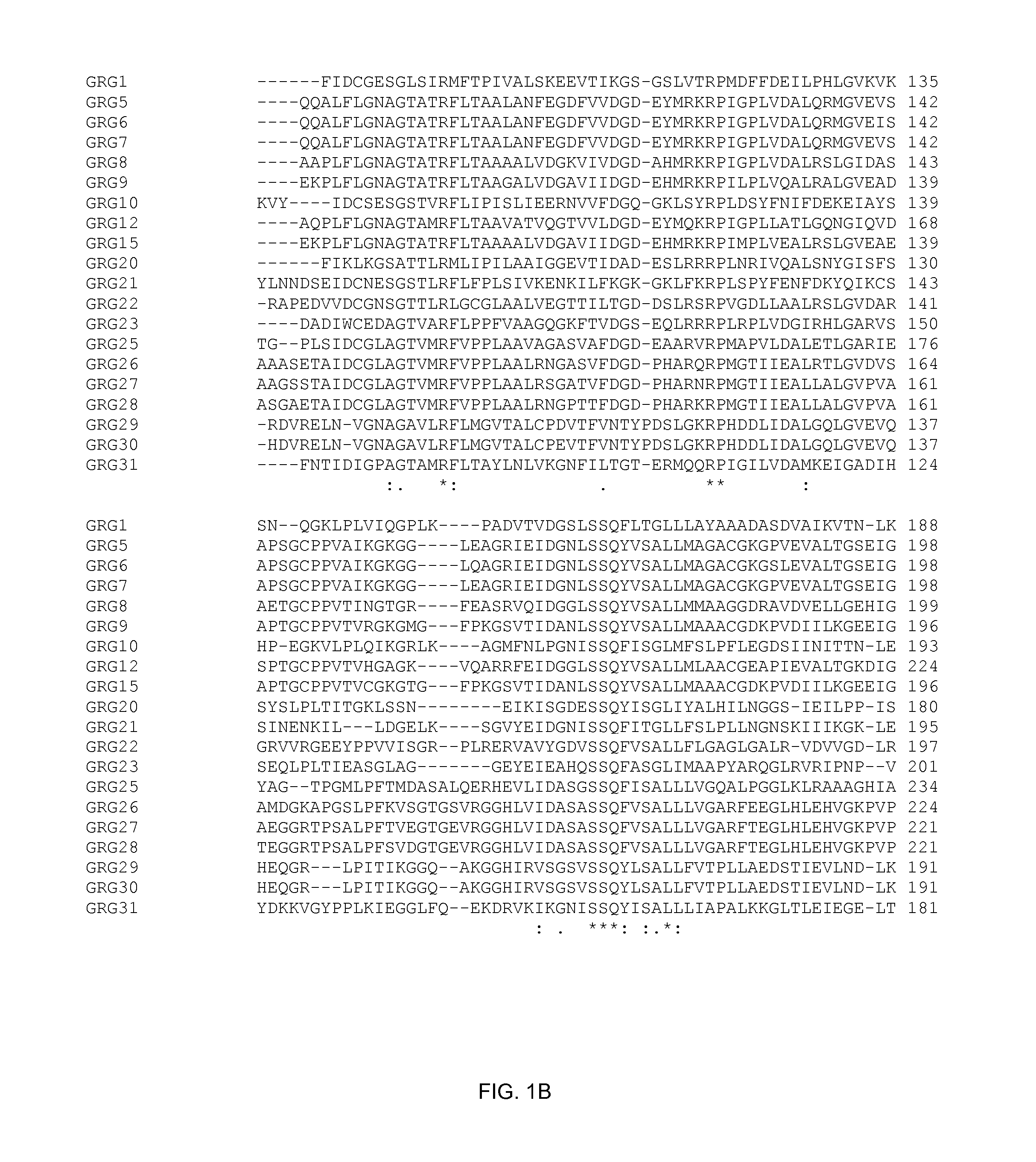
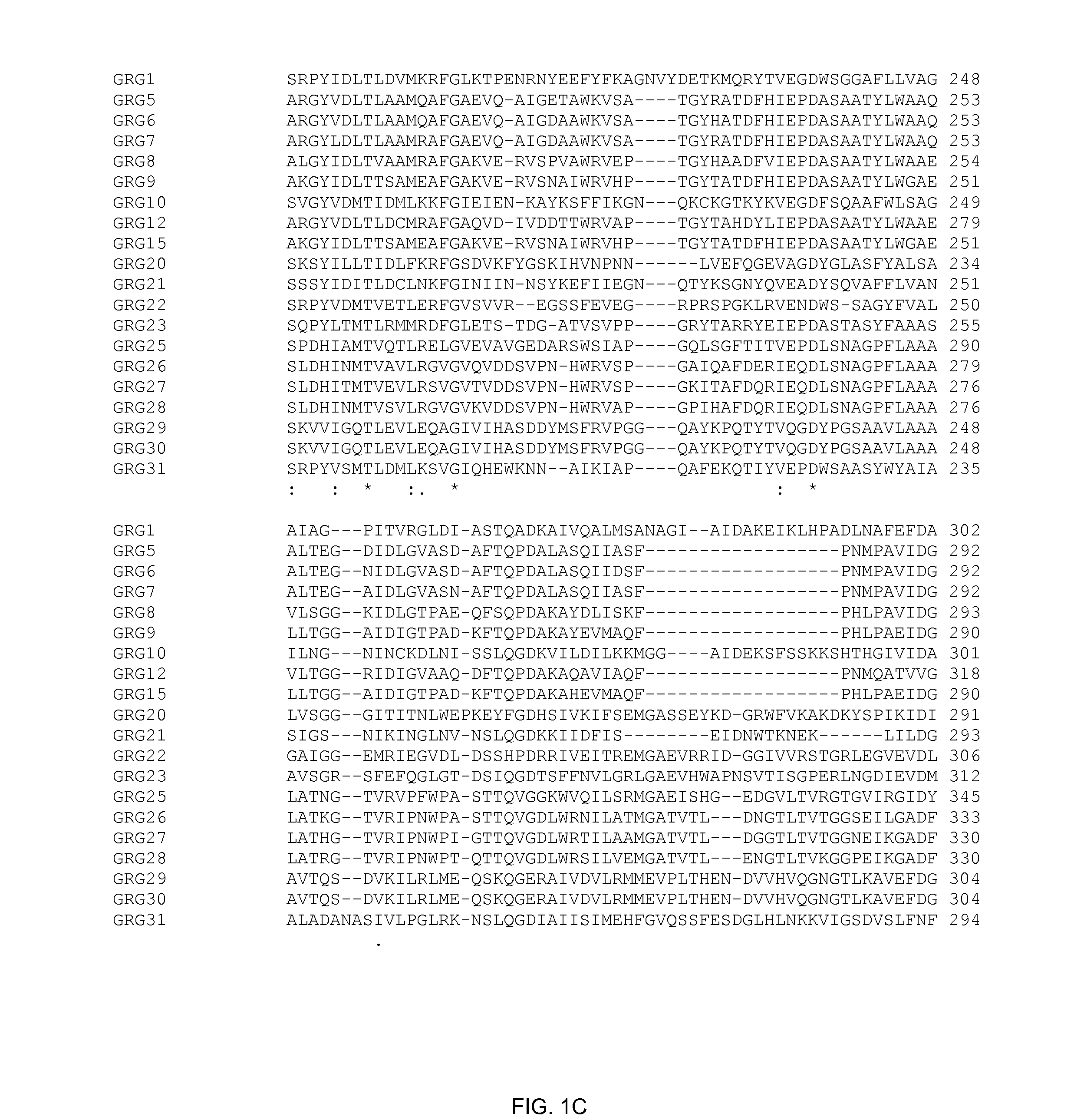
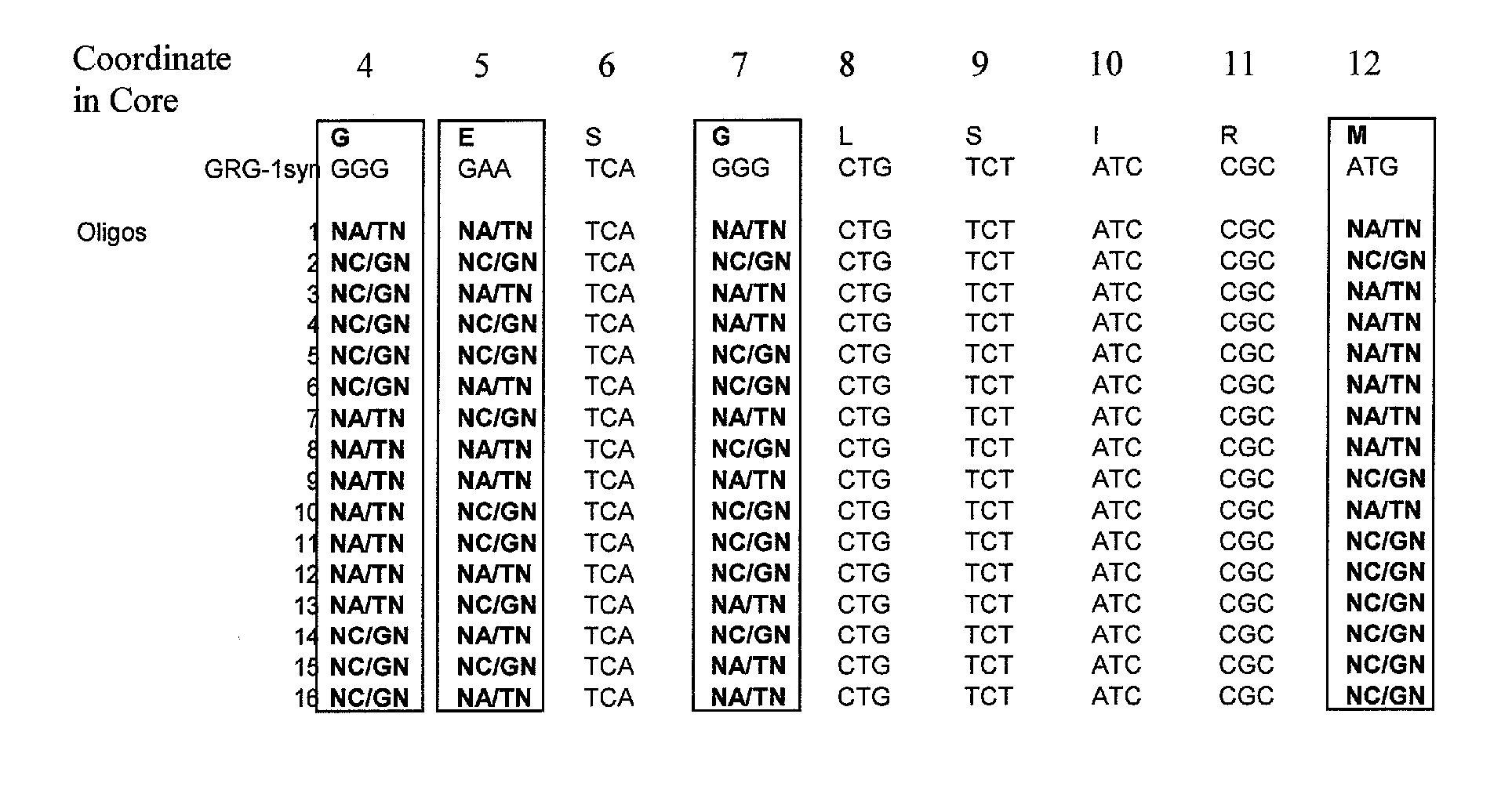
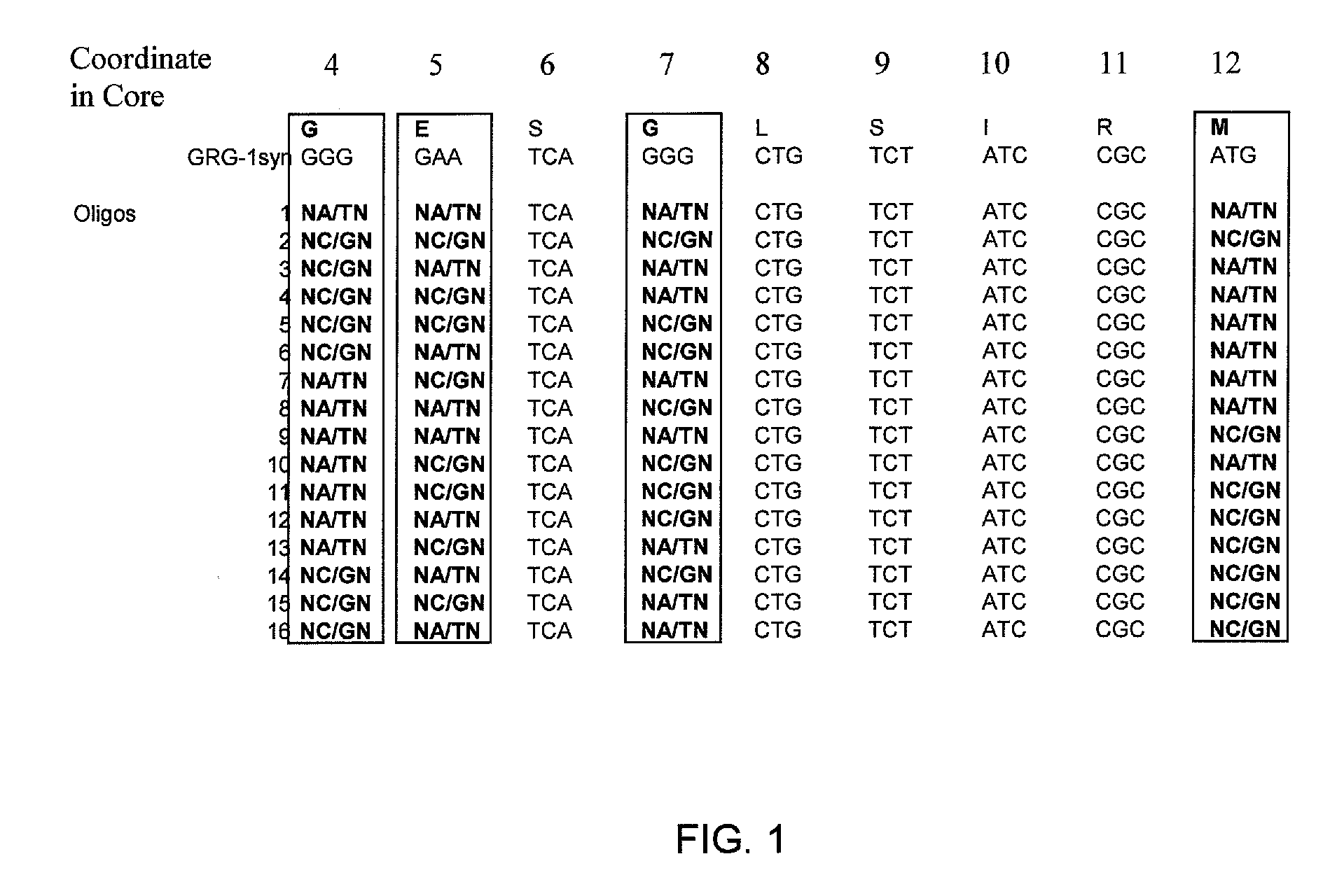
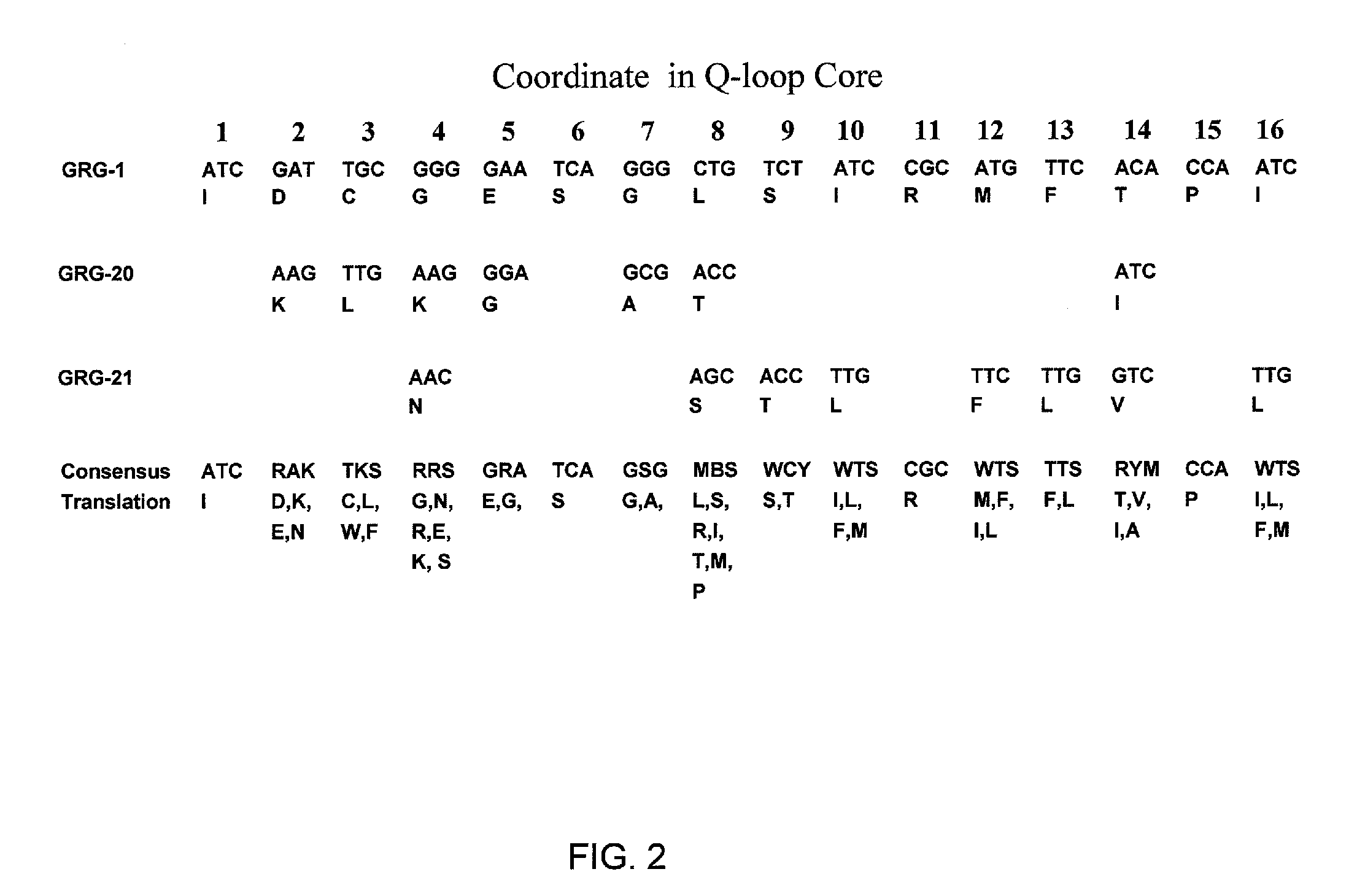
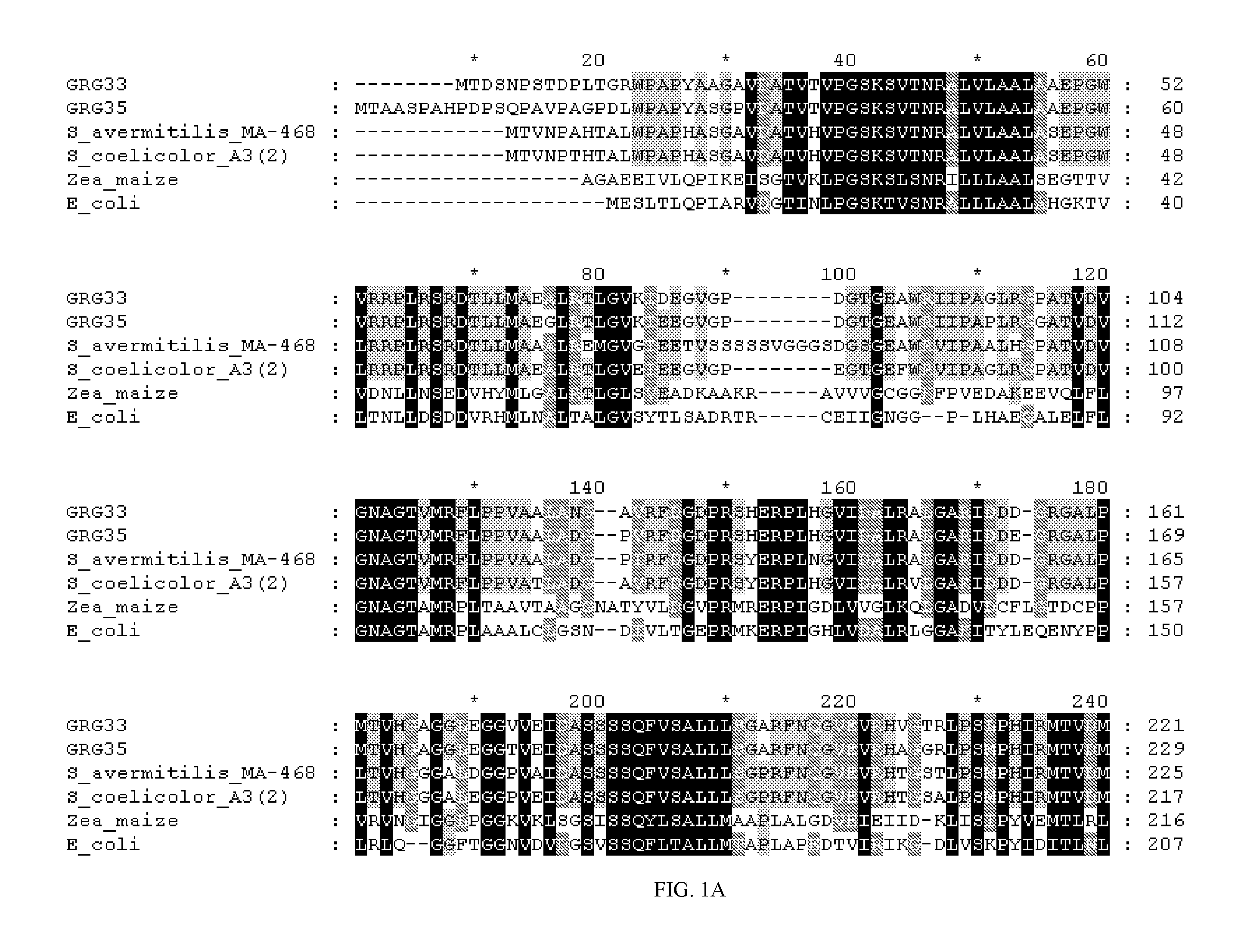
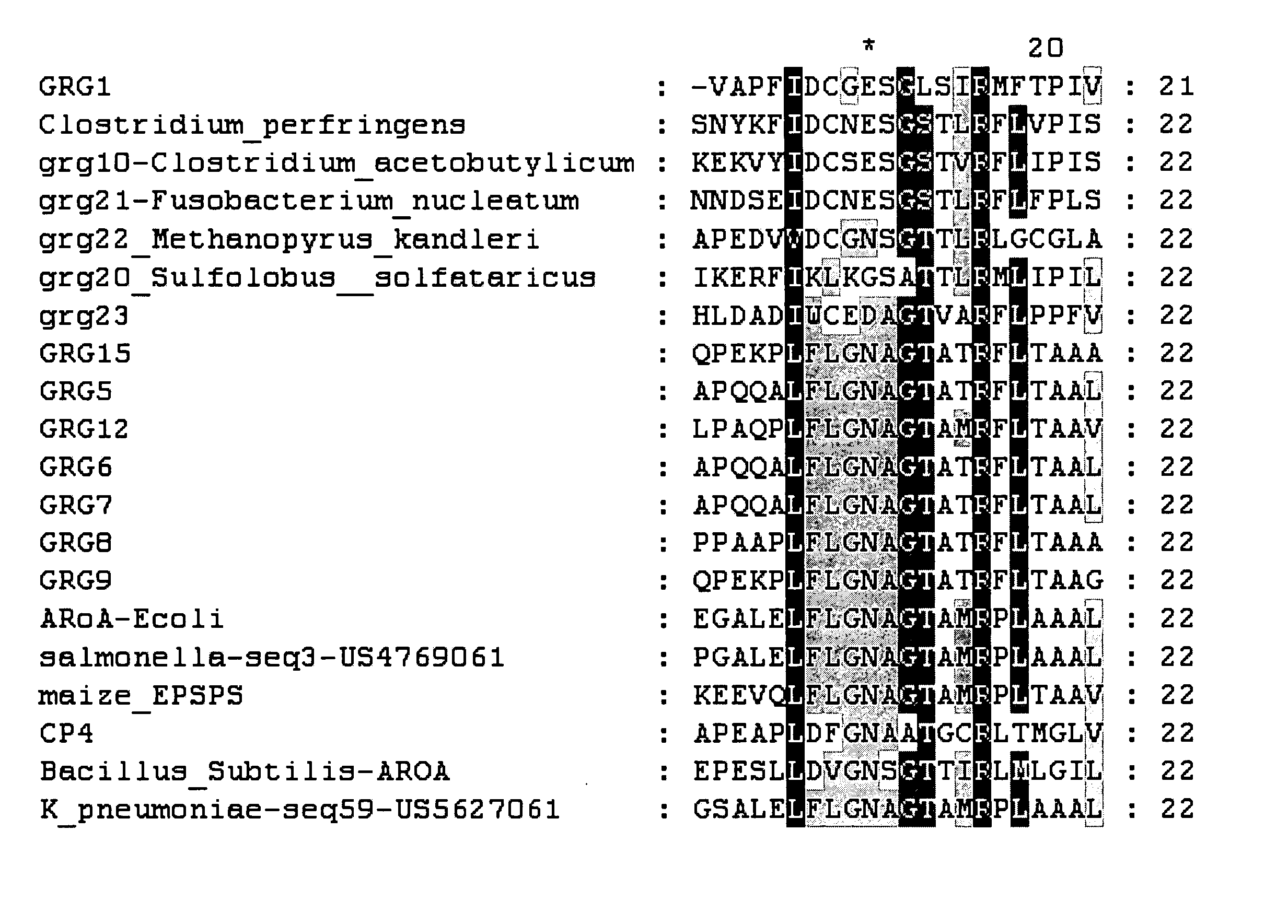
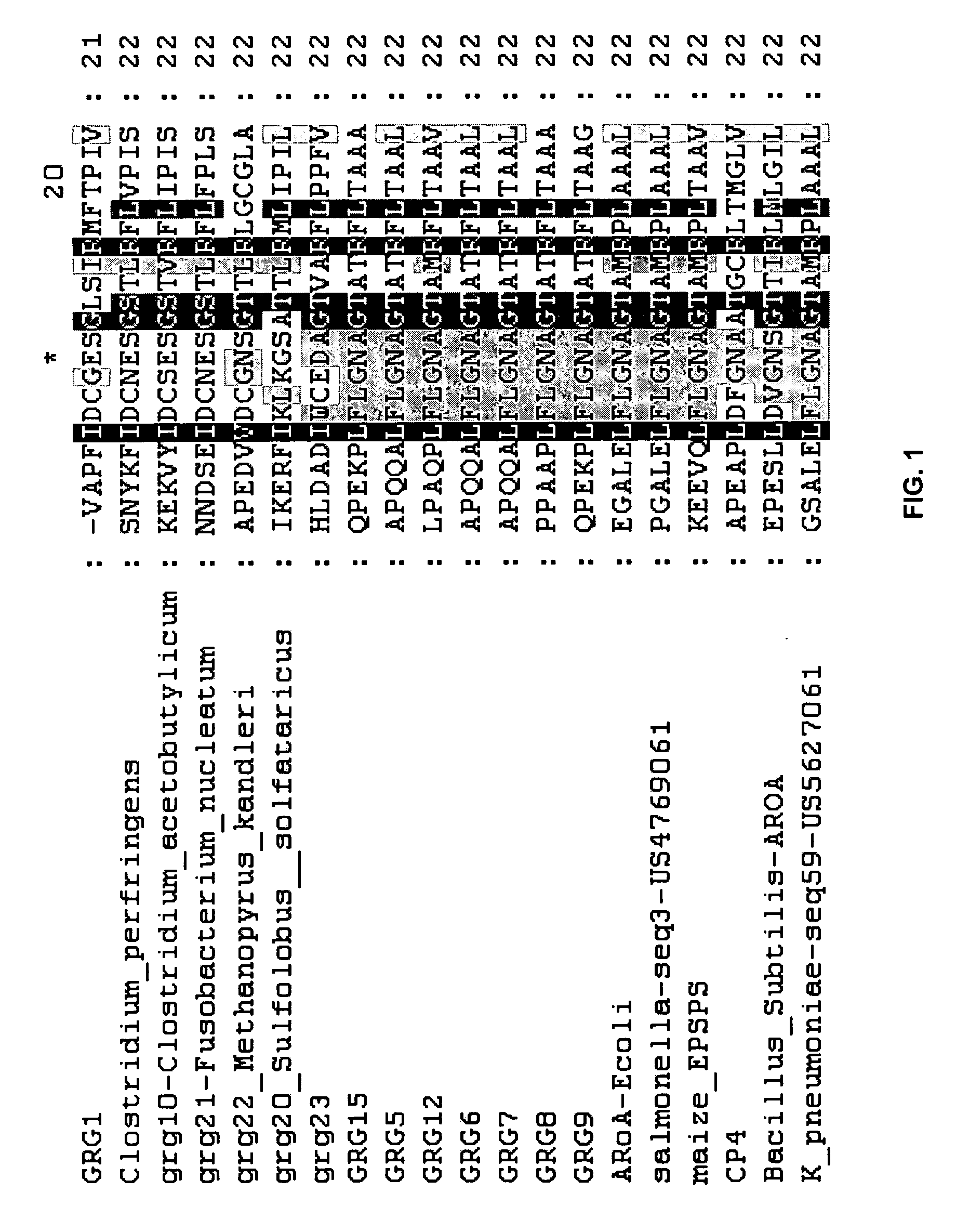
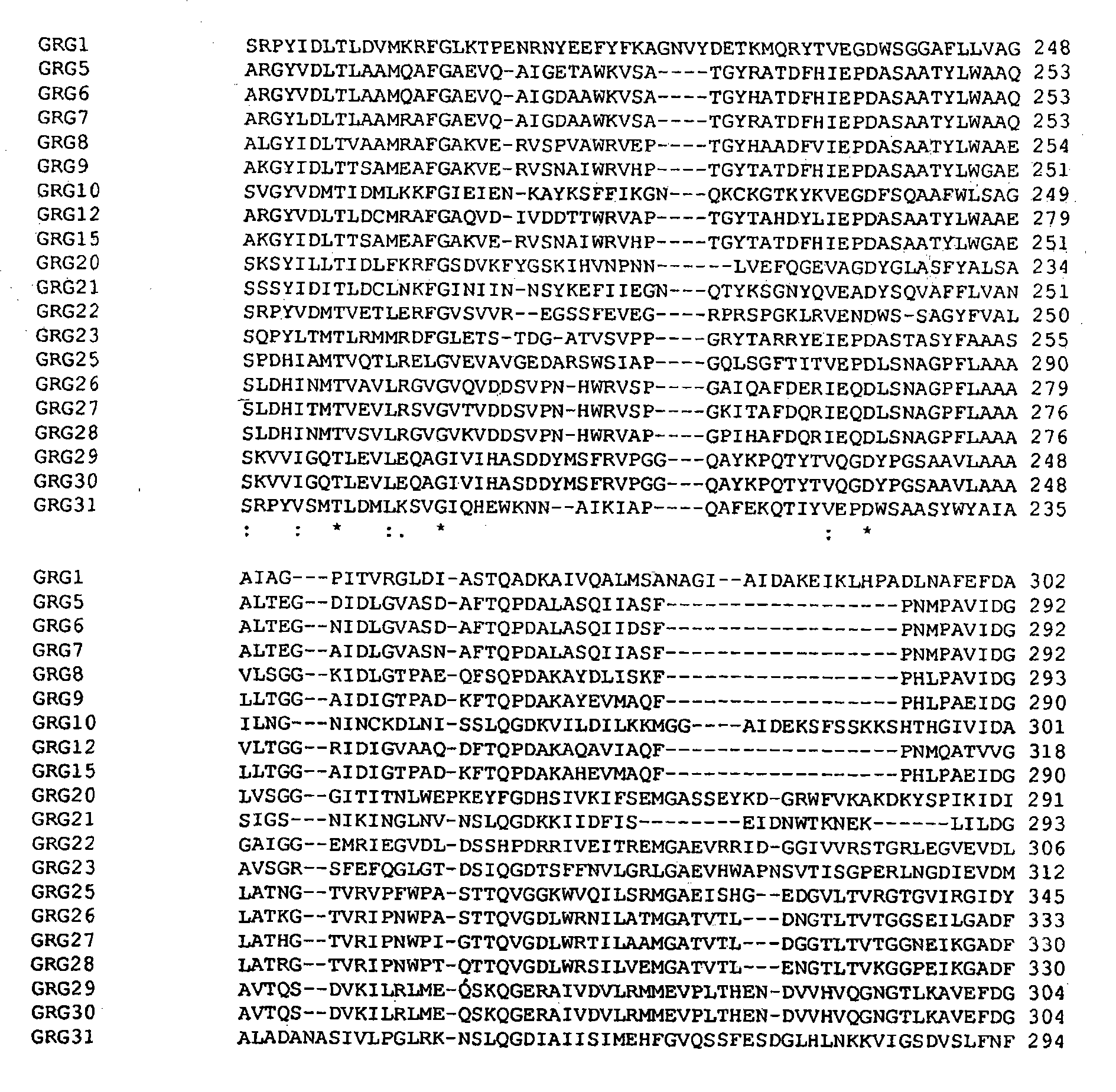
Directed evolution of grg31 and grg36 epsp synthase enzymes
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided, particularly polypeptide variants of SEQ ID NO:2 and 4. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides containing nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:7-28, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:29 or 30.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Novel epsp synthase genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a polypeptide that confers resistance or tolerance to glyphosate herbicides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated nucleic acid molecules corresponding to glyphosate resistant nucleic acid sequences are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NOS:2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, or 14 or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NOS:1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, or 34.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
EPSP synthases: compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20070295251A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesGlyphosatePlant cell
Compositions and methods for conferring tolerance to glyphosate in bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include novel EPSP synthase enzymes and nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors.
Owner:ATHENIX
Grg33, grg35, grg36, grg37, grg38, grg39 and grg50: novel epsp synthase genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include nucleic acid molecules encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, 17, 18, 20, 21, or 23, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 16, 19, or 22, the herbicide resistance nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession Nos. NRRL B-30932, B-30933, B-30934, B-30945, B-30946, B-30947, or B-30948, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Grg32: a novel epsp synthase gene conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include nucleic acid molecules encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 or 14, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, the herbicide resistance nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession Nos. NRRL B-30931, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
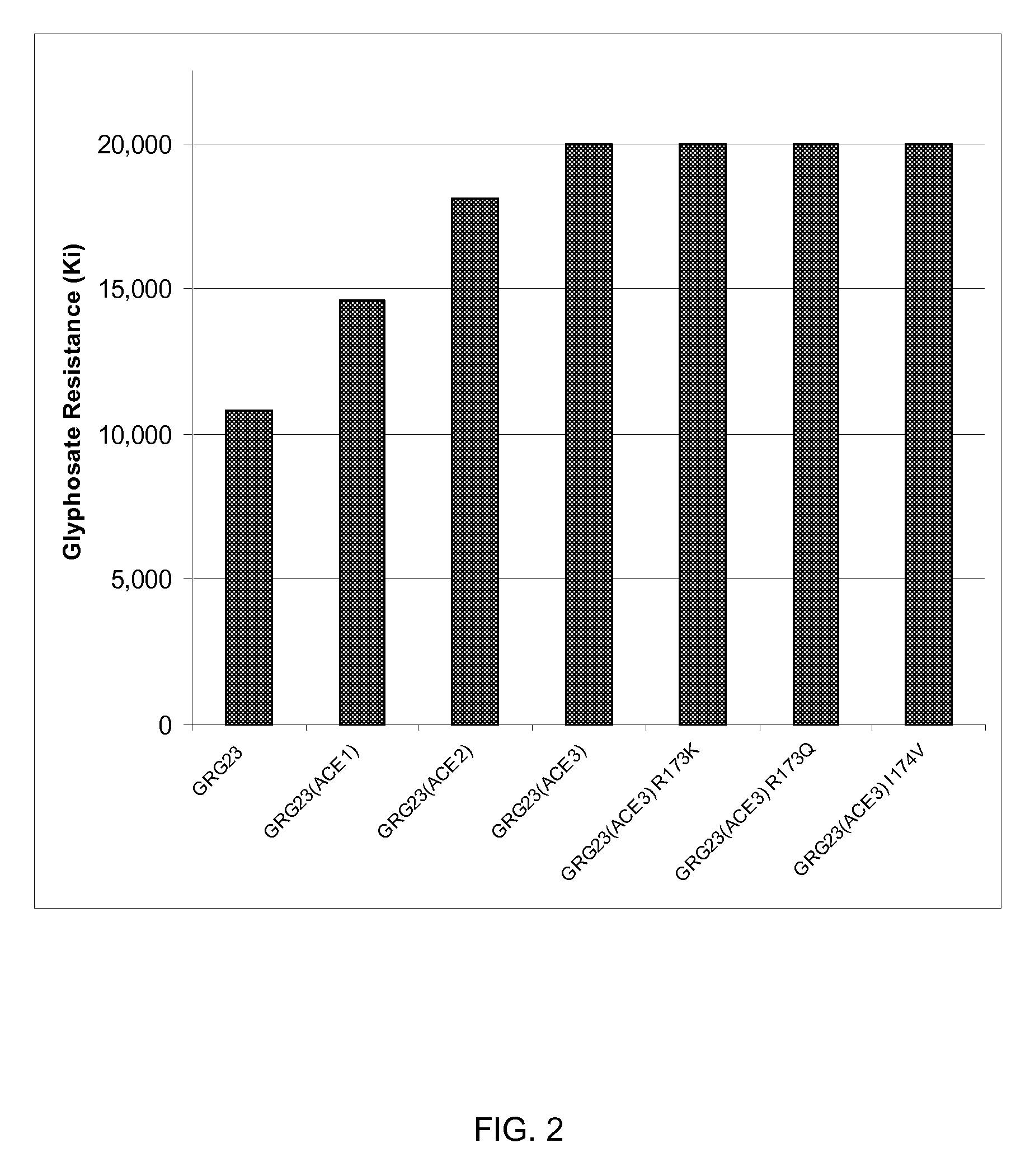
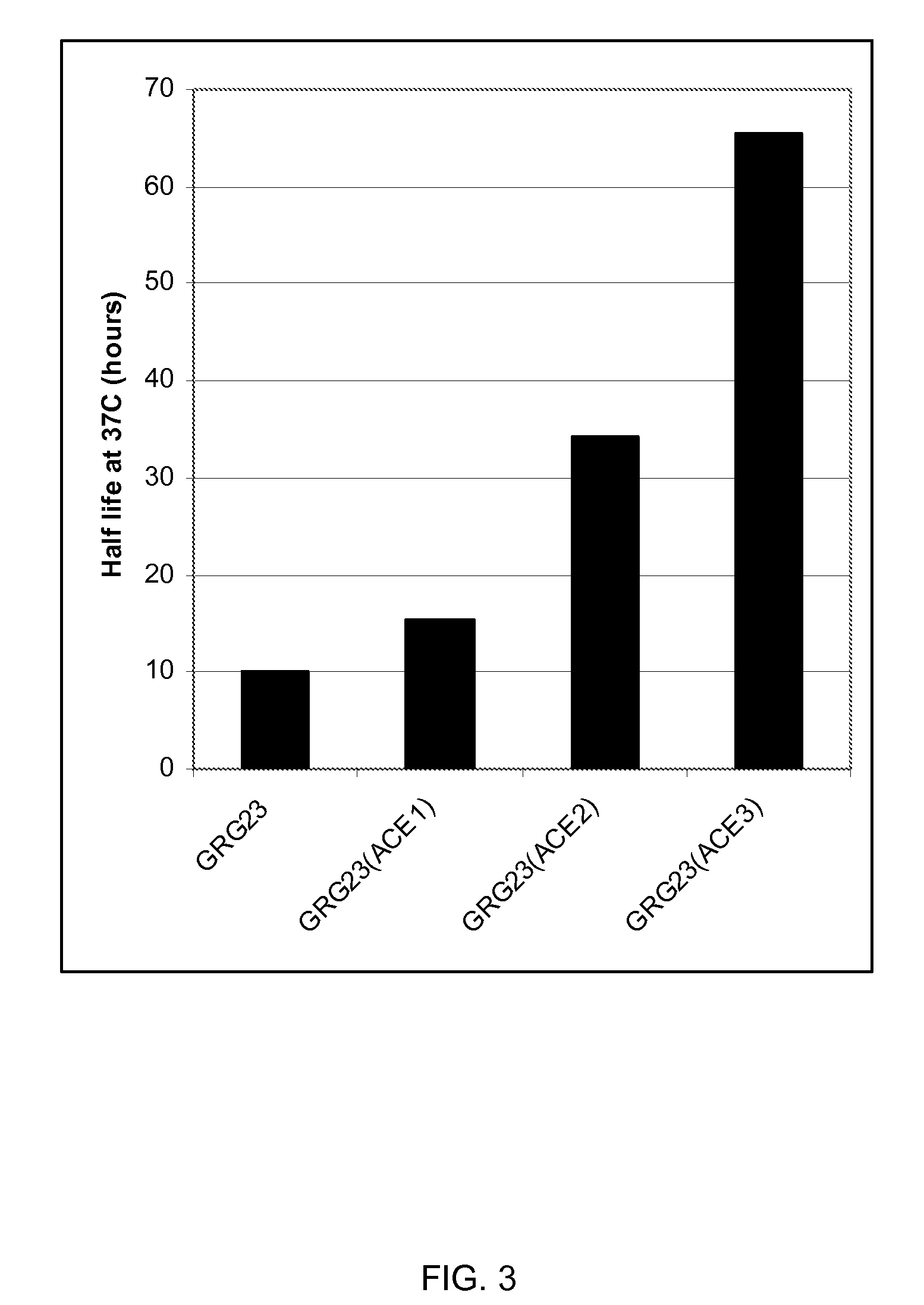
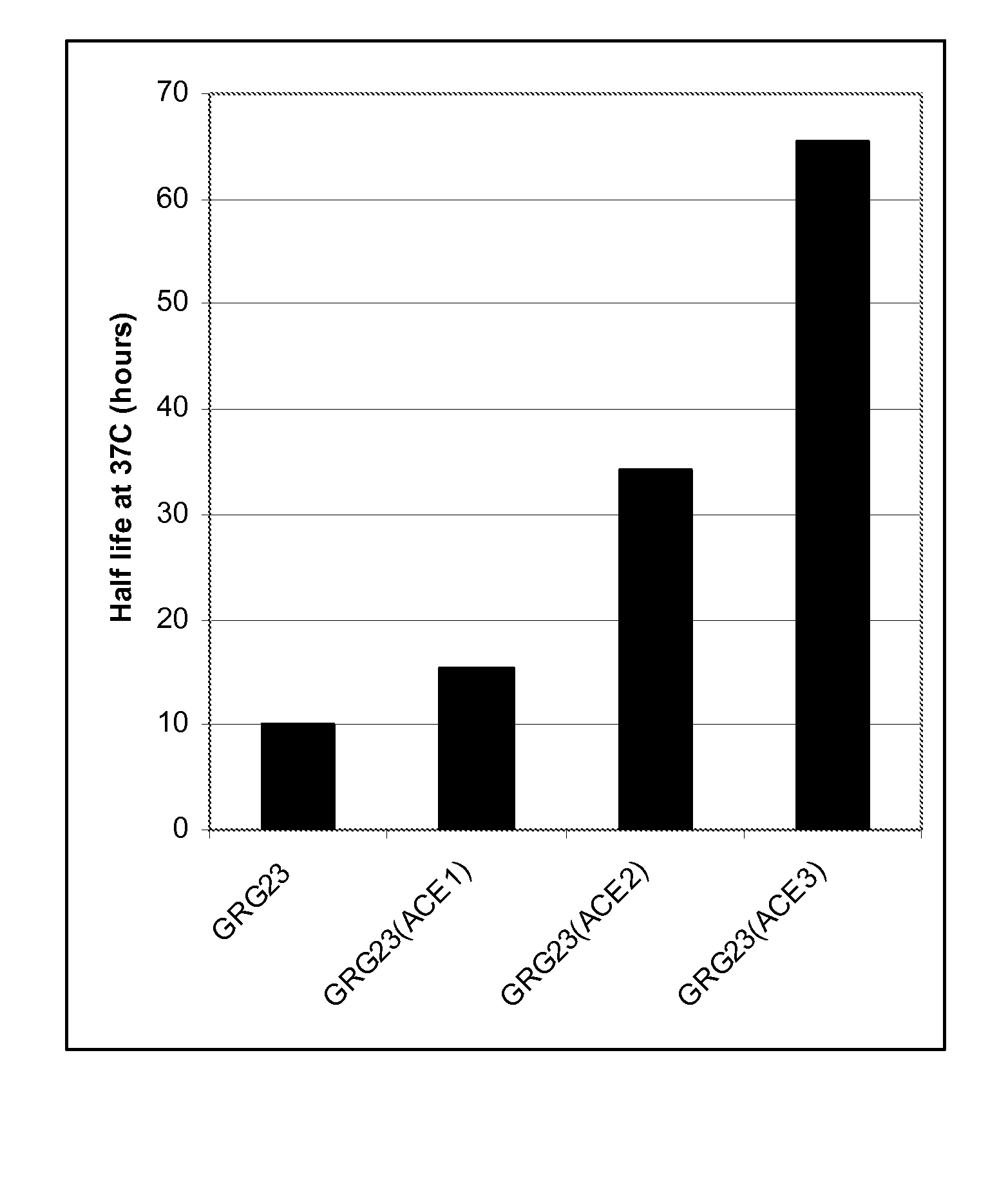
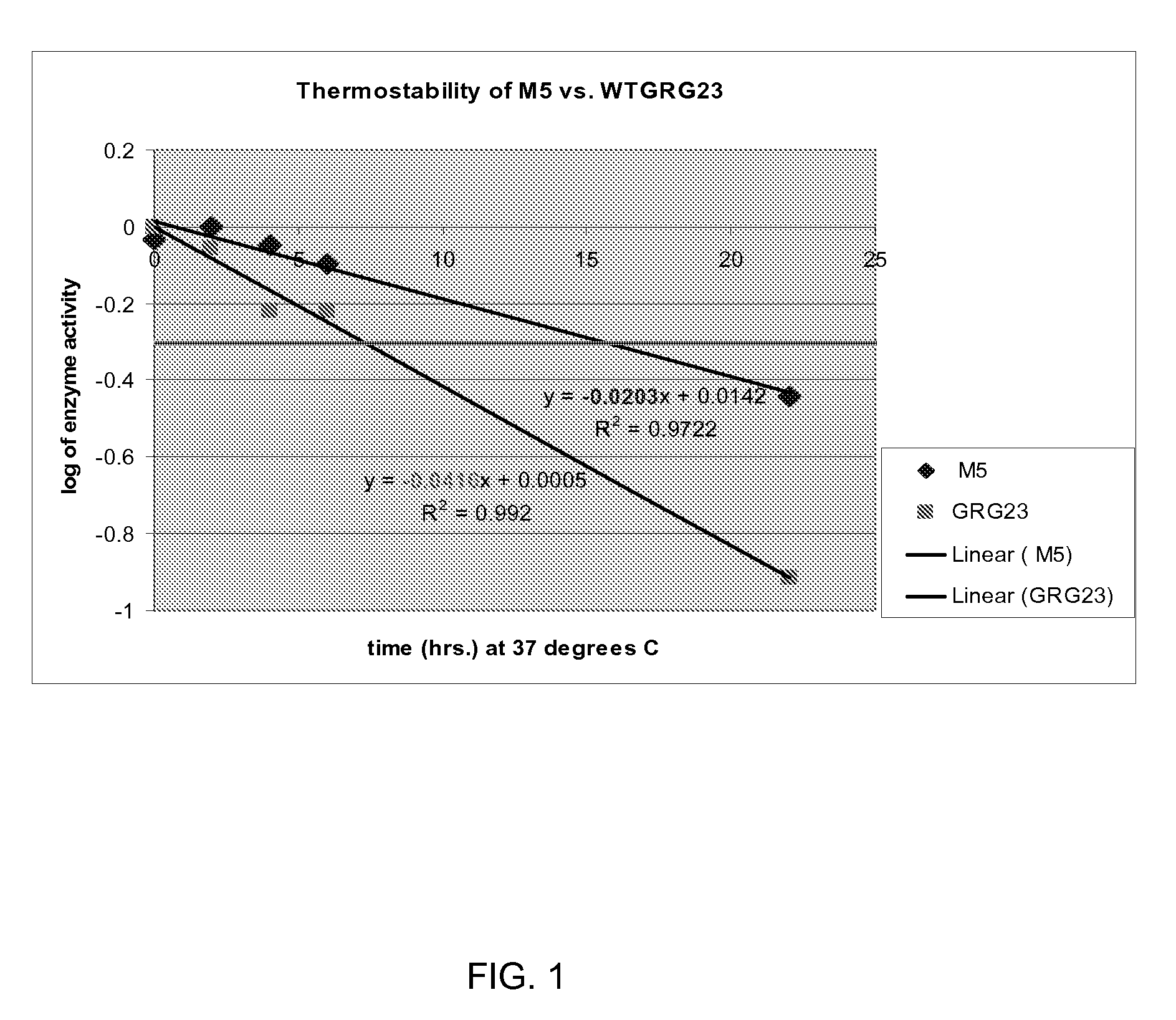
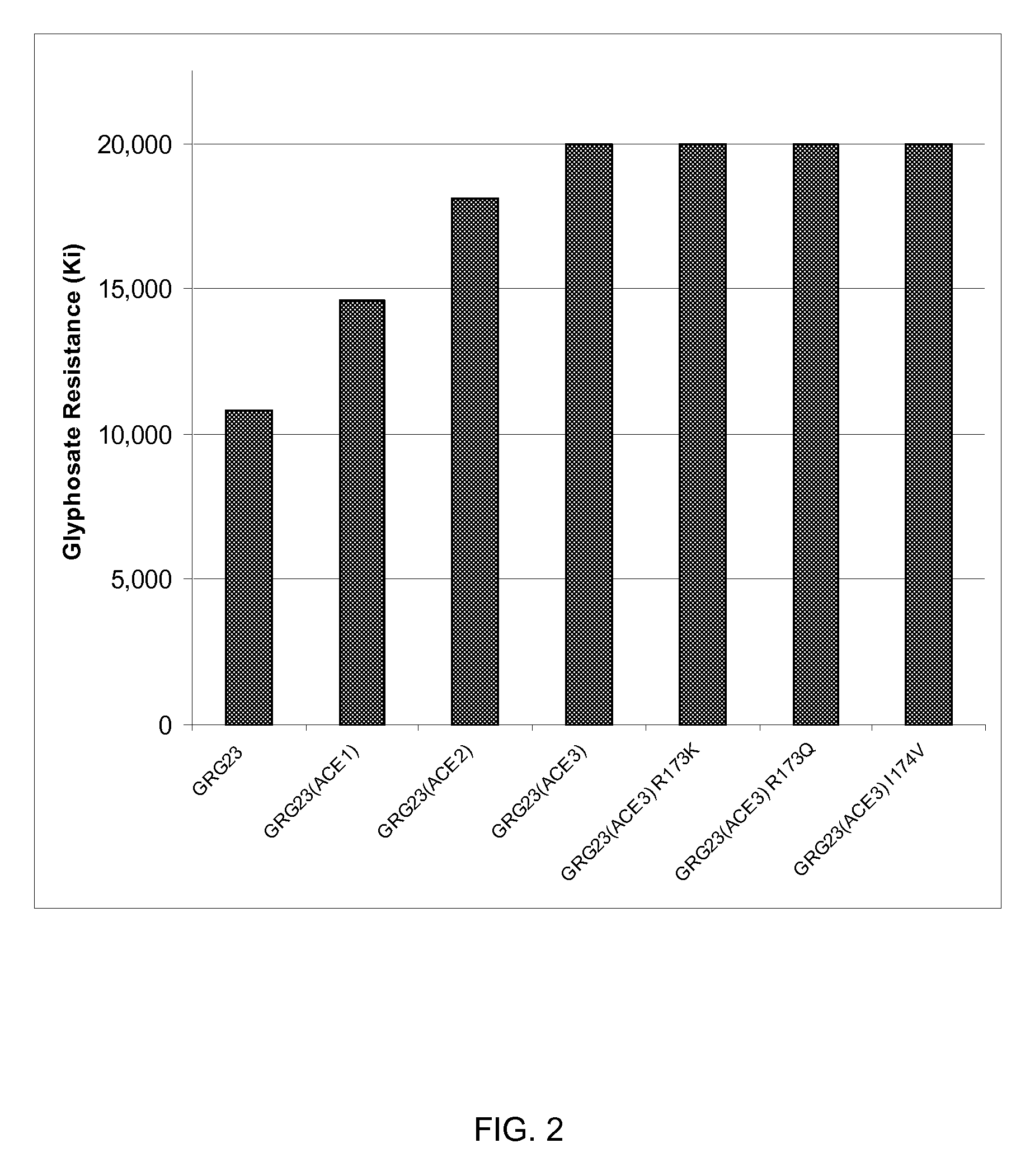
Grg23 epsp synthases: compositions and methods of use
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides containing nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, or 35, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, or 34.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
EPSP synthase domains conferring glyphosate resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring tolerance to glyphosate in bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include novel EPSP synthase enzymes and nucleic acid molecules encoding such enzymes, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The novel proteins comprise at least one sequence domain selected from the domains provided herein. These sequence domains can be used to identify EPSP synthases with glyphosate resistance activity.
Owner:ATHENIX
Herbicidal mixtures
Disclosed is a herbicidal mixture comprising (a) at least one herbicide compound selected from the pyrimidines of Formula 1, including all geometric and stereoisomers, N-oxides, and salts thereof:whereinR1 is cyclopropyl, 4-Br-phenyl or 4-Cl-phenyl;X is Cl or Br;R2 is H, C1-C14 alkyl, C2-C14 alkoxyalkyl, C3-C14 alkoxyalkoxyalkyl, C2-C14 hydroxyalkyl or benzyl; and(b) at least one additional herbicide or herbicide safener compound selected from the group consisting of (b1) ACCase inhibitors, (b2) AHAS inhibitors, (b3) photosystem II inhibitors, (b4) photosystem I electron diverters, (b5) PPO inhibitors, (b6) EPSP synthase inhibitors, (b7) GS inhibitors, (b8) VLCFA inhibitors, (b9) auxin mimics, (b10) auxin transport inhibitors, (b11) other herbicides selected from the group consisting of flamprop-M-methyl, flamprop-M-isopropyl, difenzoquat, DSMA, MSMA, bromobutide, flurenol, cinmethylin, cumyluron, dazomet, dymron, methyldymron, etobenzanid, fosamine-ammonium, isoxaflutole, asulam, clomazone, mesotrione, metam, oxaziclomefone, oleic acid, pelargonic acid and pyributicarb, (b12) herbicide safeners selected from the group consisting of benoxacor, 1-bromo-4-[(chloromethyl)sulfonyl]benzene, cloquintocet-mexyl, cyometrinil, dichlormid, 2-(dichloromethyl)-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane, fenchlorazole-ethyl, fenclorim, flurazole, fluxofenim, furilazole, isoxadifen-ethyl, mefenpyr-diethyl, methoxyphenone, naphthalic anhydride and oxabetrinil, and their salts. Also disclosed is a method for controlling the growth of undesired vegetation comprising contacting the vegetation or its environment with a herbicidally effective amount of a mixture of the invention (e.g., as a composition described herein).
Owner:ARMEL GREGORY RUSSELL +8
EPSP synthase highly tolerant to glyphosate
An isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence that is at least 62% identical to SEQ ID NO:2. The polypeptide, when present in a cell, increases the cell's ability to tolerate glyphosate. Also disclosed are related nucleic acid, antibody, vector, transgenic plant, as well as uses thereof.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECH (HAINAN) CO LTD
EPSP synthase highly tolerant to glyphosate
ActiveUS20050223436A1Improve abilitiesImprove toleranceSugar derivativesTransferasesEPSP synthaseGene
An isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence that is at least 62% identical to SEQ ID NO:2. The polypeptide, when present in a cell, increases the cell's ability to tolerate glyphosate. Also disclosed are related nucleic acid, antibody, vector, transgenic plant, as well as uses thereof.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECH (HAINAN) CO LTD
Rice EPSP synthase mutant and its coding gene, obtaining method and application
InactiveCN1810962AHigh glyphosate resistanceHigh activitySugar derivativesEnzymesAgricultural scienceShikimic acid
The present invention discloses one kind of 5-enolpyruvoyl shikimic acid-3-phosphosynthase mutant and its coding gene, obtaining method and application in culturing glyphosate resisting plant. The 5-enolpyruvoyl shikimic acid-3-phosphosynthase has the residue sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and will take important role in the culture of glyphosate resisting plant.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
EPSP synthase of high resistant glyphosate and coding sequence thereof
The invention discloses a novel 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3- phosphate synthase ( abbreviated as ' EPSP Synthase'), which is to generate EPSP Synthase with polynucleotide coding the EPSP Synthase by a recombination technique. The invention also discloses applications of the polynucleotide coding the EPSP Synthase.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Corn chloroplast transgene expression vector containing herbicide resistant gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102533844AStrong resistanceSmall molecular weightVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsChloroplastTransgene
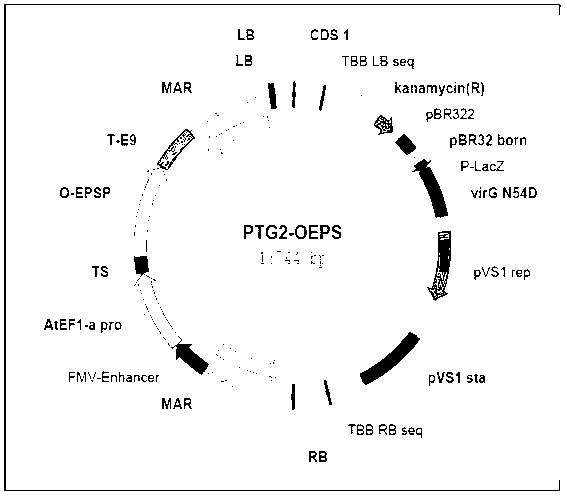
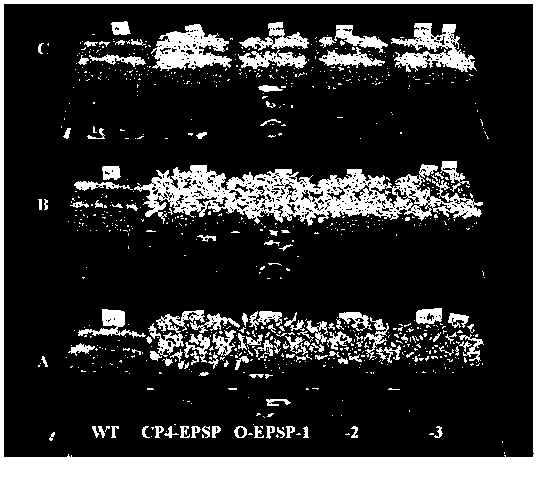
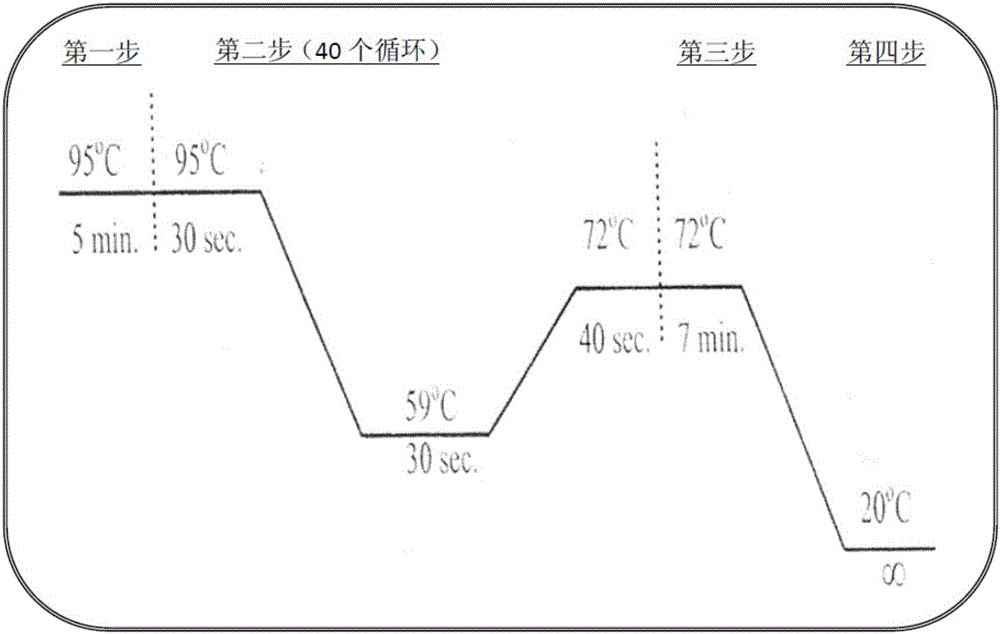
The invention provides a corn chloroplast transgene expression vector containing herbicide resistant gene and application thereof. The transgene expression vector comprises an expression box of 5-enol form acetone shellokimic acid-3-phosphate synthase (EPSP) gene, a homologous recombination fragment atpB in a corn chloroplast gene group and a homologous recombination fragment rbcL, wherein the expression box of the EPSP synthase gene is positioned between the homologous recombination fragment atpB and the homologous recombination fragment rbcL. The invention further provides a construction method of the chloroplast transgene expression vector. The invention also provides application of the chloroplast transgene expression vector in improving corn glyphosate resistance, which comprises leading the expression vector to convert callus or cells of corns, and screening to obtain resistant callus or cells; and inducing resistant callus or cells to differentiate, and regenerating to achieve corn resistance plants. The corn chloroplast transgene expression vector containing herbicide resistant gene can remarkably improve corn glyphosate resistance and has the advantages of being high in biological safety, capable of saving time, efficient, little in energy consumption, low in cost and the like.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
GRG23 EPSP synthases: compositions and methods of use
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides containing nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, or 35, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, or 34.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Directed evolution of GRG31 EPSP synthase enzyme
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Preparation of glyphosate resistance enhanced EPSPS (5-enolpyruvyl shikimate-3-phosphate synthase) mutant of Vitis vinifera and application of EPSPS mutant of Vitis vinifera
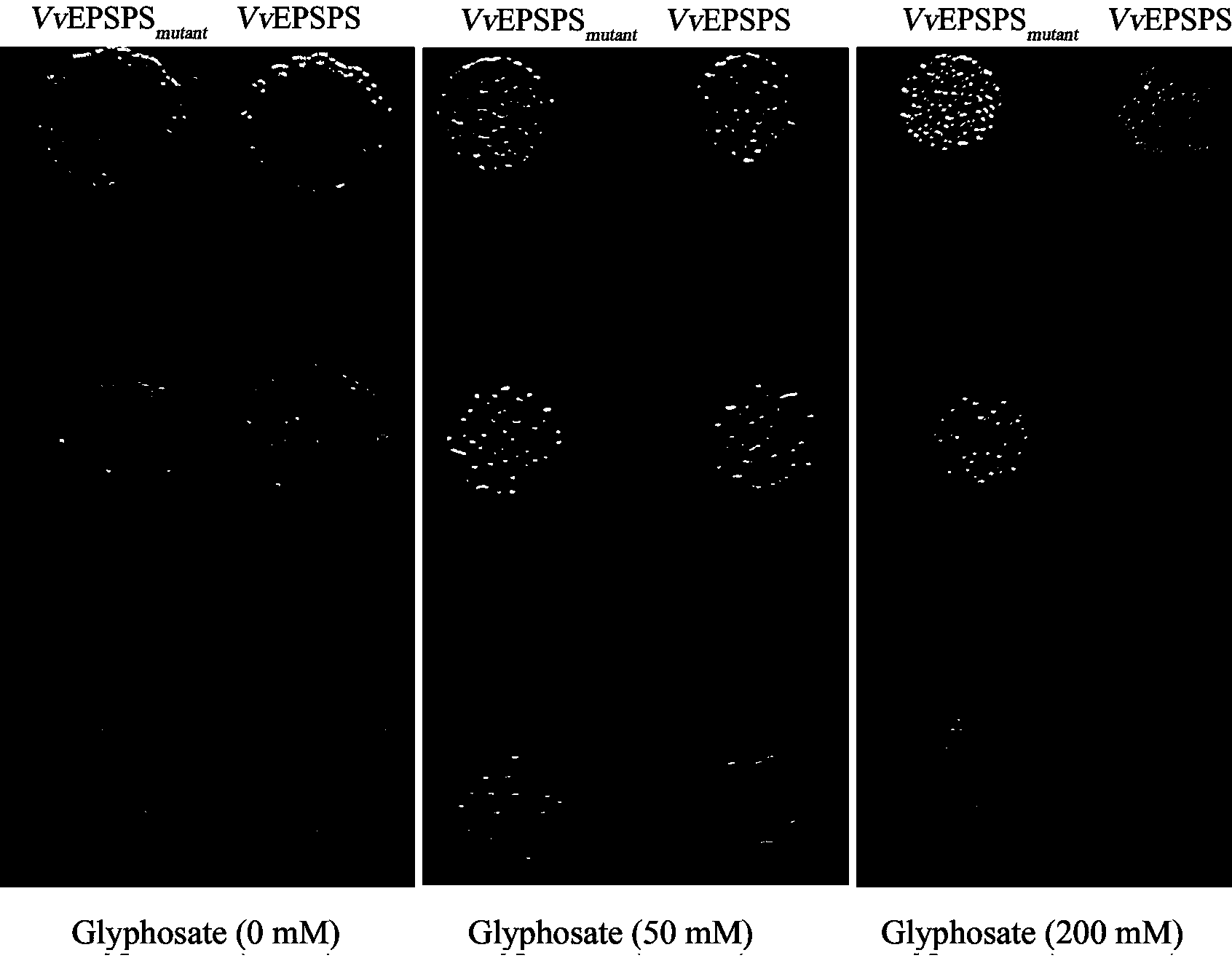
The invention discloses a glyphosate resistance enhanced EPSP (5-enolpyruvyl shikimate-3-phosphate synthase) synthase multi-site mutant which is derived from Vitis vinifera and prepared by adopting a DNA shuffling technology, as well as a coding gene and application of the mutant. The mutant comprises 7 mutation sites, wherein the amino acid sequence of the mutant is as shown in the SEQ ID No.1, and the base sequence coded by the mutant is as shown in the SEQ ID No.2. Tests indicate that the EPSP synthase multi-site mutant derived from Vitis vinifera and the gene coded by the mutant have relatively high glyphosate resistance and relatively strong PEP affinity, and the characteristics of the mutant and the gene provide possibility to the gene for culturing anti-glyphosate transgenic crops.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
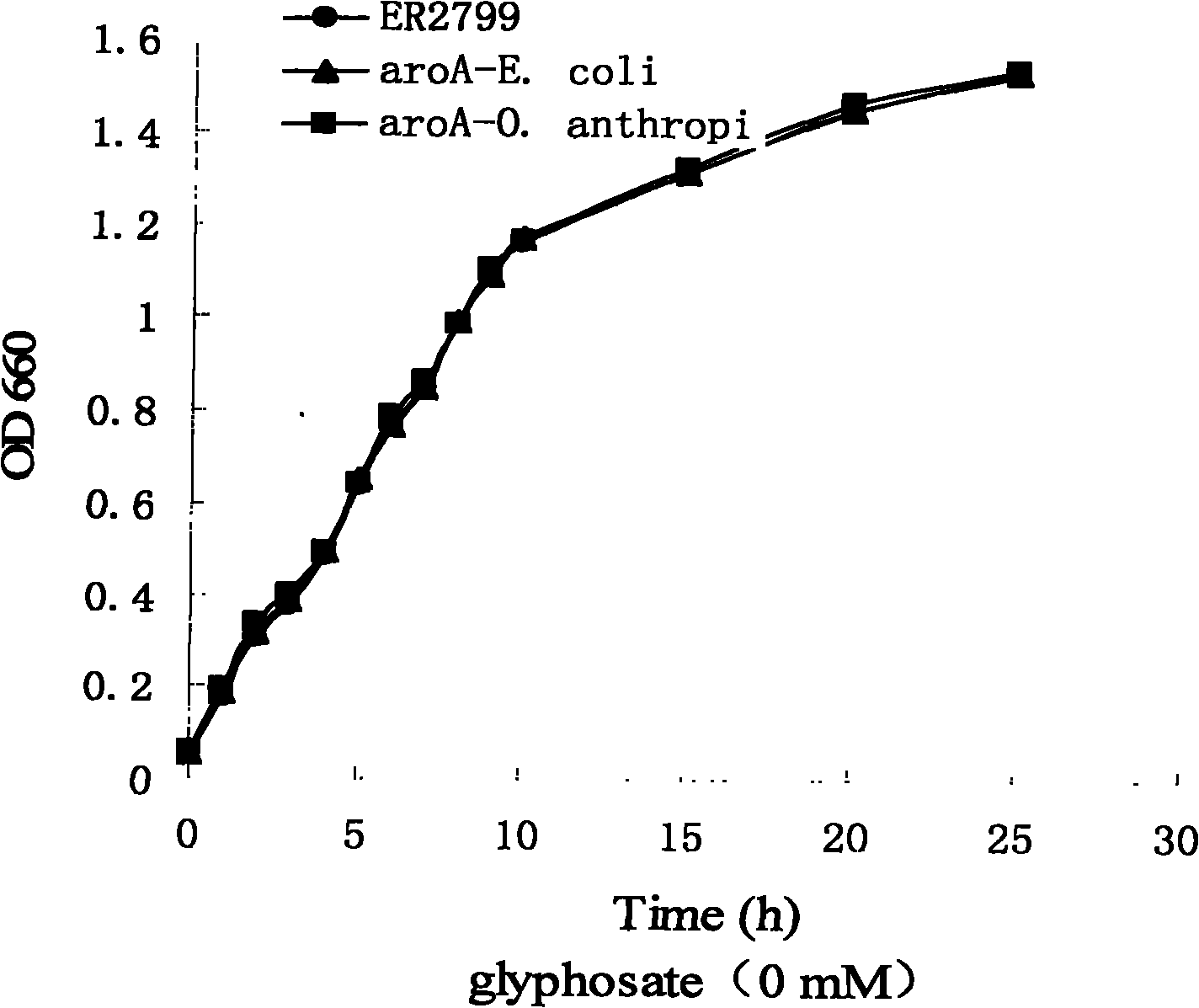
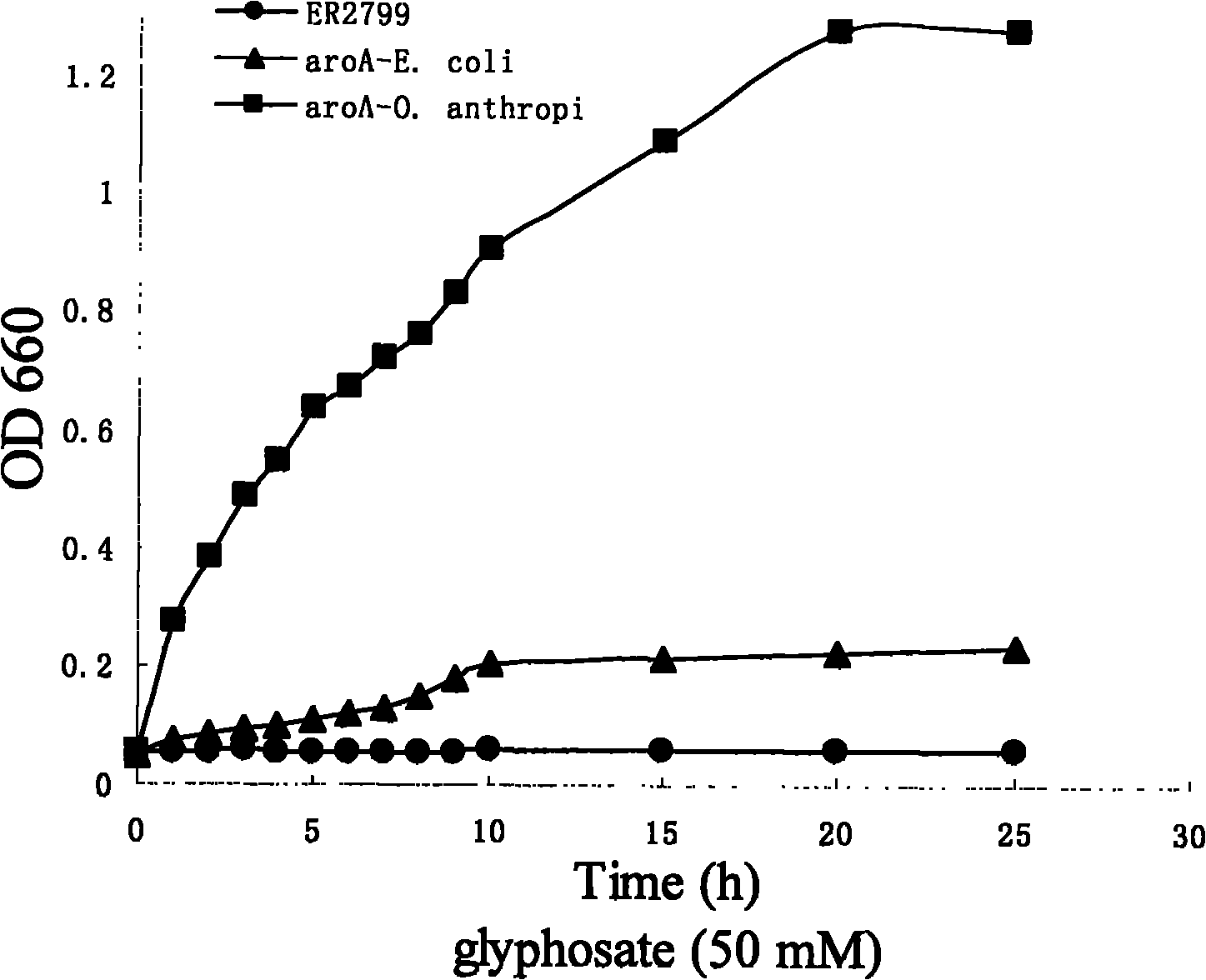
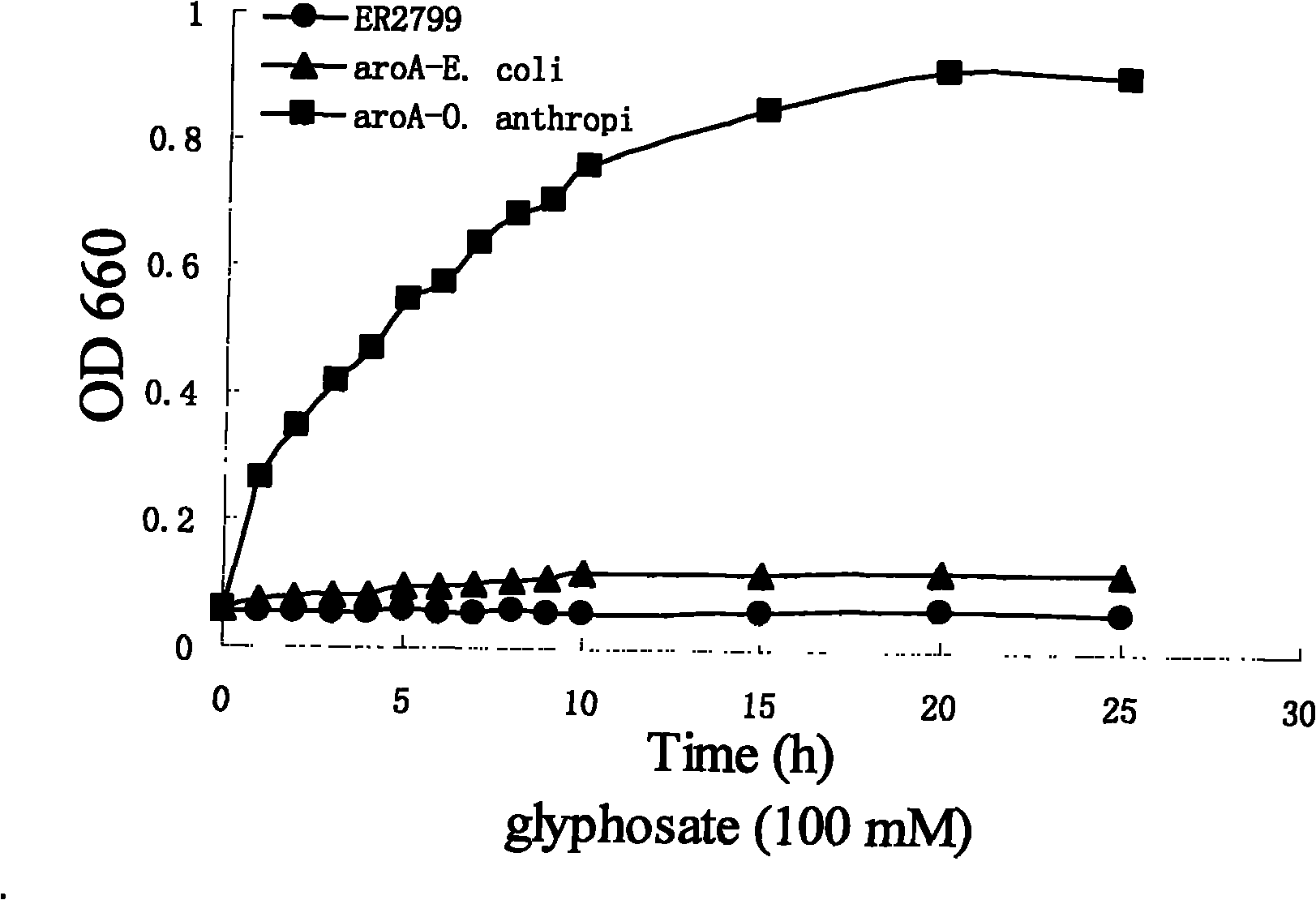
EPSP synthase gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof
InactiveCN102108363AImprove toleranceTransferasesMicroorganism based processesNucleotideGenetically modified crops
The invention discloses an EPSP synthase gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof. The EPSP synthase gene contains 1353 basic groups and 451 coded amino acids, the nucleotide sequence of the EPSP synthase gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO1, and the amino acid sequence of the coded proteins is as shown in SEQ ID NO2. The EPSP synthase gene derived from ochrobactrum anthropi disclosed by the invention is synthesized by a manual method, has high homology with the reported EPSP synthase gene derived from agrobacterium tumfaciens, has higher glyphosate tolerance, and can be used for culturing genetically modified crops.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
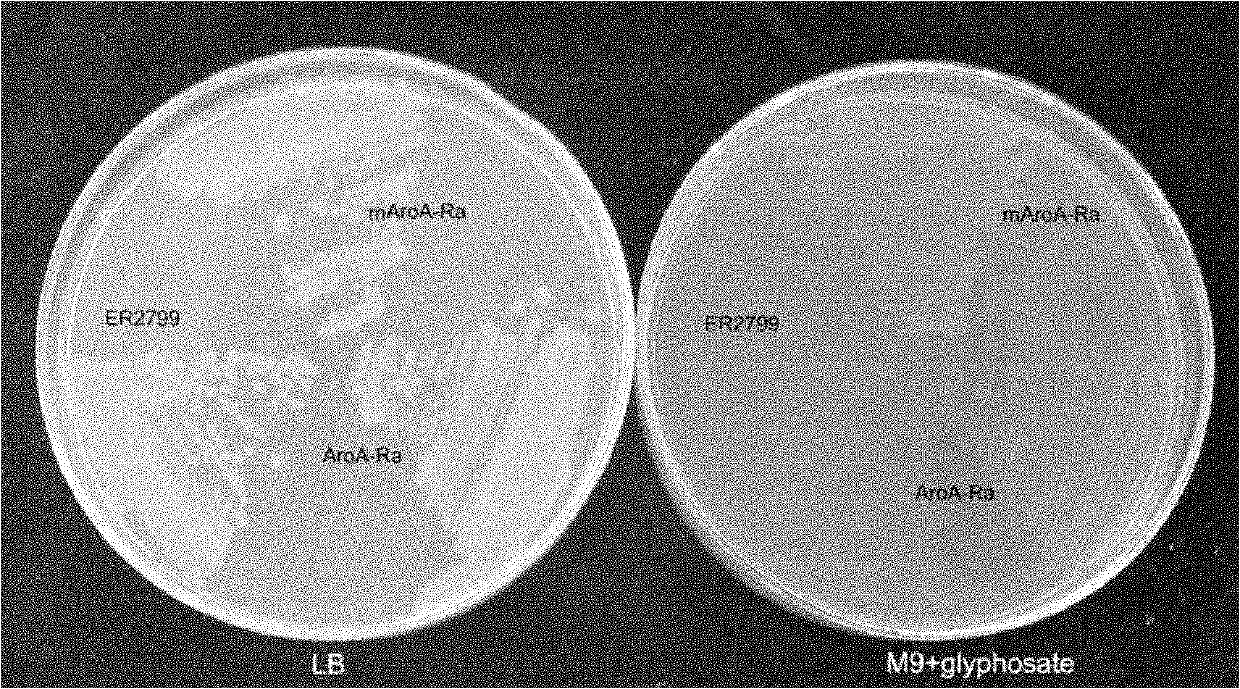
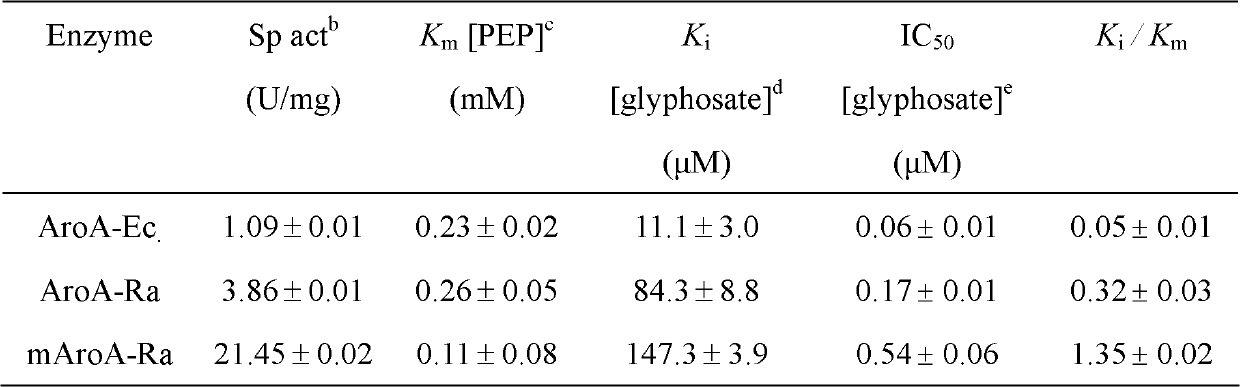
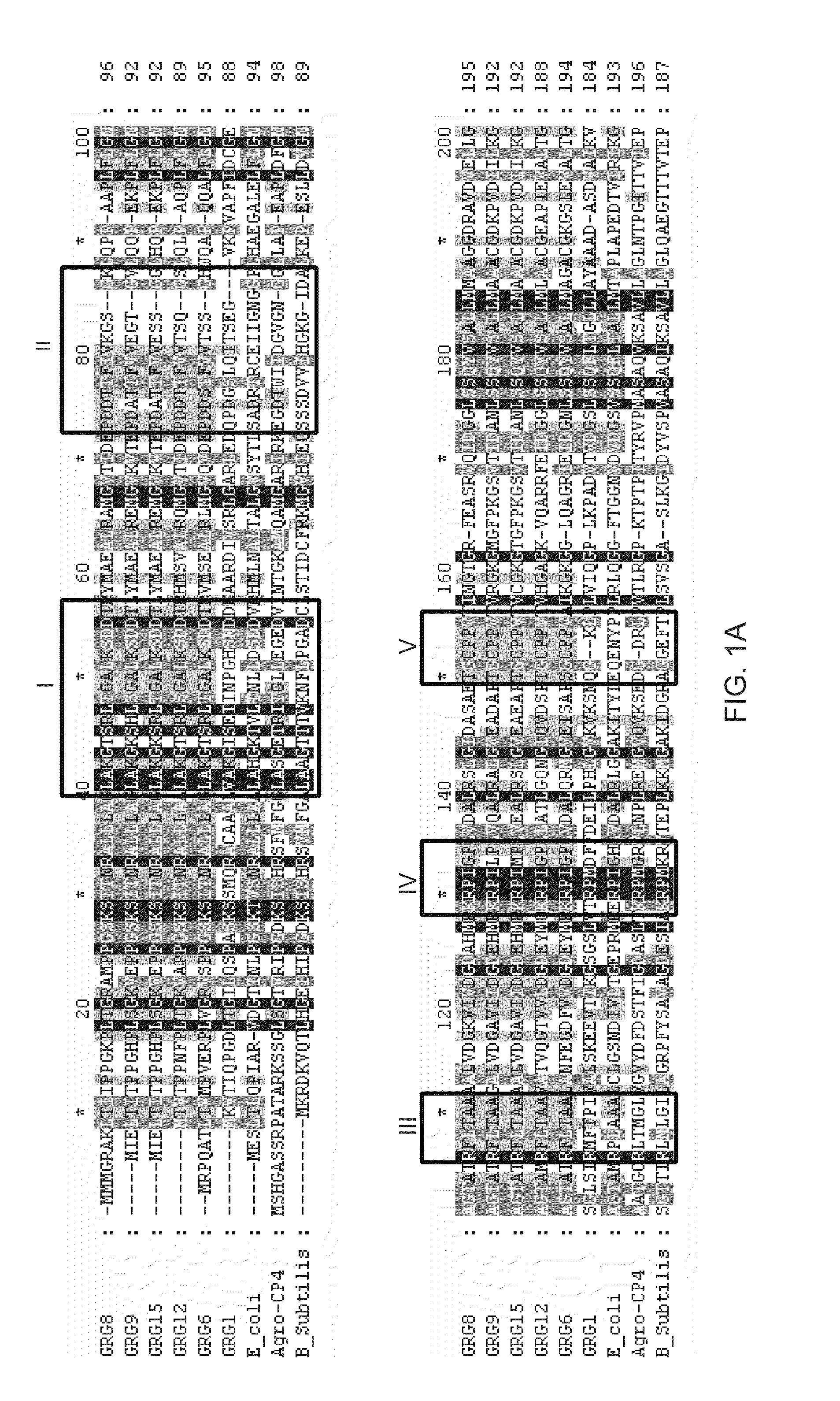
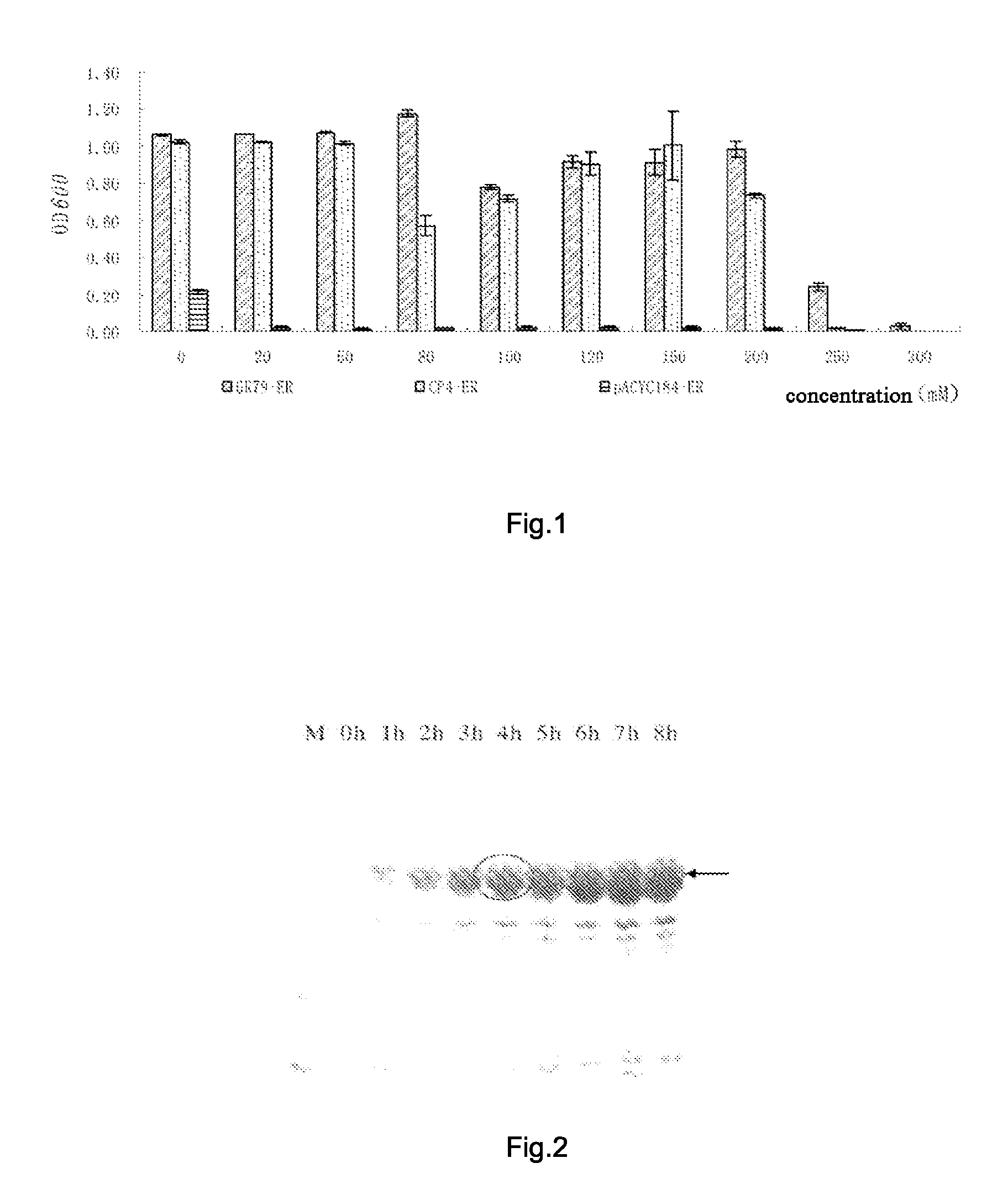
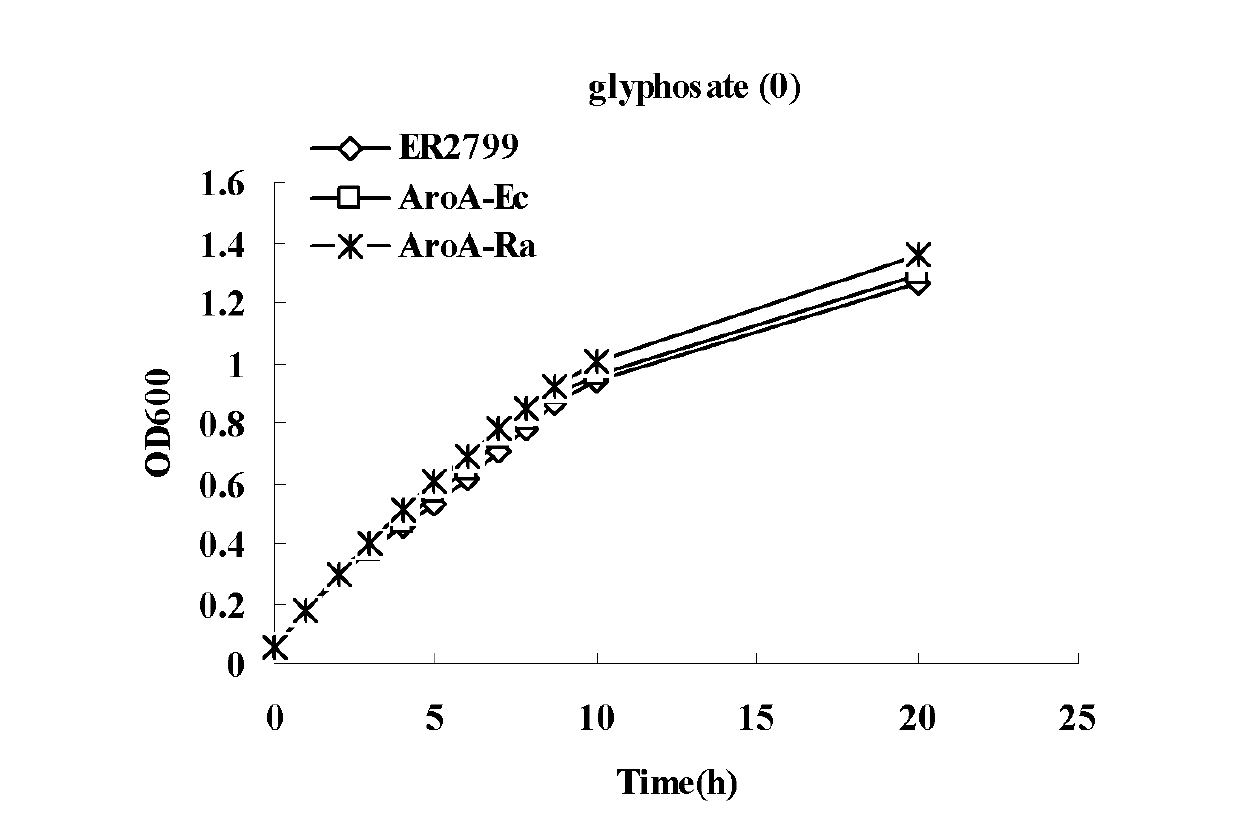
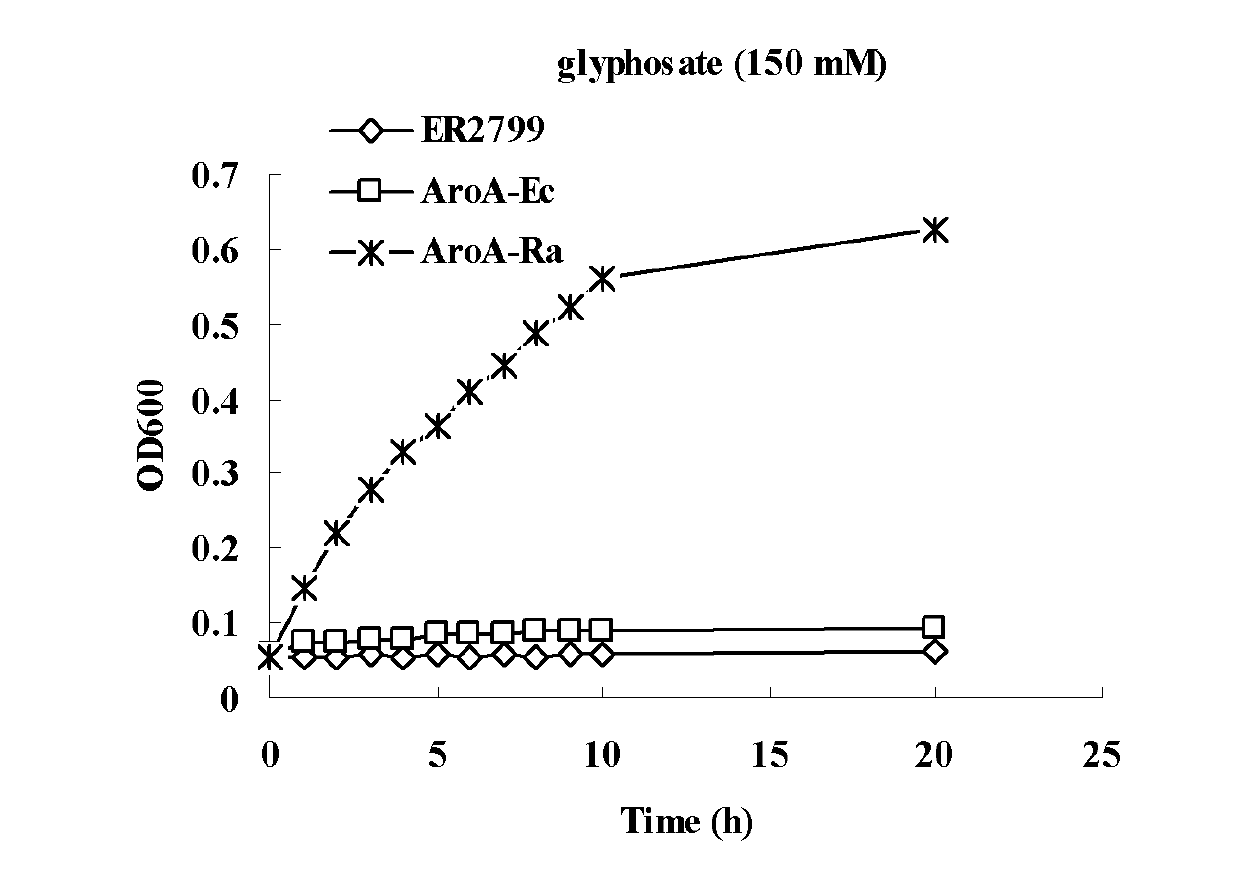
EPSP synthase AroA-Ra multisite mutant of rahnella aquatilis
InactiveCN102559708AIncrease resistanceHigh affinityEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideMolecular rearrangement
The invention relates to an EPSP synthase AroA-Ra multisite mutant of a rahnella aquatilis, particularly to the multisite mutant improved from the gene coded as 5- enol acetone shikimic acid-3-EPSP synthase of the rahnella aquatilis through DNA molecular rearrangement method and function complementation method, and the resistance of the improved multisite mutant to the glyphosate is greatly improved. The nucleotide sequence of the multisite mutant is as indicated by SEQ ID No1, the encoded amino acid sequence is as indicated by the SEQ ID No2, and the mutant has 6 different mutational sites under the same molecule. The multisite mutant not only retains the high affinity of the original EPSP synthase toward the PEP, but also reduces the affinity of the EPSP synthase toward the glyphosate herbicide, so that the glyphosate resistance of the mutant is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Identification of a new class of epsp synthases
Compositions and methods for conferring tolerance to glyphosate in bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include a novel class of EPSPS enzymes, designated Class III, and polynucleotides encoding such enzymes, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The novel proteins comprise at least one sequence domain selected from the Class III domains provided herein. These sequence domains can be used to identify EPSP synthases with glyphosate resistance activity.
Owner:ATHENIX
High-glyphosate-tolerance EPSP synthase (5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase), and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103484438AImprove toleranceSolve the real problemBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyEPSP synthase activity
The invention provides a novel 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSP synthase) and a coding gene thereof. The EPSP synthase is (1) a protein composed of amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2, or (2) a (1)-derived protein with glyphosate tolerance and EPSP synthase activity obtained by substitution, deletion or addition of one or more amino acids on the basis of the amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a preparation method of the EPSP synthase, and application of the EPSP synthase and coding gene thereof. After the EPSP synthase coding gene is transplanted and expressed into a plant, the obtained transgenic plant has higher tolerance to glyphosate.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
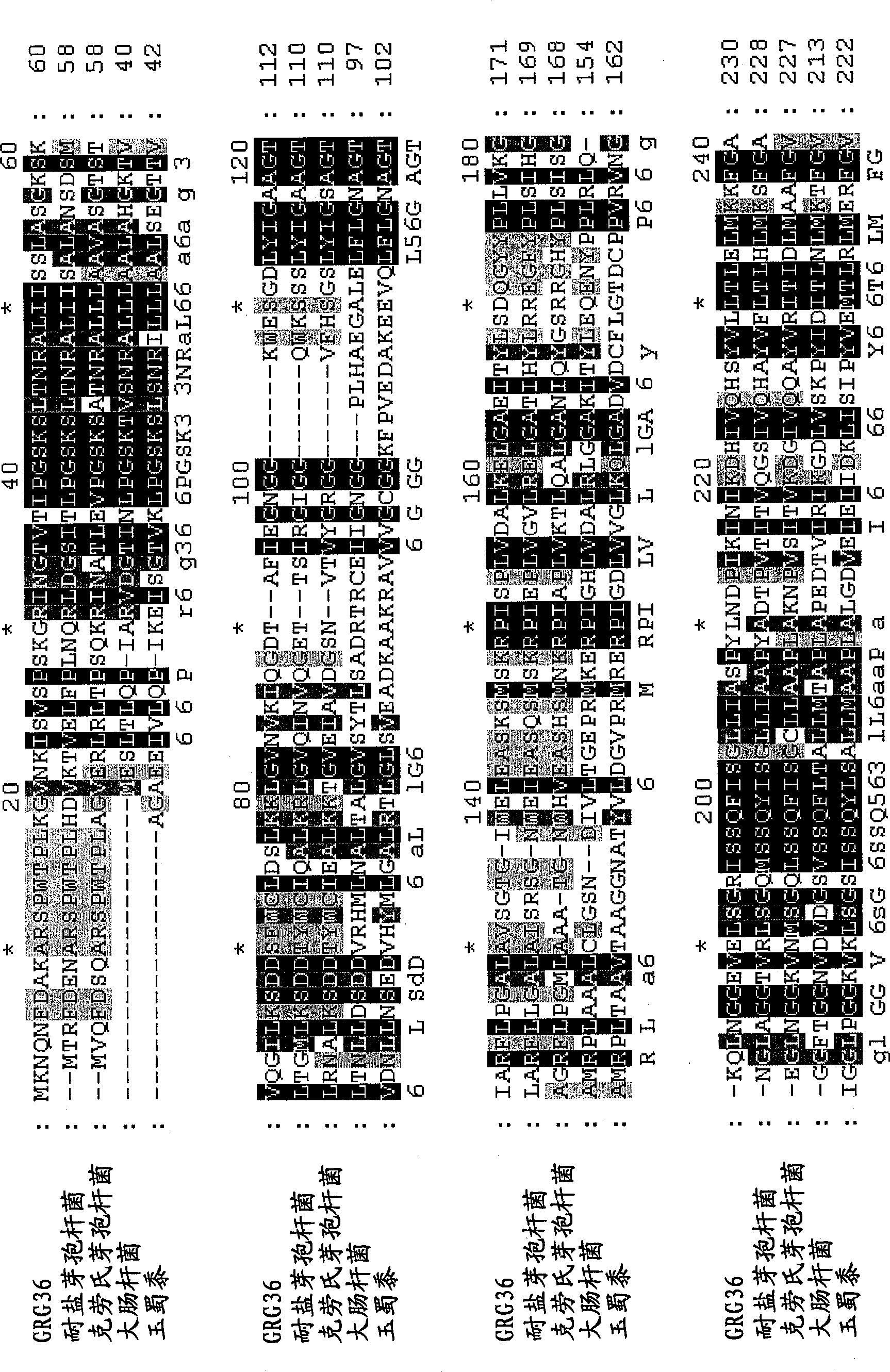
GRG36: novel EPSP synthase gene conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include nucleic acid molecules encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, 17, 18, 20, 21, or 23, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 16, 19, or 22, the herbicide resistance nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession Nos. NRRL B-30932, B-30933, B-30934, B-30945, B-30946, B-30947, or B-30948, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
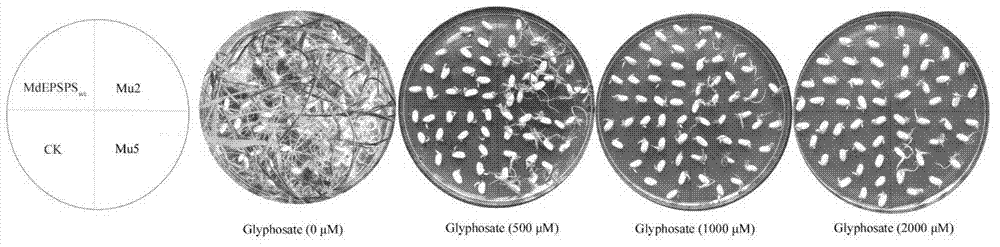
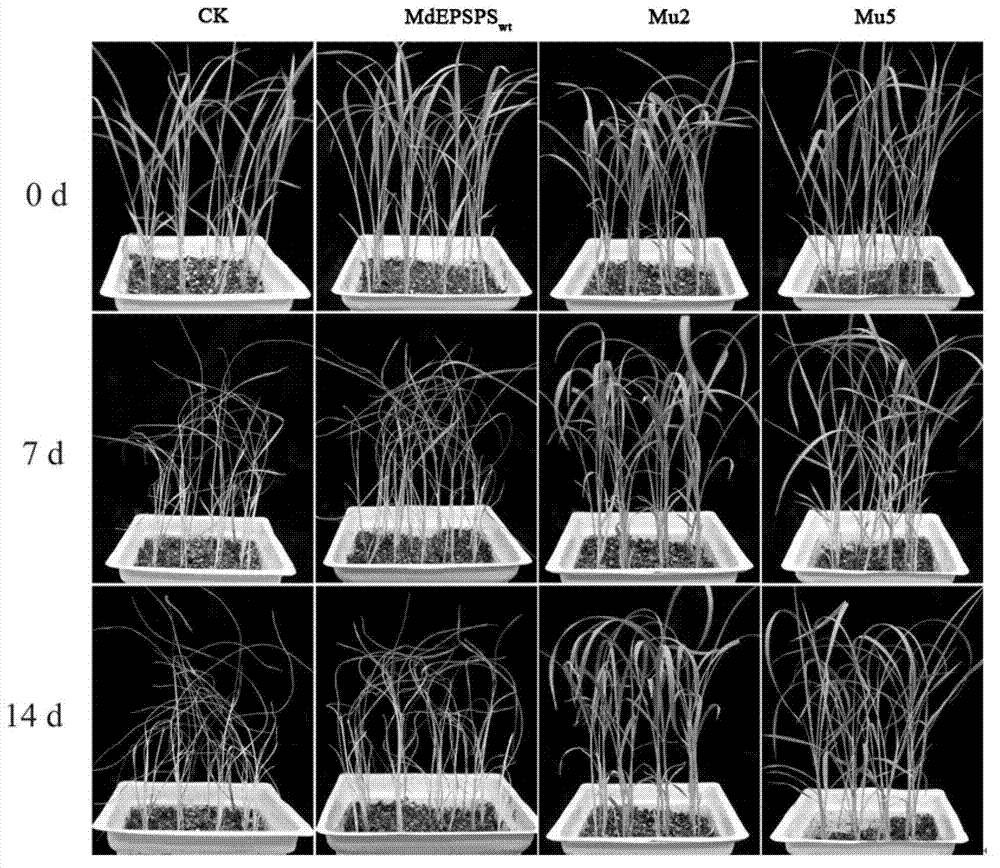
EPSP (5-enolpyruvyl shikimate-3-phosphate) synthase multisite mutant from Malus domestica, and coding gene and application of mutant
ActiveCN103205404AIncrease resistanceHigh affinityTransferasesFermentationAgricultural scienceMutant
The invention discloses an EPSP (5-enolpyruvyl shikimate-3-phosphate) synthase multisite mutant from Malus domestica, and a coding gene and application of the mutant. The mutant has 8 mutation sites, the amino acid sequence of the mutant is as SEQ ID No. 1, and the base sequence of the coding gene of the mutant is as SEQ ID No. 2. Tests show that the EPSP synthase multisite mutant from Malus domestica and the coding gene thereof have high glyphosate resistance, high PEP (phosphoenolpyruvic acid) affinity is kept, and accordingly possibility for using the coding gene for cultivation of transgenic crops is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
EPSP synthase with high glyphosate resistance and its encoded sequence
ActiveUS20110173716A1High glyphosate resistanceHigh affinitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsGlyphosateNucleotide
An EPSP synthase (5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase) with high glyphosate resistance and a nucleotide sequence encoding the synthase are disclosed. The gene encoding the EPSP synthase has low homology with the reported EPSP synthase. A transgenic plant obtained by the expression of the gene in plant has an increased resistance to glyphosate after experimental confirmation.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECH (HAINAN) CO LTD
EPSP synthase gene from Klebsiella pneumoniae 342 and application of EPSP synthase gene
The invention discloses an EPSP synthase gene from Klebsiella pneumoniae 342 and application of the EPSP synthase gene. The EPSP synthase gene comprises 1284 basic groups and 428 coding amino acid, the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO 1, and the coding amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO 2. The EPSP synthase gene from the Klebsiella pneumoniae 342 has high glyphosate tolerance and can be used for cultivating transgenic crops.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Grg33, grg35, grg36, grg37, grg38, grg39, and grg50: novel epsp synthase genes conferring herbicide resistance
InactiveCN101479387AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBacteroidesDNA construct
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include nucleic acid molecules encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 4, 6, 1, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, 17, 18, 20, 21, or 23, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 16, 19, or 22, the herbicide resistance nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession Nos. NRRL B-30932, B-30933, B-30934, B-30945, B-30946, B-30947, or B-30948, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
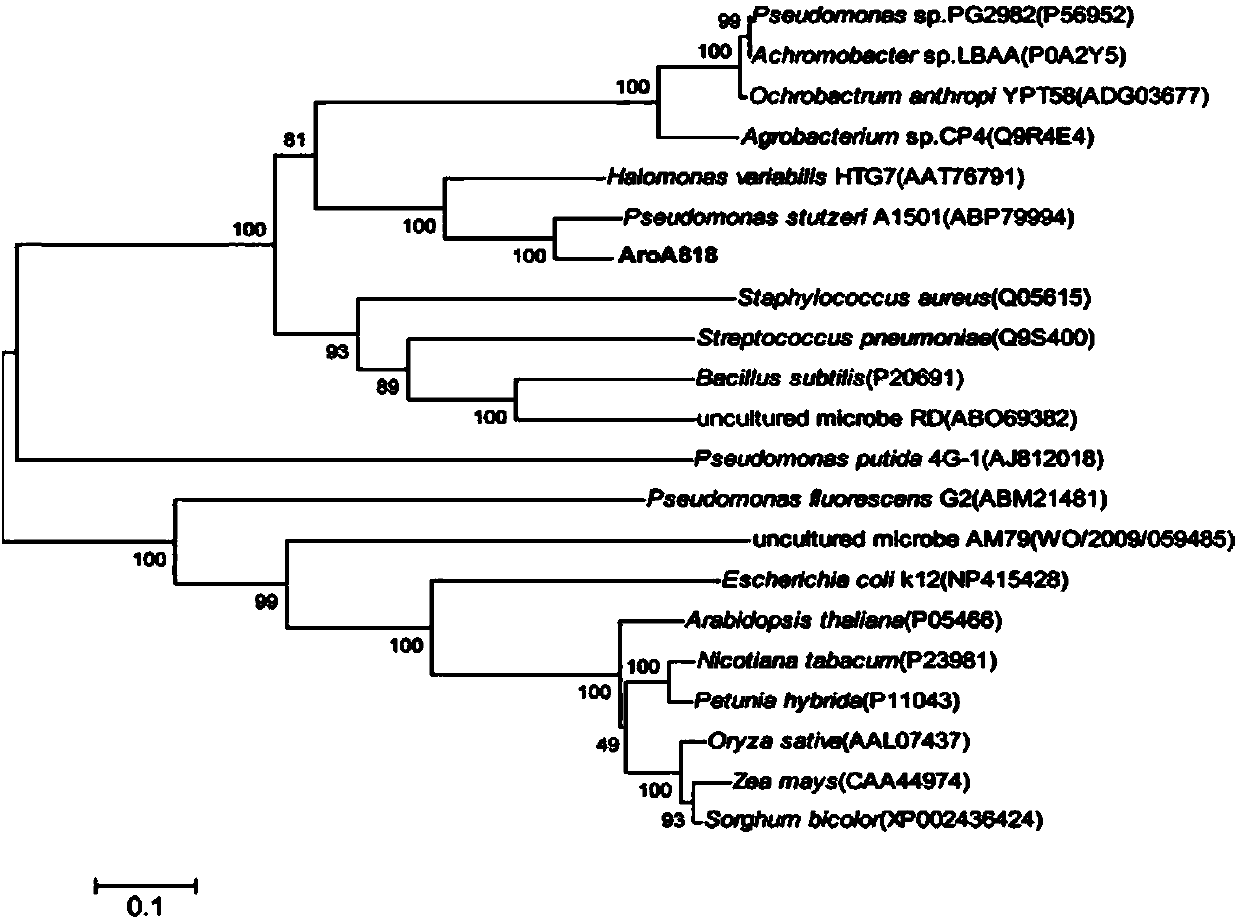
EPSP synthase of variable halomonas high resistance glyphosate and its encoding sequence
The invention discloses a novel 5-enol pyruvyl shikimate3-phosphate (EPSP), the polynucleotide for encoding the EPSP and the method for producing the EPSP through recombination technology. The invention also discloses the use of the polynucleotide for encoding the EPSP.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase gene from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof
The invention discloses a 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase gene from ochrobactrum anthropi and application thereof. The invention also provides genetic engineering intermediates (such as an expression cassette, a carrier and a cell) of the gene, a method for obtaining a plant with glyphosate resistance, and application of the method, and provides an identification method for judging whether the plant has the glyphosate resistance. The EPSP synthase gene plays an important role in research and development of the glyphosate-resistant plant.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
Polynucleotide of insect resistant plant resistant to herbicide, expression cassette including polynucleotide and application thereof
InactiveCN106047907AReduce the need to use chemical pesticidesReduce yield lossMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationPlant tissueNucleotide
The invention relates to polynucleotide of an insect resistant plant resistant to herbicide, an expression cassette including polynucleotide and application thereof. The polynucleotide of an insect resistant plant resistant to herbicide includes first polynucleotide, second polynucleotide and third polynucleotide. The first polynucleotide includes a coding area of EPSP synthase; the second polynucleotide includes a coding area of a vegetative period insecticide protein VIP3A; and the third polynucleotide includes a coding area of an insecticide protein Cry2A. The polynucleotide can code the EPSP synthase, the vegetative period insecticide protein VIP3A, and bacillus thuringiensis Delta-endotoxin, i.e., the insecticide protein Cry2A. The invention further relates to a DNA builder formed by a first expression cassette, a second expression cassette, a third expression cassette and a fourth expression cassette, and a method for transforming a plant by using the DNA builder. The transgenic plant has stronger resistance to lepidoptera insects than a first generation single-gene Bt plant through enhanced coordinate expression, and has a herbicide resistance character, thereby facilitating farmland weeding.
Owner:达尼亚·贾德·库雷西·索·贾德·萨利姆·库雷西 +1
Glyphosate-resistant herbicide gene AroA-Ra from grape crown gall antagonistic bacteria rahnella aquatilis and application thereof
The invention relates to a glyphosate-resistant herbicide gene AroA-Ra from grape crown gall antagonistic bacteria rahnella aquatilis and application thereof, particularly to a gene coded as 5- enol acetone shikimic acid-3-EPSP synthase of the rahnella aquatilis having antagonistic function against the grape crown gall from the vineyard through function complementation method, and the application to the improvement of the resistance of the plant transformed from the gene to the glyphosate herbicide.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel epsp synthase genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a polypeptide that confers resistance or tolerance to glyphosate herbicides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated nucleic acid molecules corresponding to glyphosate resistant nucleic acid sequences are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NOS:2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, or 14 or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NOS: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, or 34.
Owner:ATHENIX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com