Pulmonary valve stent with anchoring mechanism
A pulmonary artery and valve technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as limited effectiveness, and achieve the effects of improving stability, reducing friction, and good elasticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
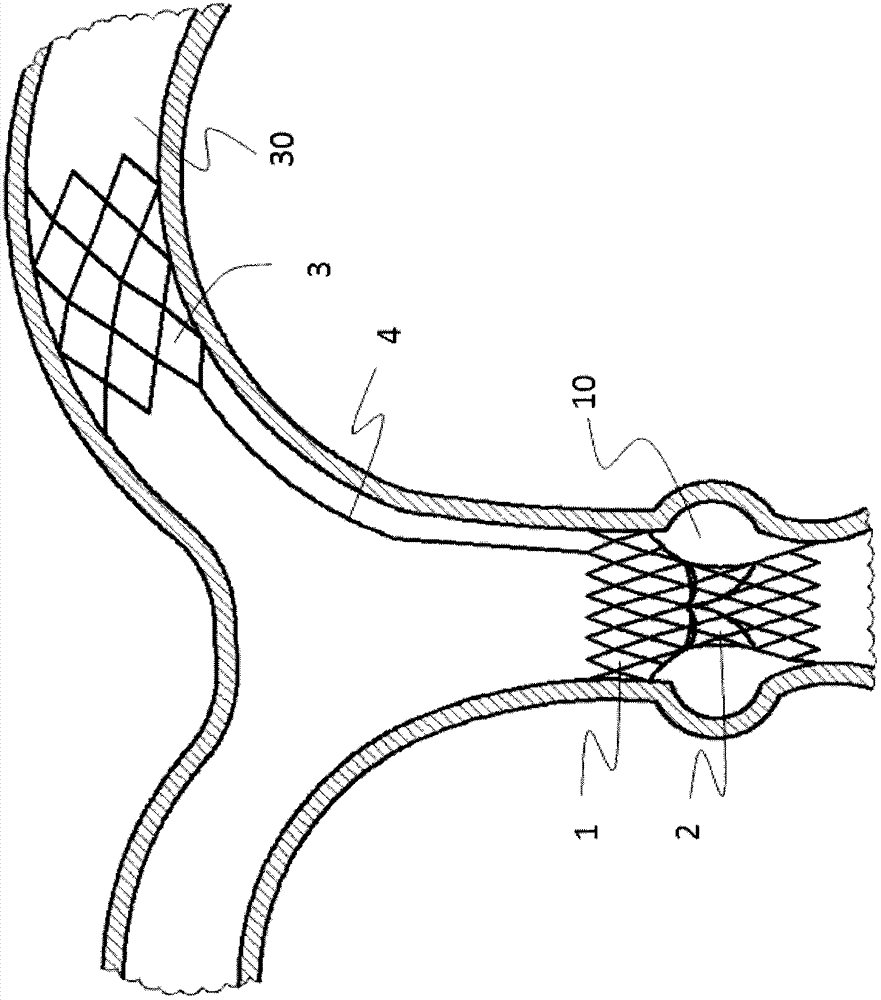
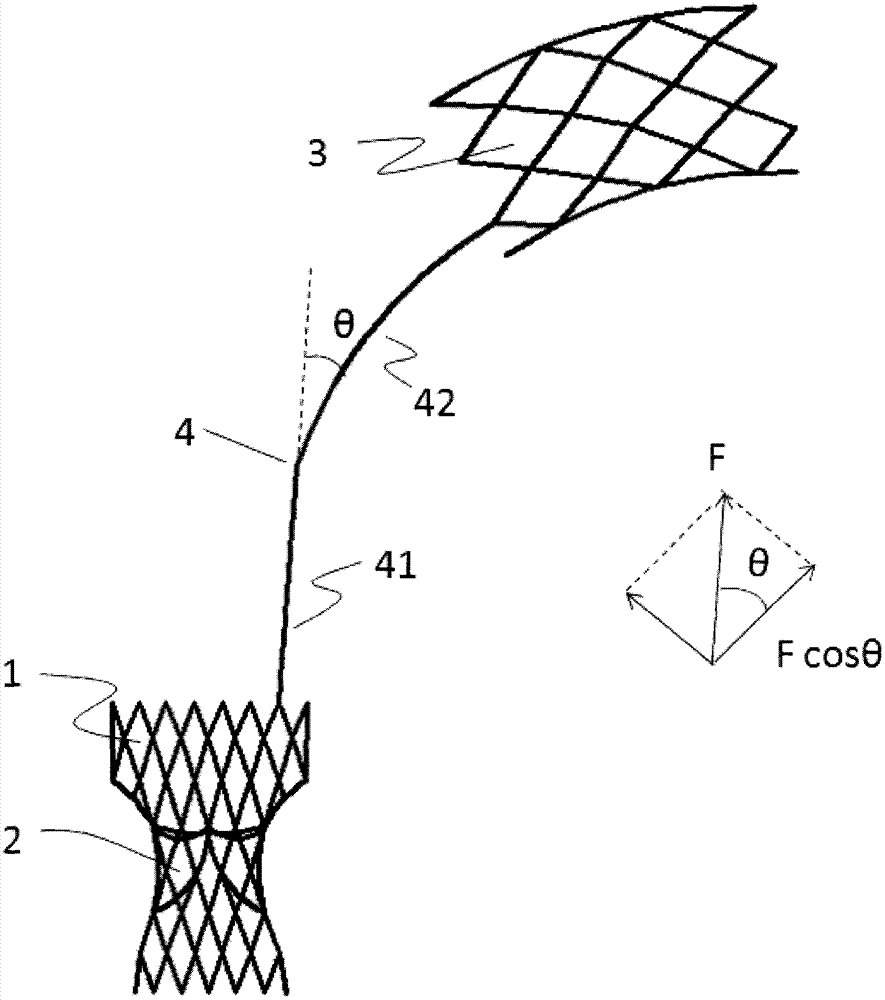
[0051] Such as figure 1 As shown, a pulmonary valve stent with an anchoring mechanism includes a valve sewing section 1 and an artificial valve 2, the artificial valve 2 is connected to the valve sewing section 1, and the valve sewing section 1 is located on the right ventricular outflow tract or the main pulmonary artery 10 when it is released, and the pulmonary valve stent also includes an anchoring mechanism 3, and the proximal end of the anchoring mechanism 3 is connected to the valve sewing section through a transition connecting rod 4 1, the anchoring mechanism 3 is located in the pulmonary artery branch vessel 30 after release. There are two reasons why the anchoring mechanism 3 is placed in the pulmonary artery branch vessel 30. The first is that patients with the second stage of tetralogy of Fallot are usually accompanied by dilation of the main pulmonary artery 10, and the expanded blood vessel loses its original elasticity. Thereby its frictional force to valve ste...
specific Embodiment 2
[0055] Such as Figure 6 As shown, a pulmonary valve stent with an anchoring mechanism includes a valve sewing section 1 and an artificial valve 2, the artificial valve 2 is connected to the valve sewing section 1, and the valve sewing section 1 is located on the right ventricular outflow tract or the main pulmonary artery 10 when it is released, and the pulmonary valve stent also includes an anchoring mechanism 3, and the proximal end of the anchoring mechanism 3 is connected to the valve sewing section through a transition connecting rod 4 1, the anchoring mechanism 3 is located in the pulmonary artery branch vessel 30 after release.
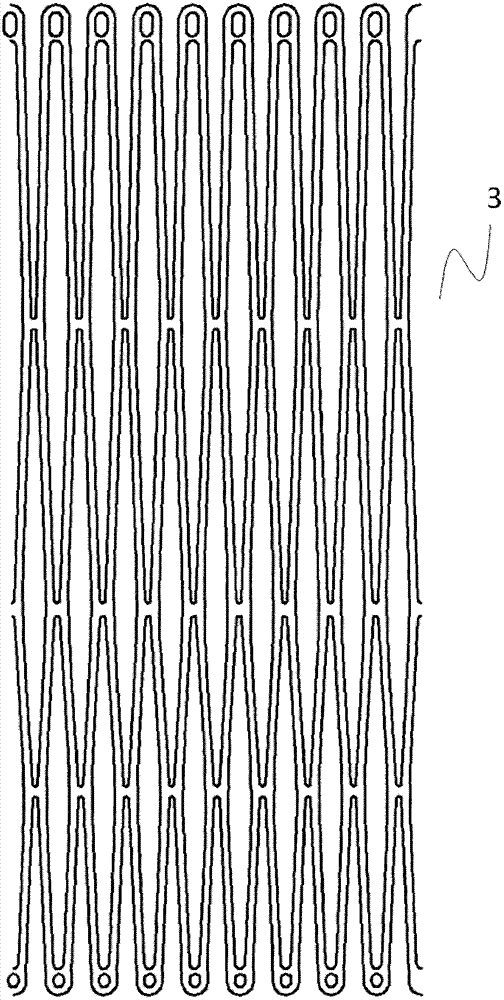
[0056] Such as Figure 7a As shown, the anchoring mechanism 3 is a braided stent made of shape memory material or elastic material, preferably nickel-titanium shape memory alloy.
[0057] Such as Figure 7b and 7c As shown, the outer surface of the anchoring mechanism 3 is fully or partially covered with a film 31 . The material of the me...
specific Embodiment 3
[0067] The difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment 2 is that the anchoring mechanism 3, the transition connecting rod 4 and the valve sewing section 1 are integrally carved with a shape memory material tube, more preferably nickel-titanium shape memory Made of alloy tube integrally carved, such as Figure 11 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com