Zoom lens
A zoom lens and lens technology, applied in the field of wide-angle zoom lenses, can solve the problems of being unsuitable for imaging devices, high manufacturing costs, and large first lens groups, achieving excellent imaging performance, realizing manufacturing costs, and suppressing aberration changes Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
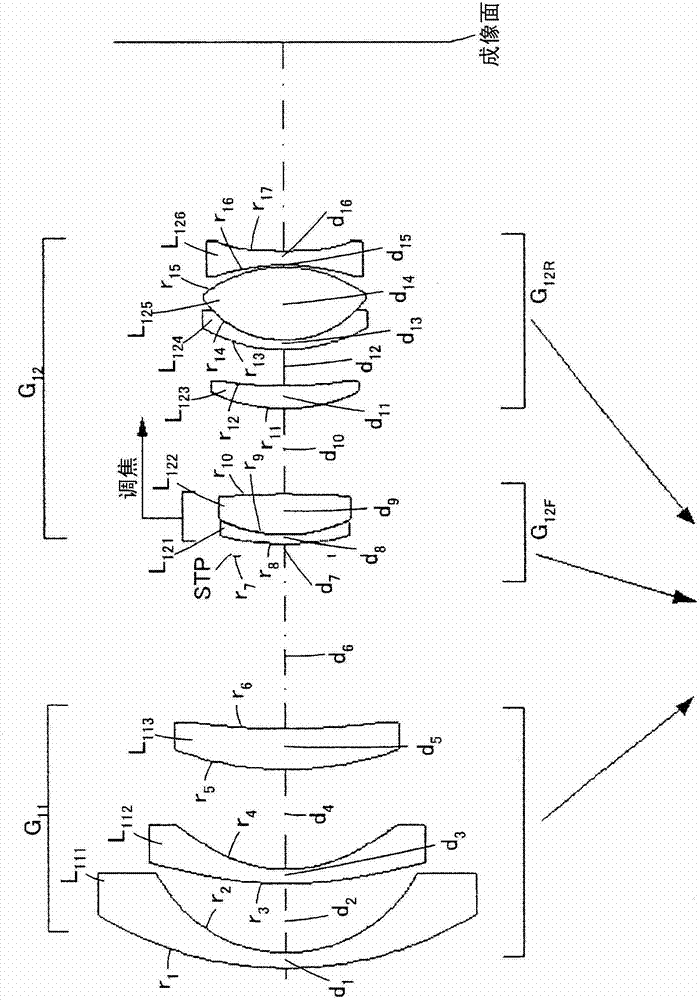
[0113] image 3 It is a sectional view along the optical axis showing the configuration of the zoom lens of the first embodiment. In this zoom lens, the first lens group G having negative refractive power is arranged in order from the object side not shown in the figure. 11 , the second lens group G with positive power 12 And constitute.
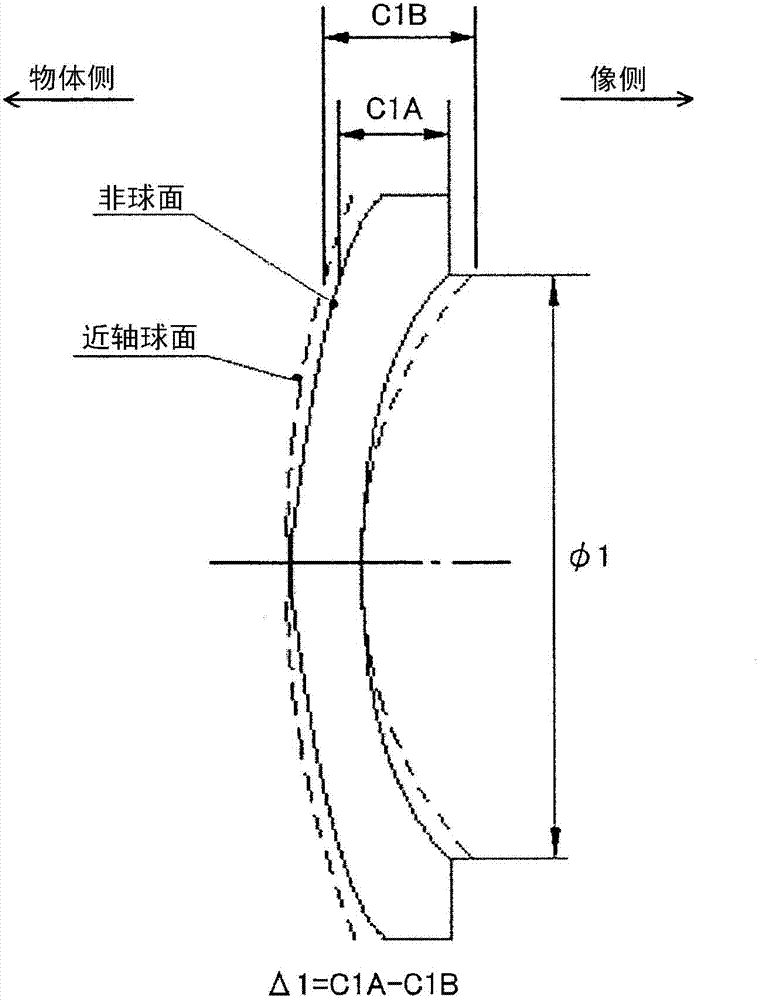
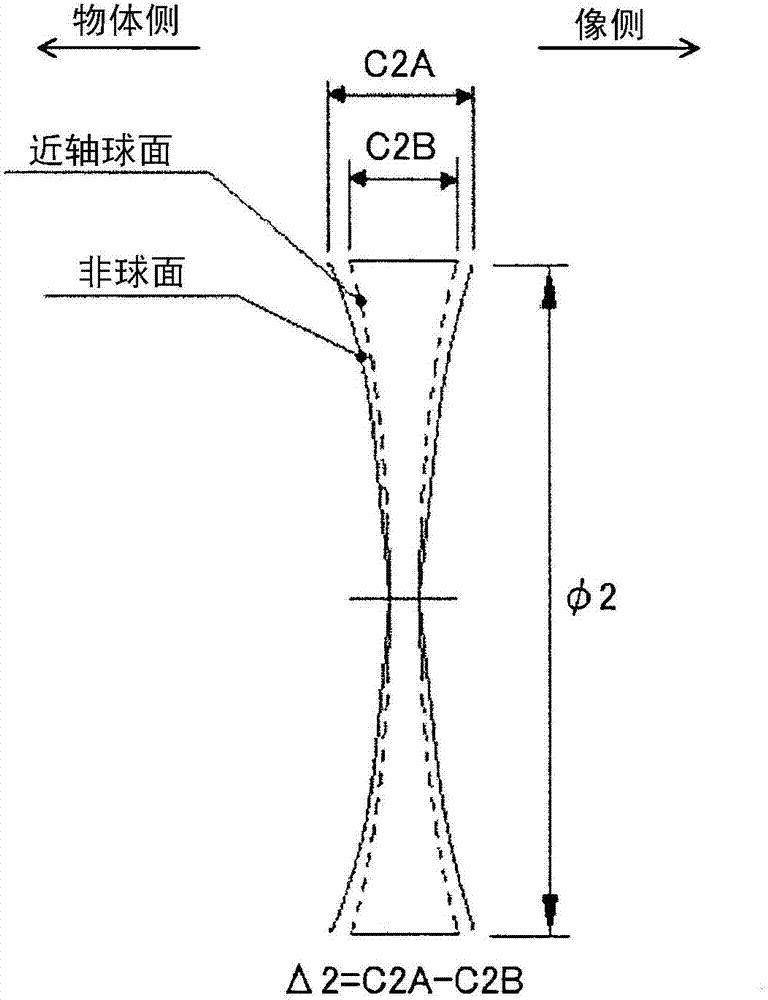
[0114] The first lens group G 11 , arrange the negative lens L sequentially from the object side 111 (first lens), negative lens L 112 (second lens), positive lens L 113 And constitute. Negative lens L 111 It consists of a meniscus spherical lens with the concave surface facing the image side. Negative lens L 112 Consists of an aspherical lens with a concave surface facing the image side. Also, in the negative lens L 112 The two sides form an aspheric surface.
[0115] Second lens group G 12 , the front group G with positive refractive power is arranged sequentially from the object side 12F , the rear group G with positive opti...
Embodiment 2
[0206] Figure 5 It is a cross-sectional view along the optical axis showing the configuration of the zoom lens of Example 2. In this zoom lens, the first lens group G having negative refractive power is arranged in order from the object side not shown in the figure. 21 , the second lens group G with positive power 22 And constitute.
[0207] The first lens group G 21 , arrange the negative lens L sequentially from the object side 211 (first lens), negative lens L 212 (second lens), positive lens L 213 And constitute. Negative lens L 211 It consists of a meniscus spherical lens with the concave surface facing the image side. Negative lens L 212 Consists of an aspherical lens with a concave surface facing the image side. Also, in the negative lens L 212 The two sides form an aspheric surface.
[0208] Second lens group G 22 , the front group G with positive refractive power is arranged sequentially from the object side 22F , the middle group G with positive optica...
Embodiment 3
[0298] Figure 7 It is a sectional view along the optical axis showing the configuration of the zoom lens of Example 3. In this zoom lens, the first lens group G having negative refractive power is arranged in order from the object side not shown in the figure. 31 , the second lens group G with positive power 32 And constitute.
[0299] The first lens group G 31 , arrange the negative lens L sequentially from the object side 311 (first lens), negative lens L 312 (second lens), positive lens L 313 And constitute. Negative lens L 311 It consists of a meniscus spherical lens with the concave surface facing the image side. Negative lens L 312 Consists of an aspherical lens with a concave surface facing the image side. Also, in the negative lens L 312 The two sides form an aspheric surface.
[0300] Second lens group G 32 , the front group G with positive refractive power is arranged sequentially from the object side 32F , the middle group G with positive optical powe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com