Identification of a new class of epsp synthases
a synthase and epsp technology, applied in the field of plant molecular biology, can solve the problems of toxic to bacterial cells, toxic to plant cells, toxic to these bacteria,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Isolation of EPSPS Genes
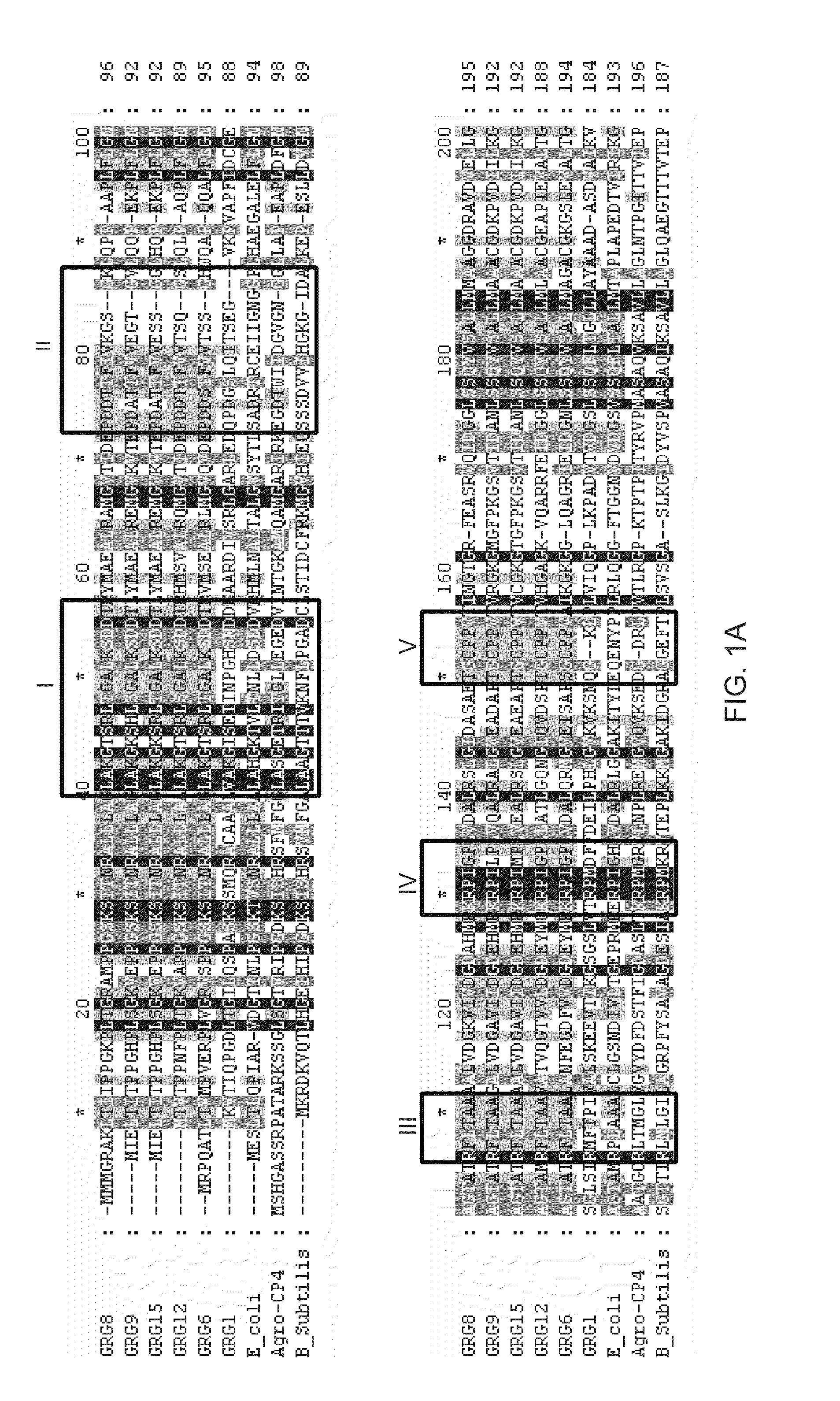
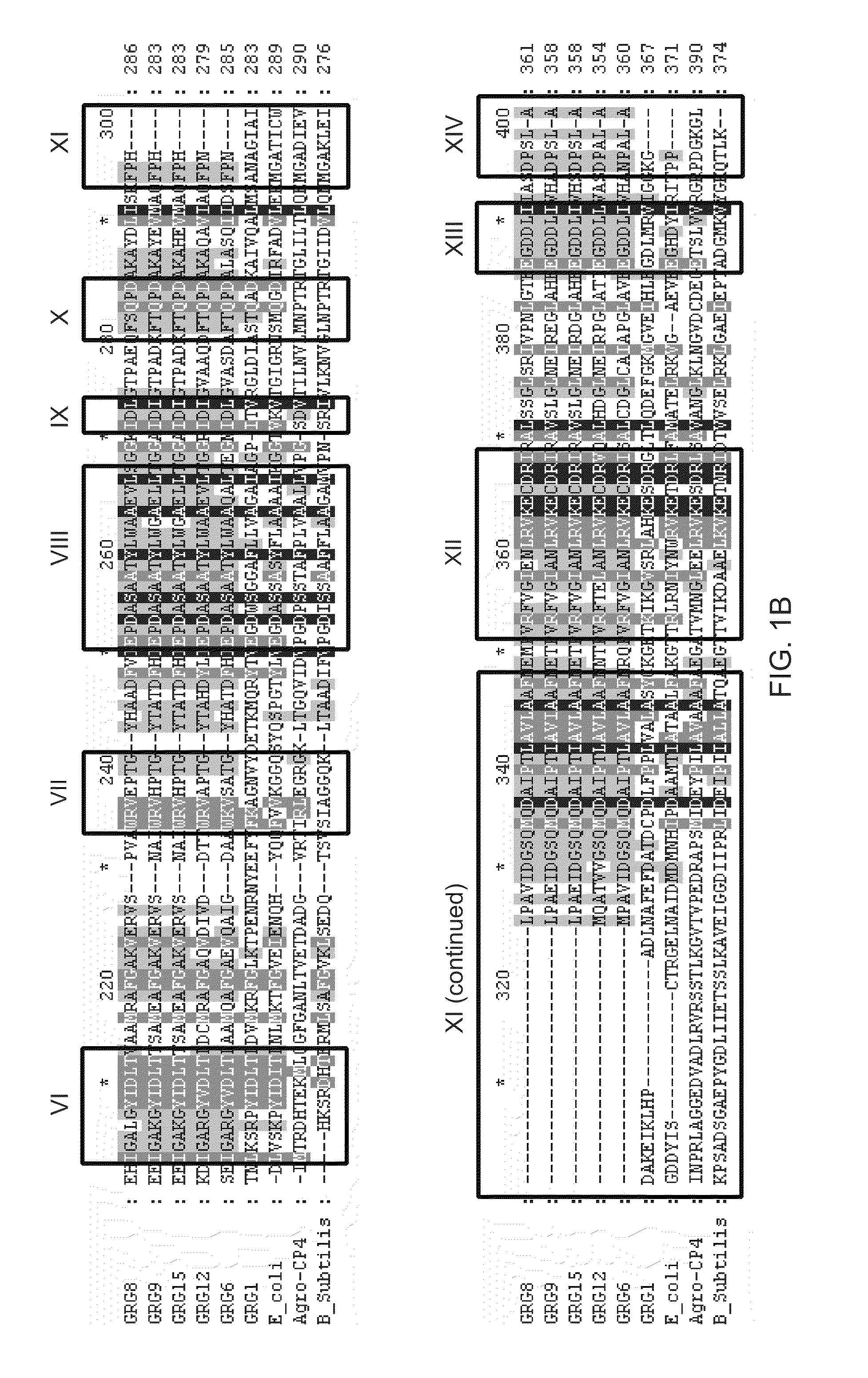
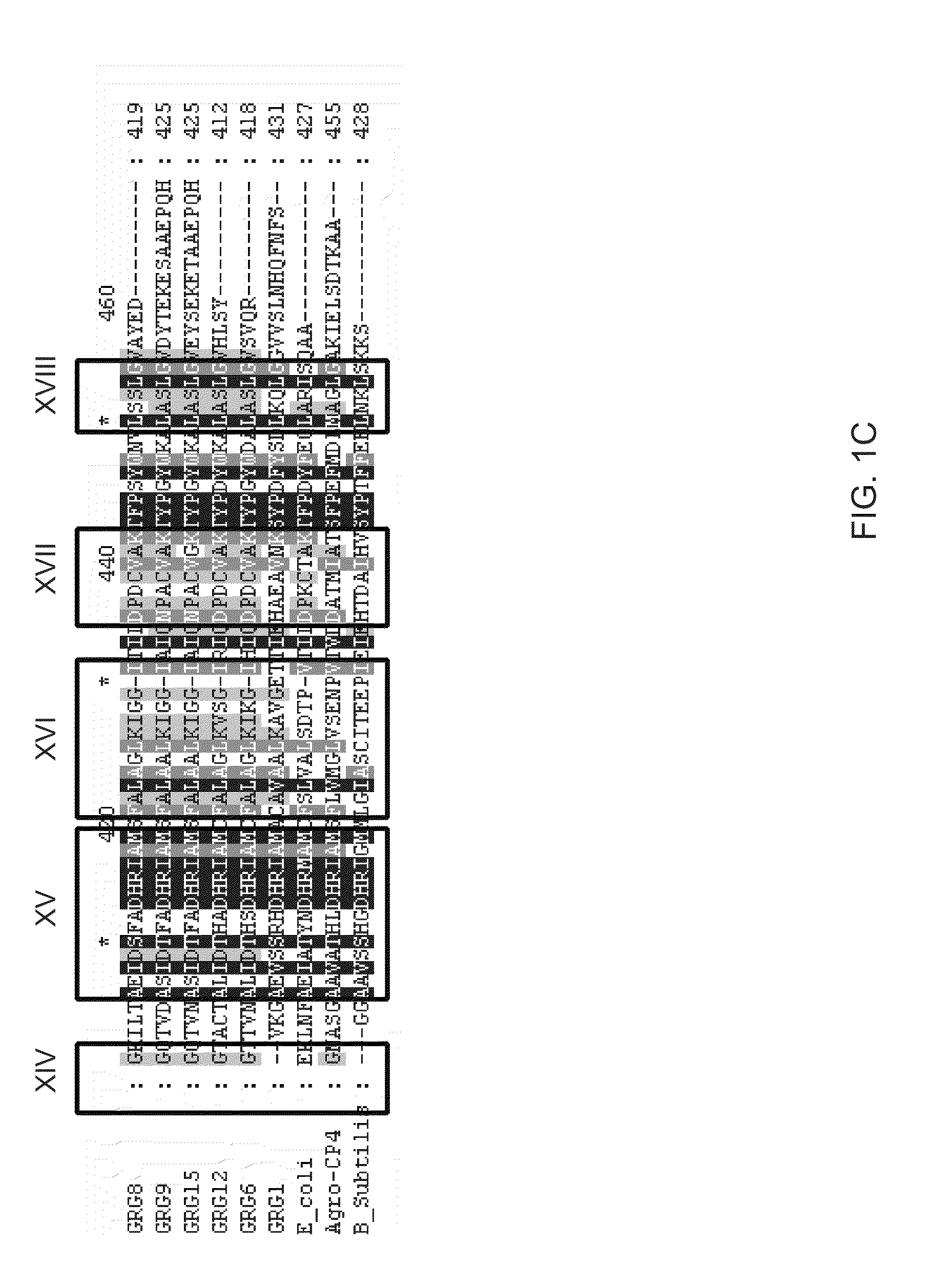
[0133]Genes coding for class III EPSPS enzymes have been isolated from seven different bacteria (Klebsiella pneumoniae, Agrobacterium radiobacter, Rhizobium sp., Brevundomonas vesicularis, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Pseudomonas syringae, and Brucella / Ochrobactrum).
[0134]The DNA coding sequence and the amino acid sequence of the grg8 open reading frame are provided in U.S. Patent Application No. 60 / 640,195, filed Dec. 29, 2004, and provided in SEQ ID NO:7 and SEQ ID NO:8 of this application, respectively.
[0135]The DNA coding sequence and amino acid sequence of the grg12 open reading frame are provided in SEQ ID NOS:57 and 10 and SEQ ID NOS:58 and 59 of this application, respectively.
[0136]The DNA coding sequence and amino acid sequence of the grg15 open reading frame are provided in SEQ ID NO:11 and SEQ ID NO:12 of this application, respectively.
[0137]The DNA coding sequence and amino acid sequence of the grg6 open reading frame are provided in GenBank Accessi...
example 2
Cloning the EPSP Synthase Gene from Pseudomonas syringae pv Tomato Strain DC3000
[0144]The EPSP synthase coding sequence was PCR-amplified from genomic DNA of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato strain DC3000 (ATCC BAA-871) using the following primers: CAGAGATCTGGCATGCGACCTCAAGCCACTCTC (upper, SEQ ID NO:61) and CAGGGCGCGCCTCAGCGCTGAACACTCACCC (lower, SEQ ID NO:62). The resultant 1.3 kb PCR product was digested with Bgl II and Asc I, ligated into modified pUC18 which had been digested with BamH I and Asc I, then electroporated into DH5α cells. Plasmid DNA was prepared from ampicillin resistant colonies and analyzed by restriction digest. One clone was chosen for further analysis. The DNA sequence of the insert was determined using techniques well known in the art and found to be 100% identical to the published sequence for strain DC3000 (Genbank accession number AE016853 bases 1,140,091 through 1,141,347). This plasmid was named pAX703, and the EPSPS ORF was named grg6.
[0145]Plasmid pAX70...
example 3
Cloning the EPSP Synthase Gene from Agrobacterium Radiobacter Strain C58
[0146]The EPSP synthase coding sequence was PCR-amplified from genomic DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain C58 (ATCC 33970) using the following primers: CAGGGATCCGGCATGATCGAACTGACCATCACCC (upper, SEQ ID NO:63) and CAGGGCGCGCCTCAGTGCTGCGGCTCGGCAGCG (lower, SEQ ID NO:64). The resultant 1.3 kb PCR product was digested with BamH I and Asc I, ligated into modified pUC18 which had been digested with BamH I and Asc I, then electroporated into DH5α cells. Plasmid DNA was prepared from ampicillin resistant colonies and analyzed by restriction digest. One clone was chosen for further analysis. The DNA sequence of the insert was determined using techniques well known in the art and found to be 100% identical to the published sequence for strain C58 (Genbank accession number NC—003304 bases 628398 through 629675). This plasmid was named pAX702, and the C58 EPSPS ORF was named grg9.
[0147]Plasmid pAX702 was transformed in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com