System, device and method for exchanging energy with an electric vehicle
A technology for exchanging energy and electric vehicles, which is applied in the fields of electric vehicles, vehicle energy storage, and electric vehicle charging technology, and can solve the problems of time-consuming, lack of constraints on the layout of charging stations, and limitation of the radius of action.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
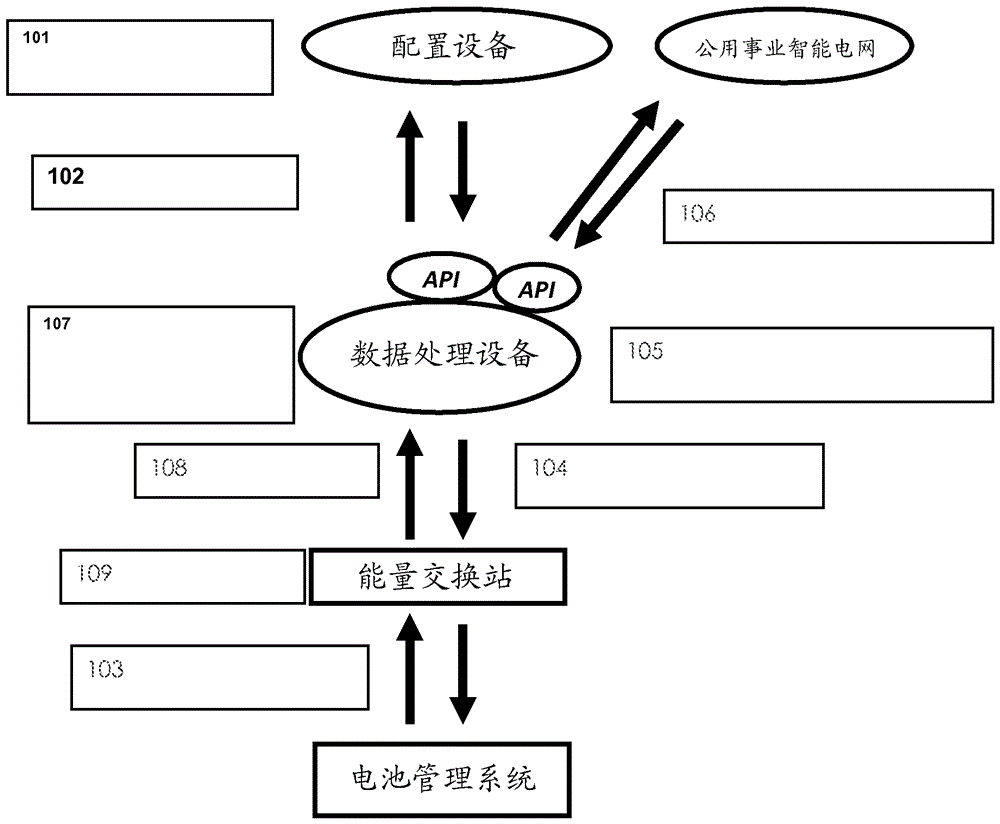
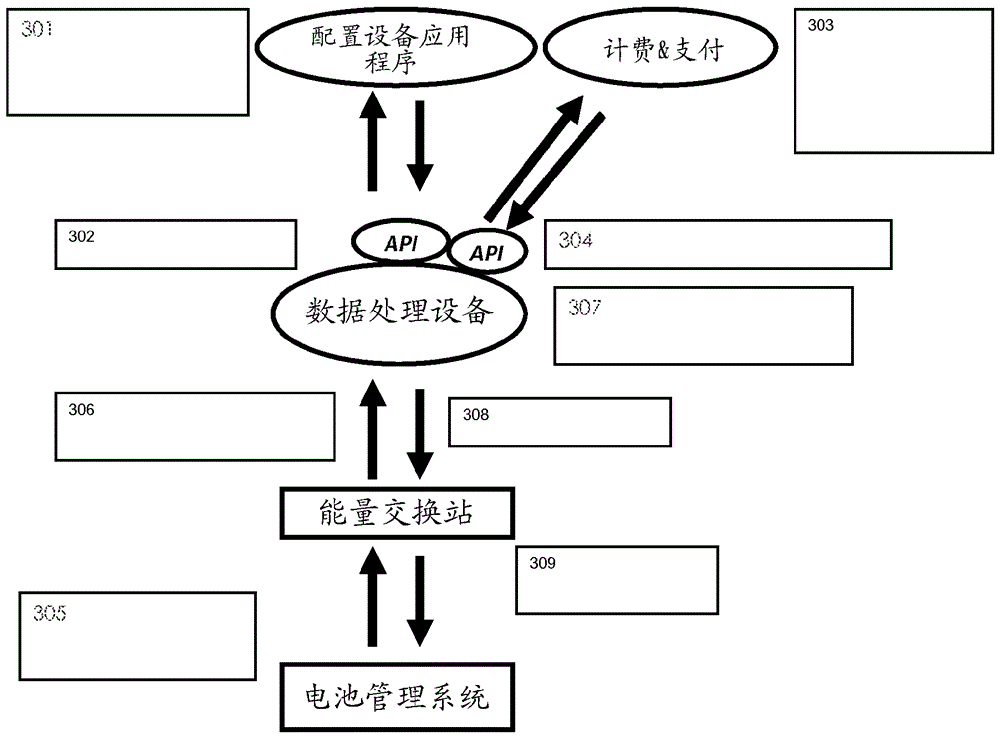
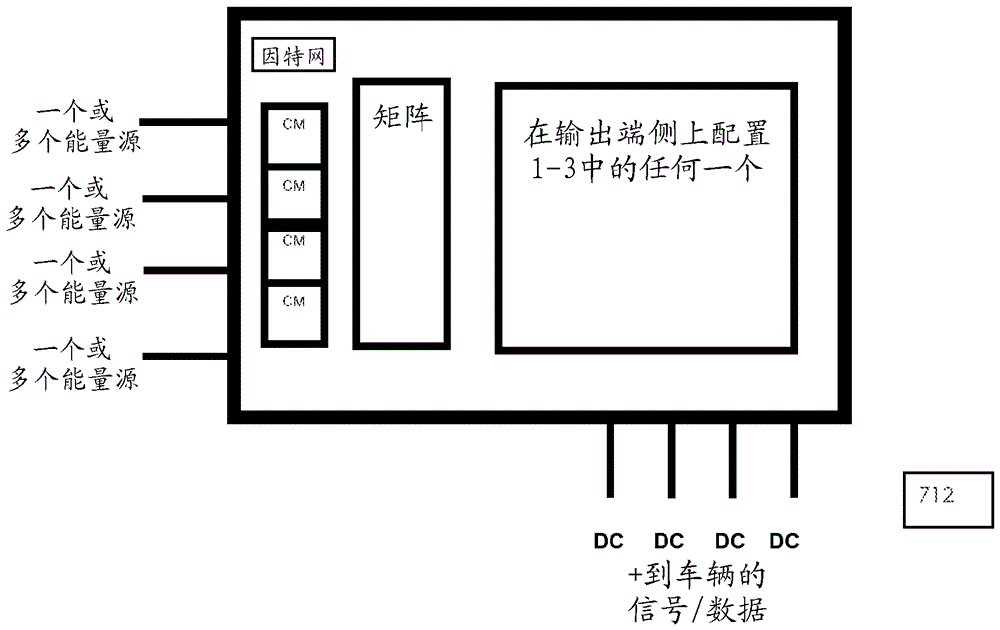
[0027] Example 1: When the power source formed by the grid has less available power than the needs of multiple vehicles, the grid power can be spread over the charging output, for example according to the priority that the vehicles will drive away. This priority can be entered in the system by a user application connected via an API to the configuration device or data processing device. This application of the system could be an advanced fleet management software system or a simple user interface where the user can enter how long they have before they have to drive away again. The available grid power may be known to pre-programmed settings in the data processing equipment, or through an API interacting with the grid provider's software (smart grid). Energy exchange settings are dynamically changed (optimized) in real time as inputs or changes occur anywhere in the system. The distribution of power from the grid to the vehicles can be proportional or disproportionate, and can...
example 2
[0028]Example 2: The system (in particular a data processing device or a configuration device) is capable of interacting through APIs between billing and payment applications running at computers of utilities or other energy providers. Likewise, the system can limit the amount of charging power at a particular charging outlet based on the type of subscription the user has for energy delivery. A premium subscription may for example mean that the vehicle is able to receive 50 kW of charging power and be charged very quickly, while a basic subscription may mean that the user can only receive 20 kW and be charged more slowly.
example 3
[0029] Example 3: If the system has energy exchange ports (power outlets) for the vehicle and one energy exchange port for the power supply, such as an AC input, the system is able to calculate the power distribution on the power outlets. Likewise, one needs only 1 officially certified AC energy consumption meter at the input and still know how much energy goes to each power outlet.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com